Orchestrating the Advanced Plan Using the Microsoft SQL Server Database
This section shows you how to orchestrate an Advanced deployment plan using the Microsoft SQL Server Database.
By orchestrating a deployment plan using the Advanced mode, you can:
-
Modify and add servers to an existing orchestration that was created using the Quick Start wizard.
- Create a new orchestration with no guidance from a wizard. Unlike the Quick Start wizard, the Advanced mode will not guide you through the required sequence of machines to satisfy dependencies of the configuration. For example, the allowable pathcodes for an Enterprise Server are dependent on the schemas previously selected for the Database Server.
Prerequisites
- You must have configured the administrator passwords for the WebLogic Server and the Server Manager Console in the Configure section of the JD Edwards One-Click Provisioning Console.
-
Before orchestrating an Advanced deployment plan, the recommended practice is to first orchestrate a basic deployment plan using the Quick Start mode. The Quick Start procedure is documented in the section "Orchestrating the Quick Start Plan Using the Microsoft SQL Server Database" of this Learning Path. After this Quick Start orchestration is created, you can use the Advanced mode to modify, delete, or add additional server instances.
Alternatively, experienced users, who are aware of the required sequence of creation and the interdependencies, can use the Advanced mode to create an orchestration from start.
Orchestrating the Advanced Plan Using the Microsoft SQL Server Database
The required sequence of adding instances to an orchestration and the rules related to the machines and pathcodes are as follows:
- Database Server
You can create five database instances if you select one schema per instance.
- Enterprise Server
One or many Enterprise Servers can be created. At least one Enterprise Server must be created with the selected pathcodes from the schemas that were selected for the Database Server. An Enterprise Server must be configured before you can add HTML Servers. If multiple Enterprise Servers are deployed, at least one must be configured as a Logic Server per pathcode. Additional Enterprise Servers can be added to an orchestration and they can be deployed after your initial plan is deployed.
- HTML Servers
HTML Server. Web Servers include the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne HTML Server. There are two types of HTML Servers: Standard JAS and Dedicated HTML for AIS.
One to many HTML Server instances can be created and each will be associated with one specific pathcode that is available on the Enterprise Server. Additional HTML Servers can be added to an Orchestration and they can be deployed after your initial plan is deployed.
Refer to the Fundamentals section of this Learning Path for a description of each type of HTML Server.
AIS Server. Another type of Web Server for JD Edwards EnterpriseOne is the AIS Server, which must be installed and configured along with a Dedicated HTML Server for AIS.
Zero to many AIS Server instances can be created and each will be associated with a specific HTML Server instance. Additional AIS Server instances can be added on to your plan and deployed after your initial plan is deployed.
Important: If you do not specify at least one AIS Server, the full functionality of certain JD Edwards EnterpriseOne applications will not be available. If you used the Quick Start mode to configure a basic environment, the workflow required the inclusion of this server.Important:You cannot specify a single HTML Server instance to also support an AIS Server; that is, you cannot combine two servers in the same instance. You must create a separate instance for each AIS Server.
- AIS Servers
You can either create or not create an AIS Server instance. Multiple AIS Server instances can be created and each will be associated with a specific HTML Server instance. Additional AIS Server instances can be added to your plan and deployed after your initial plan is deployed.
Important:If you do not specify at least one AIS Server, the full functionality of certain JD Edwards EnterpriseOne applications will not be available.
Important:You cannot specify an HTML Server instance to also support an AIS Server. You must create a separate instance for each AIS Server.
- Deployment Server
A single Deployment Server can be created and all the pathcodes can be selected regardless of the pathcodes selected for your runtime servers.
For any orchestration created or modified using the Advanced Mode deployment plan, you can click the Options function from the menu bar to change your Global Settings or to reset your settings (that is, to delete your configuration details, global settings, and orchestration data).
To use the JD Edwards Provisioning Console to orchestrate and deploy an Advanced deployment plan:
On the JD Edwards Provisioning Console page, click the Orchestrate icon.
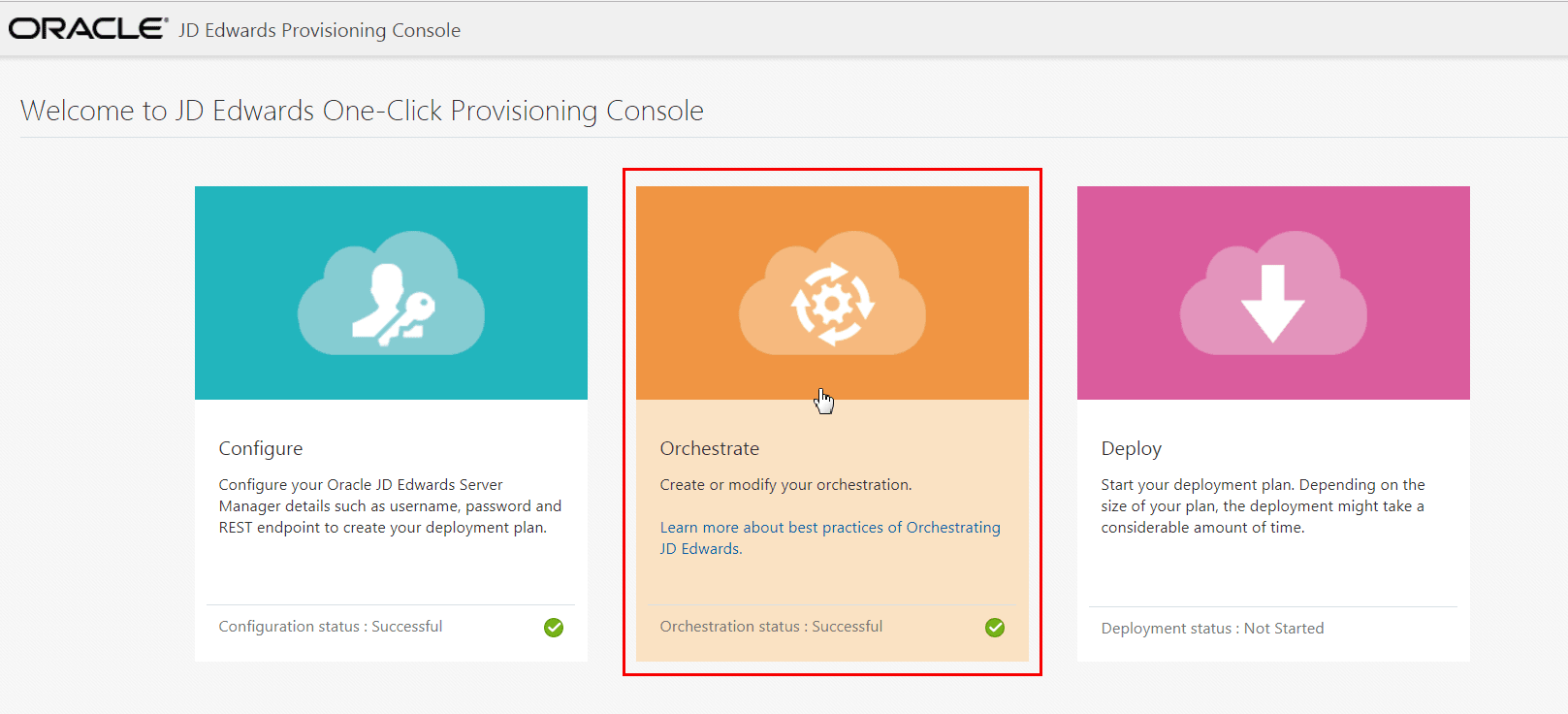
-
On the JD Edwards Servers page, click the instance of an existing server, or click the New Server icon to add a new JD Edwards service. Alternatively, you can select the desired server from Service Types on the left tab, and then click New Server to add a new server.
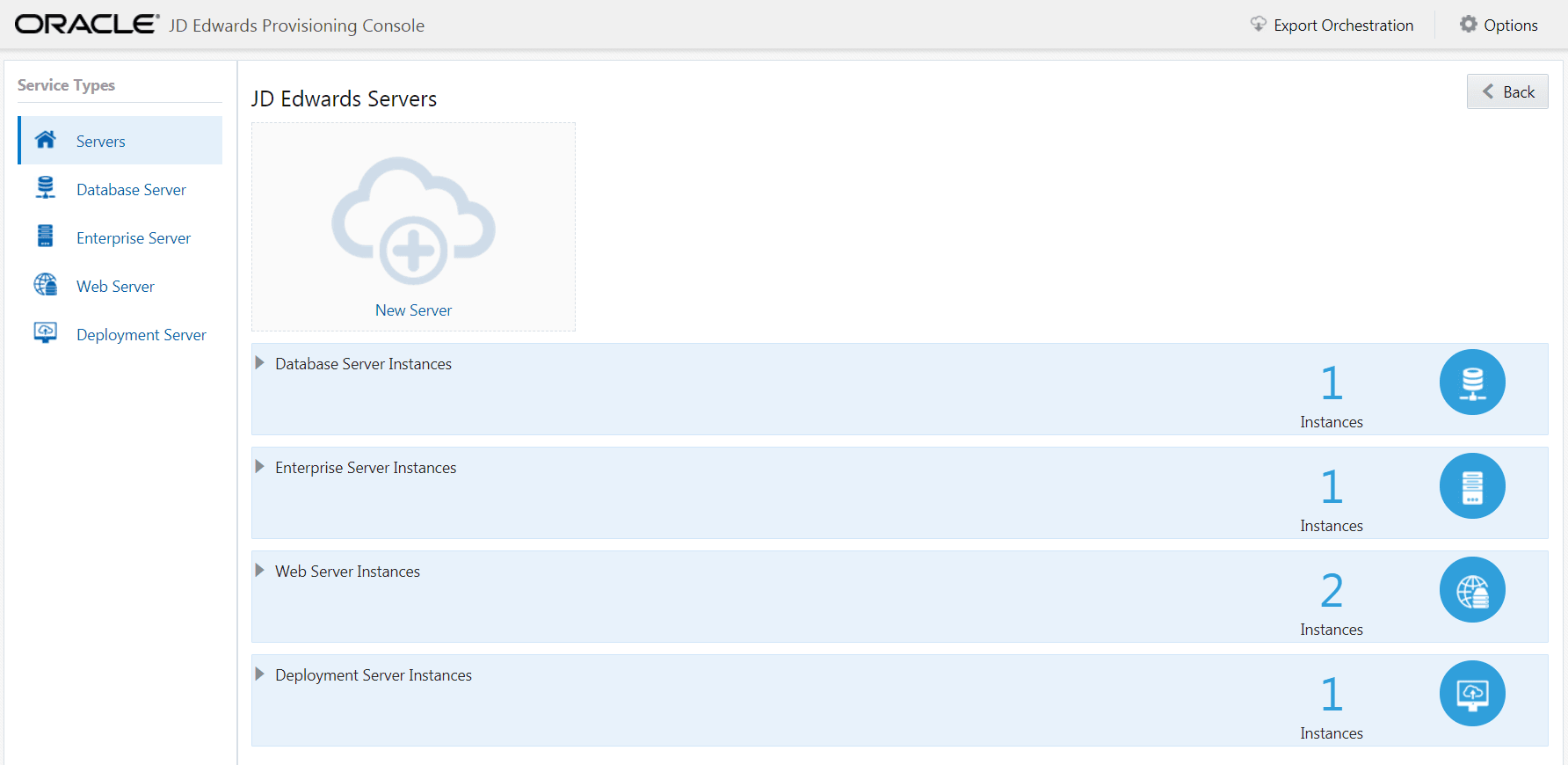 Note:
Note:The remainder of this procedure includes steps to either add (where allowed) or modify (existing) these instances:
- Database Server
- Enterprise Server
- Web Server (for example, HTML Server and AIS Server)
- Deployment Server*
* The Provisioning Console will not allow you to add more than one server because only one server of this type is supported per deployment.
Database Server
You can create five database instances if you select one schema per instance. For example, if you select Development and Shared schemas for an instance, you can create three more database instances. For one deployment instance, you can have a maximum of five schemas distributed across one or many database instances.
You can provision the Database Server instance with the available schemas as required. The following schemas are available for the database instance:
- Development
-
Shared (required)
- Prototype
- Production
- Pristine
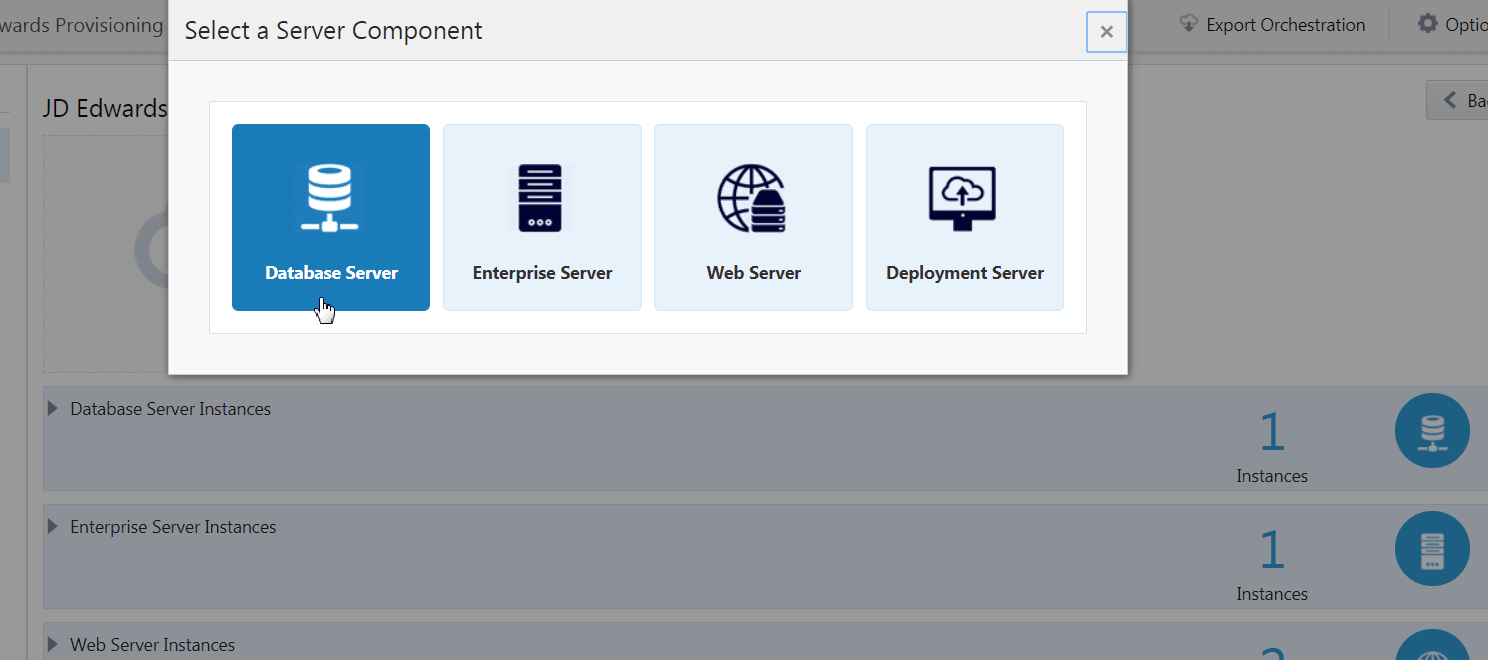
To add a Database Server instance:
- Click the New Server icon and select Database Server from the
Select a Server Component window.
