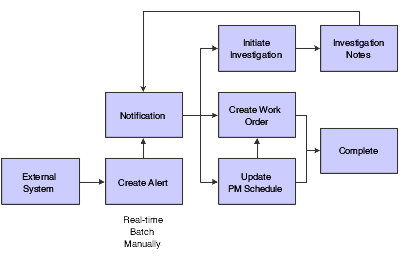
Process Flow for Condition-Based Maintenance
These steps provide an example of the typical flow of events and processes within JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CBM:
An external system determines whether an equipment reading is at an alert status.
The external system sends alert details to the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CBM system.
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CBM system imports the alert details to the condition-based alerts table.
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CBM system sends a notification message to the maintenance coordinator.
The maintenance coordinator reviews the message about the equipment in alert.
The maintenance coordinator sends an investigation message to the responsible technician
Alternatively, the equipment alert causes the system to automatically send an investigation message to the responsible technician
The technician reports back to the maintenance coordinator with the results of the investigation.
The maintenance coordinator uses the investigation results to determine whether to create a work order.
If necessary, the maintenance coordinator creates a work order or updates the preventive maintenance schedule to create a work order.
Alternatively, the equipment alert causes the system to automatically create a work order to respond to the alert condition.
This flowchart illustrates the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne CBM process: