RegRead Method
The RegRead method reads the property details from the xml and
returns the values of the property based on the provided type.
Example:
In the case of dbConnection type it returns a database connection string along with the database provider based on property name specified by the user.
Syntax
WshellObj.RegRead(propertyName)
Arguments:
propertyName – Its equivalent to the name attribute of property element in the xml specified by the user whose type is dbConnection.
The following steps must be followed to use RegRead Method:
-
Create an xml file containing properties details. Please refer to the screenshot below for the format of the xml file.
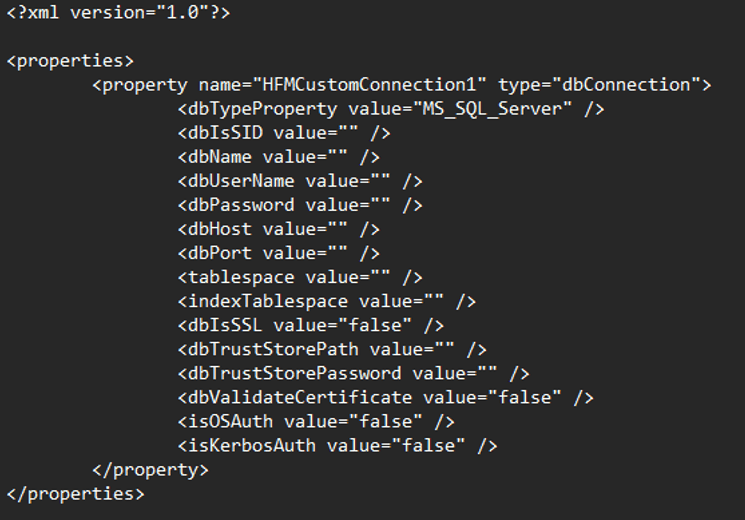
-
Insert a new entry with parameter name
FMRegPropertyFilePathinto the tables XFM_PARAMETERS and XFM_PARAMETERS_DEFAULT whose value should point to xml file path created in previous step.Below is an example of queries that can be executed in the database to add the required parameter in both tables respectively.
-
Insert into XFM_PARAMETERS (ParameterName,ClusterName,ServerName,ApplicationName, CategoryName,Value) Values ('FMRegPropertyFilePath’, 'ALL','ALL','ALL','ALL', 'C:\sample.xml')
-
Insert into XFM_PARAMETERS_DEFAULTS (name,Type,Hidden,Validation, Description,DefaultValue) Values ('FMRegPropertyFilePath’, 1,1,'',' XML File path for FM Registry Property for DB Connection ', 'C:\sample.xml')
-
-
In the script file, enter the
propertyNameinRegReadmethod that is equivalent to the name attribute of property element in the xml file created by the user whose type is dbConnection.
Example:
Public Const strKey = "HFMCustomConnection1"
Set objShell = CreateObject("WScript.Shell")
strDBConnection = objShell.RegRead(strKey)
Output: - strDBConnection will contain string in the below format
Provider=providerType;DRIVER=driverDetails
Note:
To reflect new changes made in xml, users need to close and reopen the application as the xml details are cached while opening the application itself, which is used later.