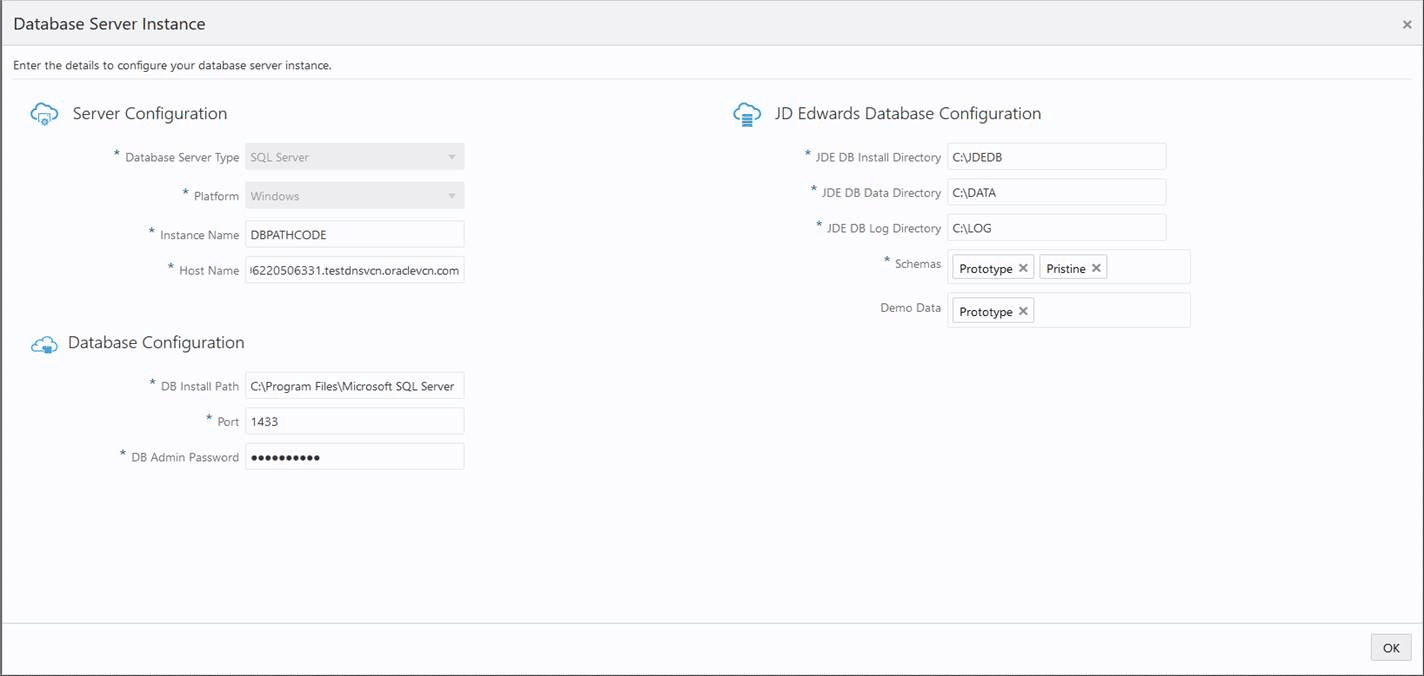
On Database Server Instance page, complete the following fields to create and configure the Database Server instance.
Server Configuration
-
Database Server Type
Select the Database Server Type as SQL Server. The server types available are: Oracle Database and SQL Server.
-
Platform
This field is disabled and it is automatically populated as Windows.
-
Instance Name
Create an instance name for your database instance.
-
Host Name
Enter the host name.
Tip: To determine a currently set host name, refer to the section "Retrieve a Host Name" of this Learning Path.
Database Configuration
-
DB Install Path
Enter the path of the directory where you have installed the SQL Server database components.
-
Port
Enter a unique port number.
Note:You must use a static port value.
-
DB Admin Password
Enter the password of the database administrator.
Note:JD Edwards EnterpriseOne One-Click Provisioning specifically supports only these special characters for the SQL Server database admin password:
Underscore (_)
At sign (@)
Tilde (~)
Plus sign (+)
Hyphen (-)
Asterisk (*)
JD Edwards Database Configuration
-
JDE DB Install Directory
Enter the installation path.
Path Rules: All the directories in the specified path must preexist, except the last directory in the path. The name of the last directory must be unique. One-Click validation checks that the parent directory exists. The child directory is created by One-Click using the name provided in the input. If there are sub folders leading to the child directory, they must be created manually. For example, if the specified JDE DB Install directory is
C:\JDEdwards\DBInstallPath, thenC:\JDEdwardsis the parent directory and it must be created manually.DBInstallPathis the child directory and should not be created manually, One-Click uses the name provided in the input and creates it. -
JDE DB Data Directory
Enter the path to install the table data.
Path Rules: All the directories in the specified path must preexist, except the last directory in the path. The name of the last directory must be unique. One-Click validation checks that the parent directory exists. The child directory is created by One-Click using the name provided in the input. If there are sub folders leading to the child directory, they must be created manually. For example, if the specified JDE DB Install directory is
C:\JDEdwards\Data, thenC:\JDEdwardsis the parent directory and it must be created manually.Datais the child directory and should not be created manually, One-Click uses the name provided in the input and creates it. -
JDE DB Log Directory
Enter the path to save the log files.
Path Rules: All the directories in the specified path must preexist, except the last directory in the path. The name of the last directory must be unique. One-Click validation checks that the parent directory exists. The child directory is created by One-Click using the name provided in the input. If there are sub folders leading to the child directory, they must be created manually. For example, if the specified JDE DB Install directory is
C:\JDEdwards\Log, thenC:\JDEdwardsis the parent directory and it must be created manually.Logis the child directory and should not be created manually, One-Click uses the name provided in the input and creates it. -
Schemas
Click the Schemas field and select the schemas you want from the auto-suggest text. The schemas available are: Shared, Development, Prototype, Production, and Pristine with Demo data.
