Oracle E-Business Suite
The infrastructure provides a reference architecture to help run Oracle E-Business Suite Release (EBS) 12.2.7 and later on Google Cloud Compute Engine VMs with low-latency connectivity to Oracle Database@Google Cloud (Oracle Database 19c running on Oracle Exadata Database within Google Cloud).
Oracle E-Business Suite enables you to adapt quickly to changing business and compliance requirements while reducing risk, improving controls, and delivering faster, more accurate insights to your stakeholders.
The intended audience for this document include cloud architects, administrators of Oracle Database, and Oracle E-Business Suite application administrators. Familiarity with Oracle E-Business Suite applications, Oracle Database, and Google Cloud services is recommended.
Single Availability Domain
In this architecture, applications and databases are deployed in a single Google Cloud zone within the same Google Cloud region.
Application users access the Oracle E-Business Suite application through a Google Cloud load balancer, which distributes requests to the Oracle HTTP Server (OHS), the application server, and Oracle Database. Administration users can manage the Oracle E-Business Suite application through the Bastion host in the application subnet.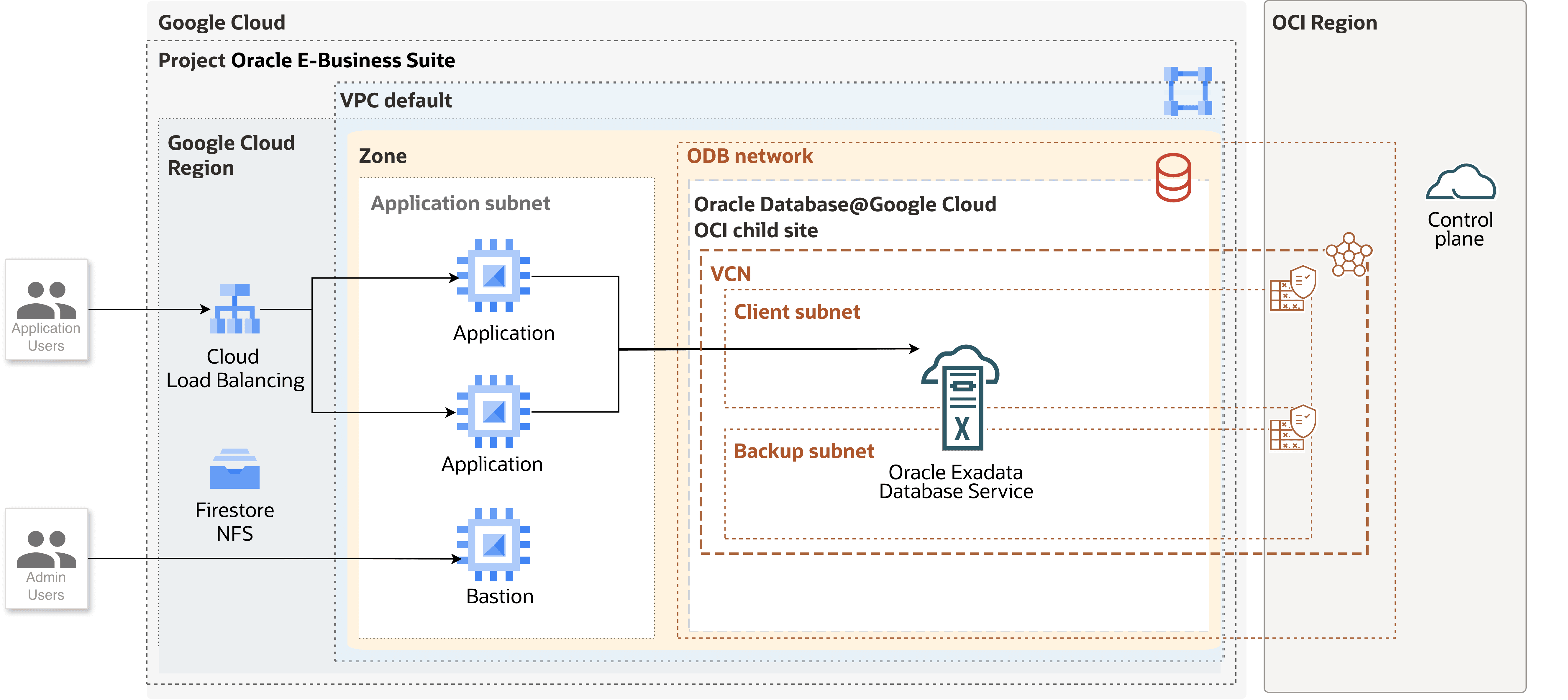
| Component | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Regional external Application Load Balancer | The load balancer receives user requests and distributes them to the Oracle E-Business Suite web servers. To ensure session affinity, the load balancer is configured to use generated cookies. |
| Oracle E-Business Suite OHS | The Oracle E-Business Suite OHS tier consists of web servers that run independently on Compute Engine VMs. |
| Filestore (NFS) | A Filestore instance contains the web server binaries and backups. The Filestore instance is mounted on all of the Compute Engine VMs. |
| Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) network | All of the Google Cloud resources in the architecture use a single VPC network. The web servers, mid-tier components, and databases are in separate subnets. |
| Oracle Database@Google Cloud |
Oracle Database@Google Cloud is a database service that enables you to access OCI managed Oracle Exadata Infrastructure inside Google Cloud data centers. The Oracle E-Business Suite applications read data from and write to Oracle Databases in Oracle Exadata Database Service. You can provision an Oracle Exadata Database Service by using Oracle Database@Google Cloud. You use Google Cloud interfaces like the Google Cloud console, the Google Cloud CLI, and APIs to create Oracle Exadata Infrastructure instances. Oracle sets up and manages the required compute, storage, and networking infrastructure in a data center within Google Cloud region on hardware that's dedicated for your project. |
| Exadata Infrastructure instance | The Exadata Infrastructure instance contains two or more physical database servers and three or more storage servers. These servers, which aren't shown in the diagram, are interconnected using a low-latency network fabric. When you create the Exadata Infrastructure instance, you specify the number of database servers and storage servers that must be provisioned. |
| Exadata VM Clusters |
Within the Exadata Infrastructure instance, you create one or more Exadata VM Clusters. For example, you can choose to create and use a separate Exadata VM Cluster to host the databases that are required for each of your business units. Each Exadata VM Cluster contains one or more Oracle Linux VMs that host Oracle Database instances. When you create an Exadata VM Cluster, specify the following:
The VMs within Exadata VM Cluster are not Compute Engine VMs. |
| Oracle Database instances | You can create and manage Oracle Database instances through the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) console and other OCI interfaces. Oracle Database software runs on the VMs within Exadata VM Cluster. When you create an Exadata VM Cluster, specify the Oracle Grid Infrastructure version and choose the license type. You can either bring your own licenses (BYOL) or opt for the license-included model. |
Considerations
Use the architecture described as a starting point to deploy Oracle E-Business Suite on Oracle Database@Google Cloud.
- The maximum availability architecture (MAA) is not represented in this architecture. To enable database-layer disaster recovery using Oracle Active Data Guard, consider deploying a standby in a different zone or region.
- Consider deploying the application subnet in the same VPC as the database tier to minimize network hops. To optimize latency between the application and the database, deploy the application in the same zone as the Exadata Infrastructure instances.
For more information on Multicloud support, see Support Policy for Oracle E-Business Suite Running in a Multicloud Environment (Document KA1144).