Defining Import Format Mappings
The import format identifies the content structure of the source file or system. When you create an import format, you define the settings and the import format mapping definition between the source and target system dimensions. You can create:
-
One-to-One Mappings—Single Segment and Single Chartfield mappings:
-
Define a simple one-to-one mapping between source segments and target dimension members.
-
Pull all members from the source value set as members into the target dimension.
Note:
The topic is unavailable for file-based data load definitions.
The following figure shows a one-to-one mapping between segments or chartfields in a source system and dimensions in a target EPM application.
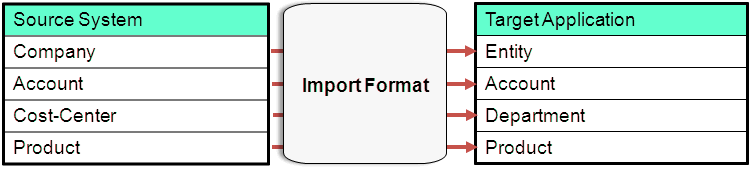
Note:
Each member in the source is created as a single member in the target dimension.
Note:
When importing a mapping file that has maps for one dimension, the dimension name needs to be in the first field of the file.
-
-
Many-to-One Mappings—You can concatenate segments or chartfields to map multiple segments or chartfields from the source into a single EPM dimension member.
When dimensions are mapped as a concatenated segment, the new dimension is created based on the traversal order that you define for the source hierarchies into the concatenated member target dimension. Unlimited number segments may be concatenated into the target dimension. The following table shows how the segments map to dimensions. In this example, two segments (Company and Department) map to one dimension (Entity).
Table 2-5 Segment Mappings to EPM Dimensions
Segment/Chartfield EPM Dimension Company Entity Department Product Product Account Account -
Concatenations of any number of source segments for Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) sources like Oracle E-Business Suite and PeopleSoft.