Note:It is mandatory to add the Shared schema.
Important:At this point, you should ensure that you specify all the schemas you might use. The schemas you choose to install on the Database Server can only be deployed once, which is specified at this point in the Provisioning Console. You can use the Provisioning Console to programmatically add additional schemas after deploying the orchestration.
-
Demo Data
Click the Demo Data field and select the available demo data from the auto-suggest text. Demo data will be available depending on the schema selected. For example, if you select the schema as Development, the Development demo data will be available.
-
- Click the Next button. Because you will be connecting to an existing Oracle Cloud Infrastructure database instance, the system validates all the inputs that are provided. If the validation is successful, the JD Edwards Enterprise Server page is displayed.
- You should now be able to view multiple instances of the Database Server.
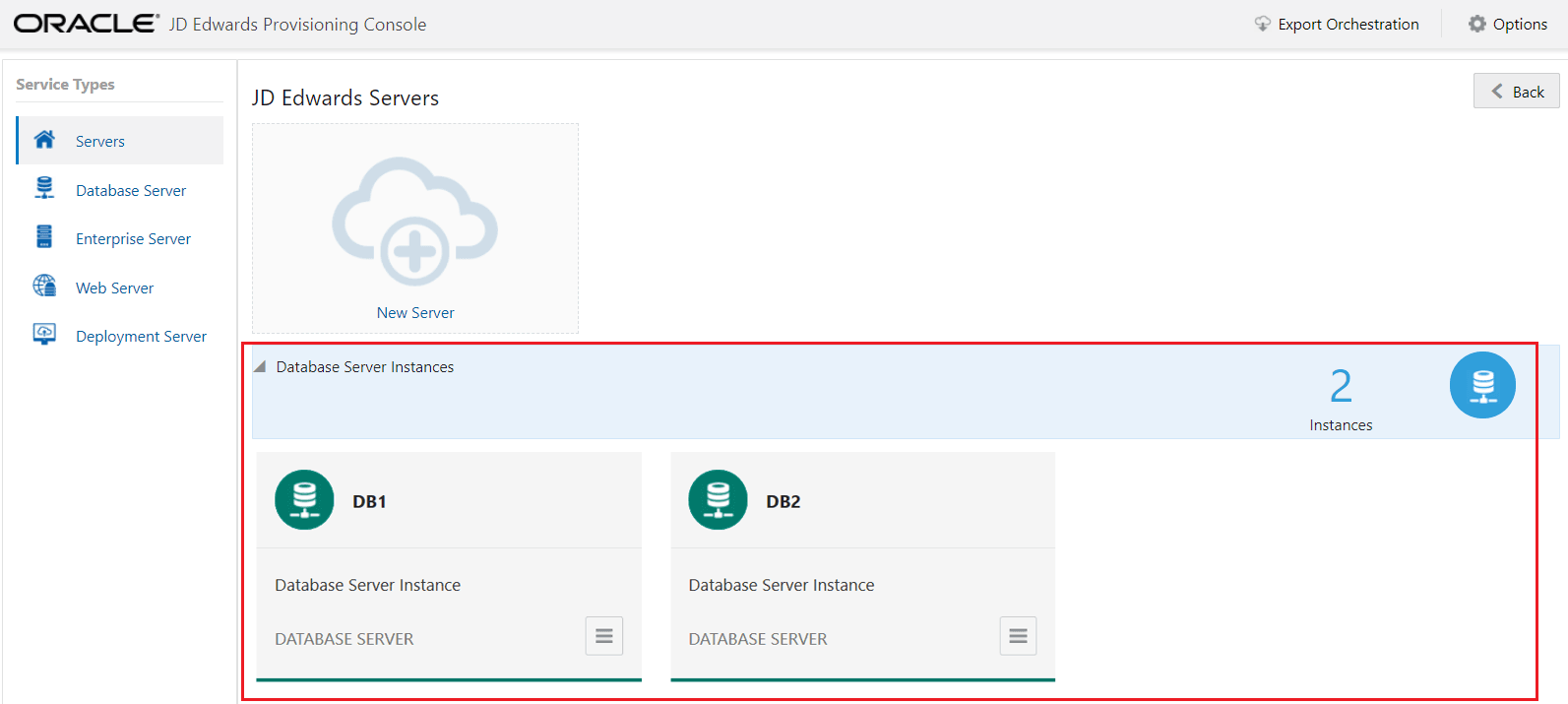
- Click View from the Application Options menu selection of an instance to
view the existing configuration for the Database Server. To modify the instance
configuration, use the Edit option.
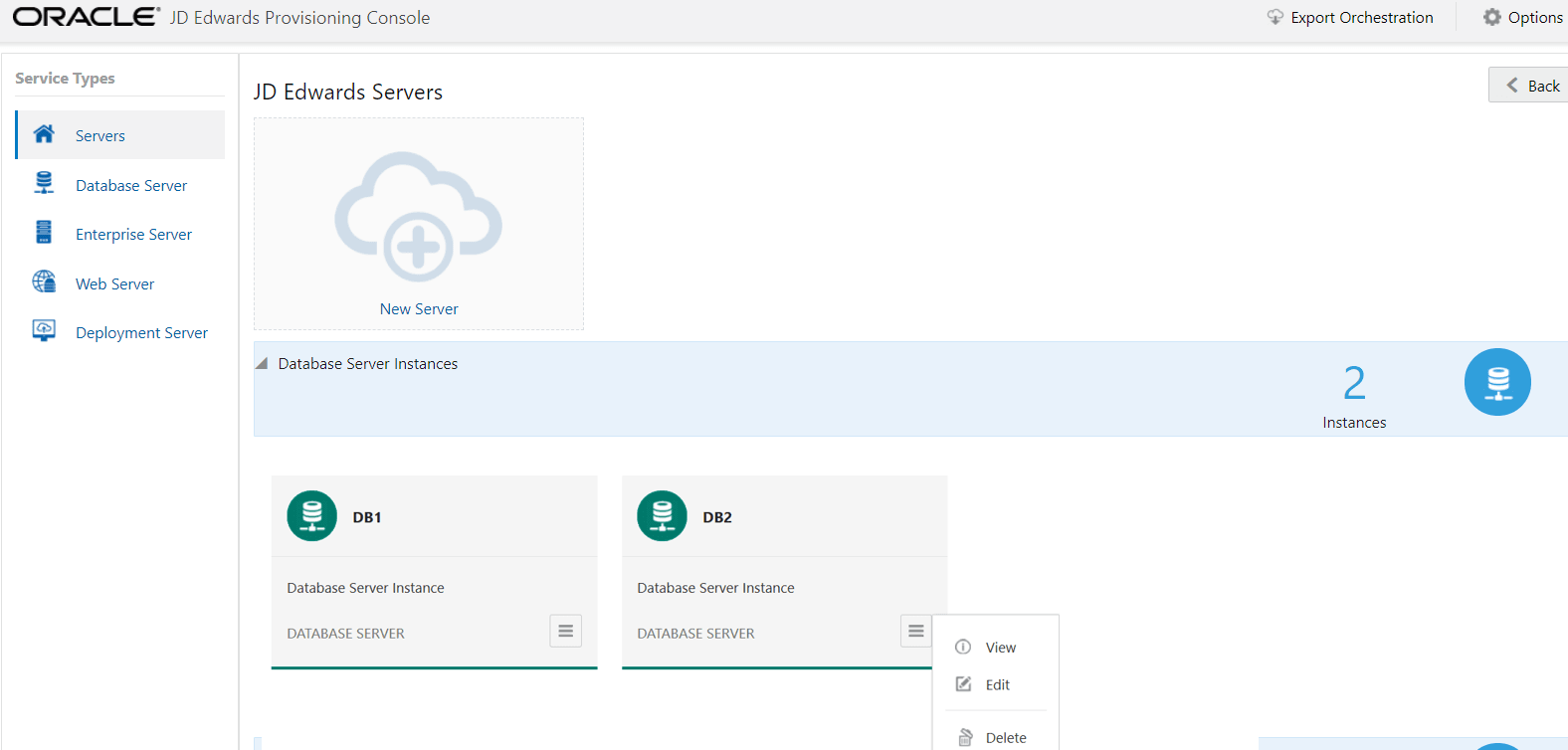 Important:
Important:The Provisioning Console for One-Click Provisioning allows you to edit the schemas and demo data settings for an existing Database Server post-deployment.
- To delete the instance, select the Delete option.
Enterprise Server
You can define any number of Enterprise Server instances. If you want only one Enterprise Server, you should define it to run both Logic and Batch. If you want to define multiple Enterprise Servers, at least one must be a Logic Server per pathcode.
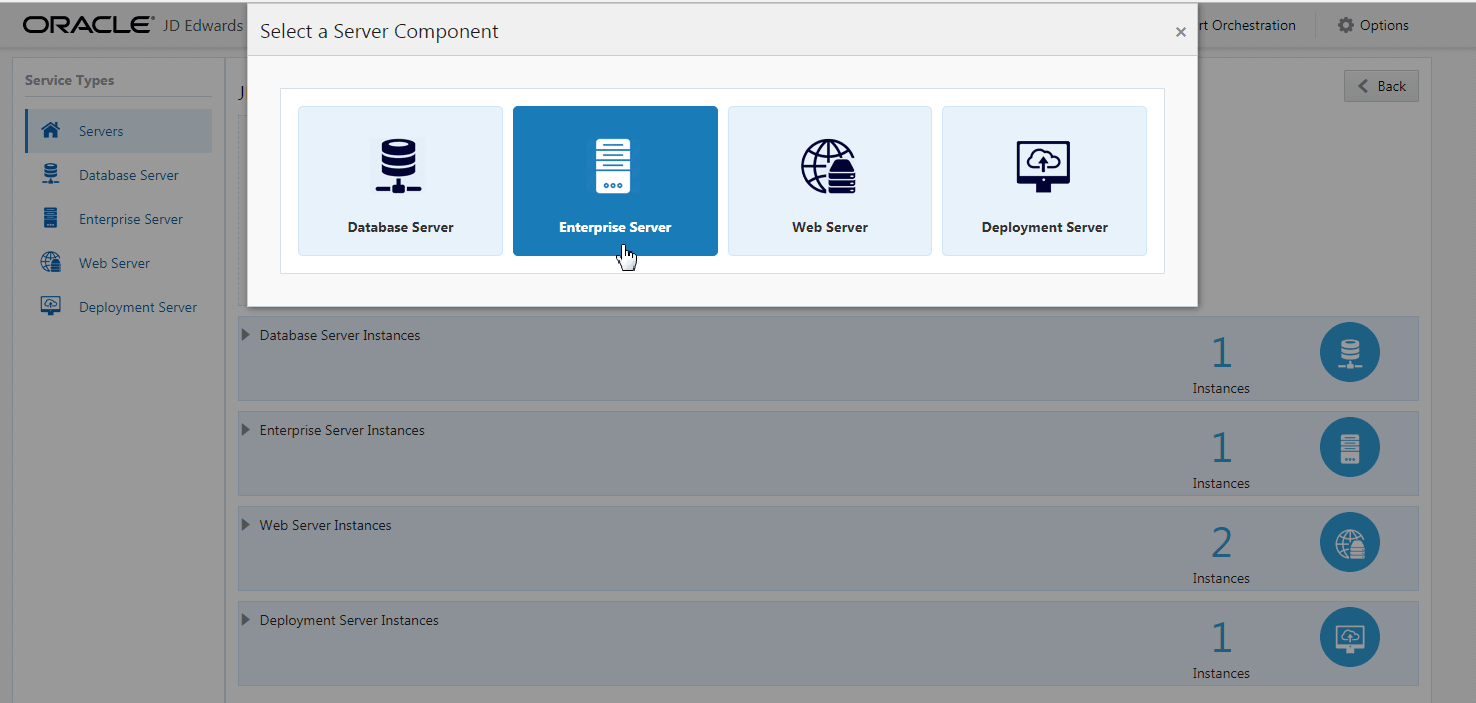
To add an Enterprise Server:
- Click the New Server icon and select Enterprise Server from the Select a
Component window.
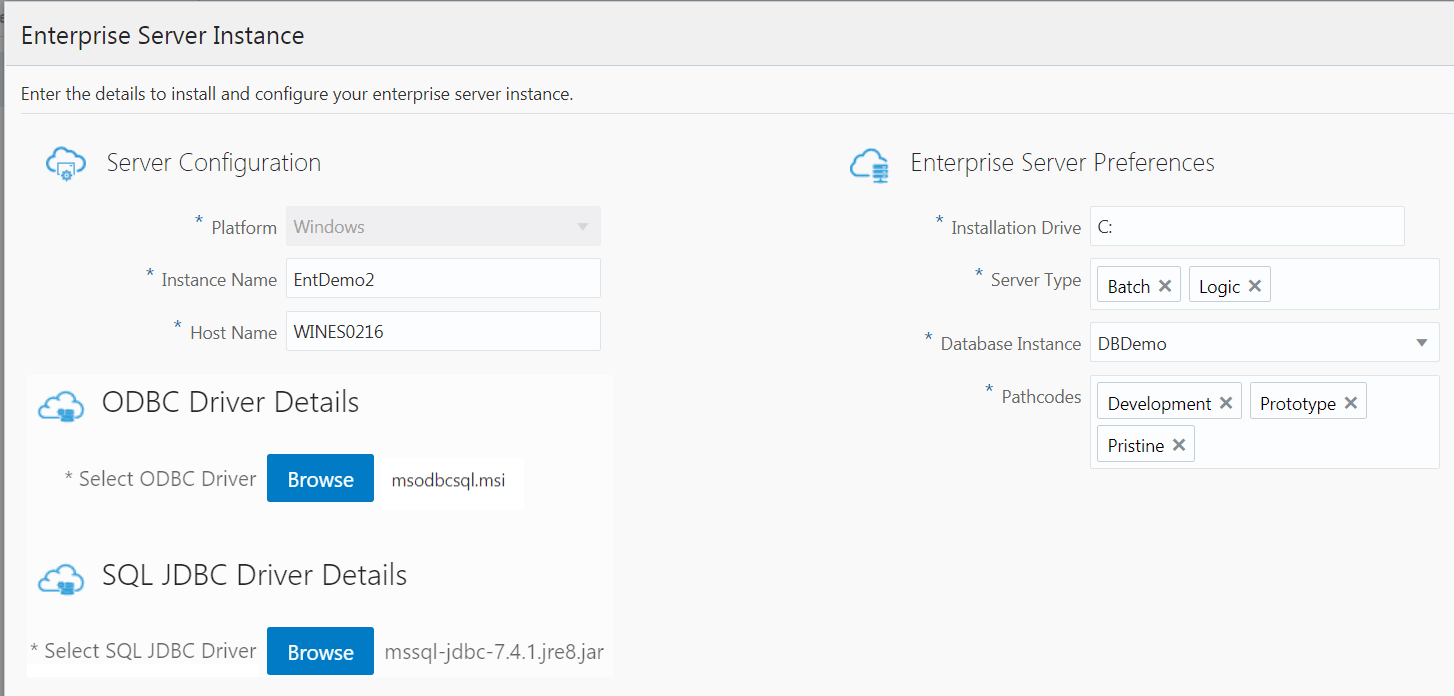
On Enterprise Server Instance page, complete these fields to create and configure the Enterprise Server instance.
Server Configuration-
Platform
This field is disabled and it is automatically populated as Windows.
-
Instance Name
Create an instance name for the Enterprise Server. The conditions to set the service name are displayed in the tooltip when you click the field.
-
Host Name
Enter the host name.
Tip:To determine a currently set host name, refer to the section "Retrieve a Host Name" of this Learning Path.
ODBC Driver Details
-
Select ODBC Driver
Browse and select the 64-bit ODBC driver that is used to connect to the SQL Database Server from the Enterprise Server. For example, msodbcsql.msi.
Refer to Oracle Certifications for the supported driver version.
SQL JDBC Driver Details
-
Browse and select the SQL Server JDBC driver that is required for connectivity between the Enterprise Server and the SQL Server database server. For example, mssql-jdbc-7.4.1.jre8.jar.
Refer to Oracle Certifications for the supported driver version.
Enterprise Server Preferences
-
Installation Drive
Enter the Installation Drive.
-
Server Type
Select one or both of the available server types for this Enterprise Server.
Single Enterprise Server. If you are deploying only a single Enterprise Server, select both Logic and Batch.
Multiple Enterprise Servers. If you are deploying multiple Enterprise Servers, at least one must be specified as a Logic server per pathcode. The others can be specified as Batch servers.
-
Pathcodes
Click the Available Pathcodes field and select the pathcodes required from the auto-suggest. The four available pathcodes are: Development, Prototype, Pristine, and Production.
Important:It is a good practice to select pathcodes here that correlate to the schemas you selected for the Database Server. The Provisioning Console programmatically enforces this correlation. If you select pathcodes on the Enterprise Server that are a superset of the database schemas you selected, the Enterprise Server will not be able to access the data required to function correctly. The pathcodes you choose to install on the Enterprise Server can only be deployed once, and these pathcodes need to be specified at this point in the Provisioning Console. After the configuration is deployed, you can use the Provisioning Console to programmatically add additional pathcodes.
-
- Click the OK button.
- You should now be able to view multiple instances of the Enterprise
Server.
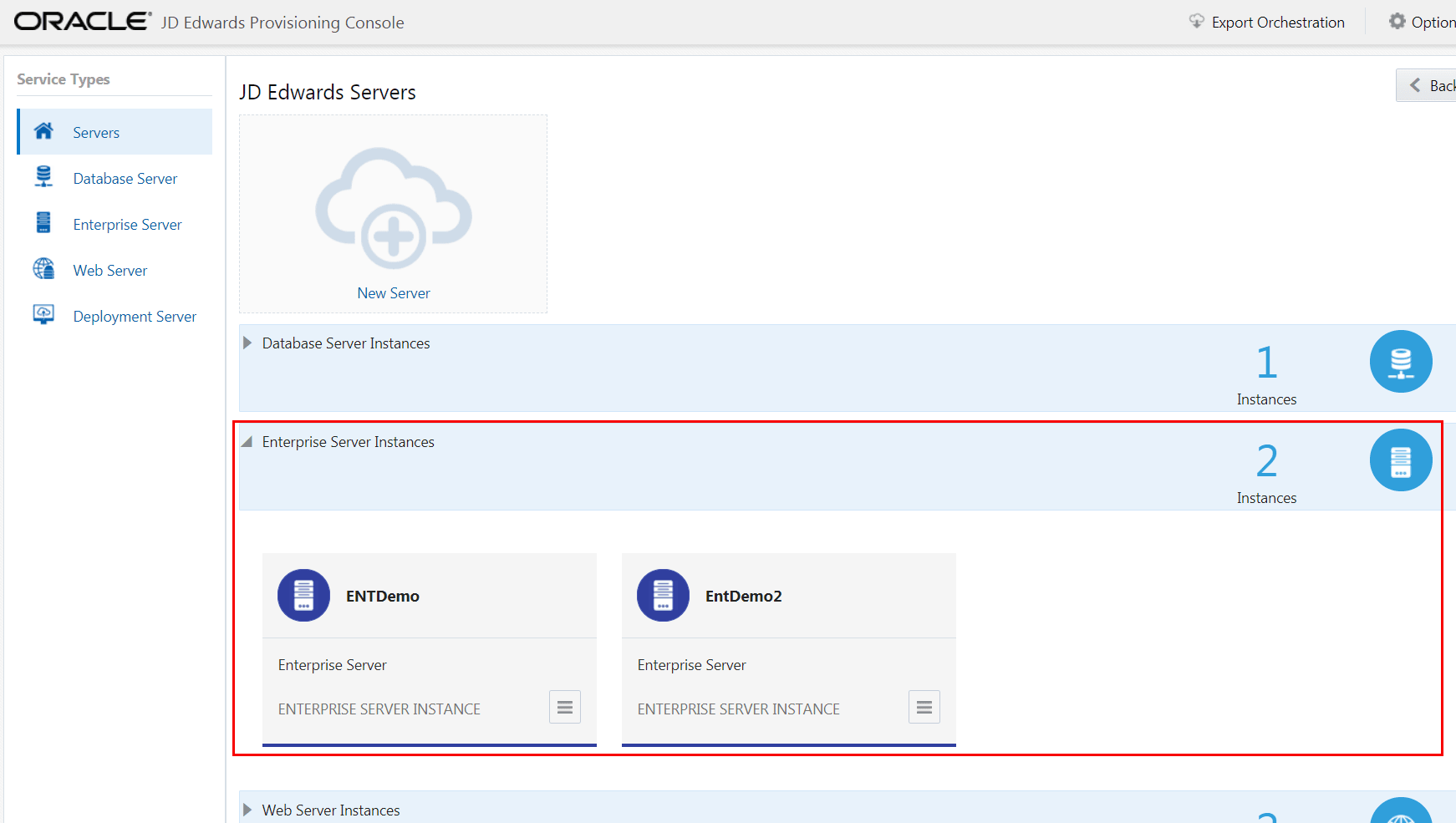
- Click View from the Application Options menu to view the existing
configuration for the Enterprise Server. To modify the instance configuration,
use the Application Options menu and select Edit. Use the Clone
option to clone the Enterprise Server instance.
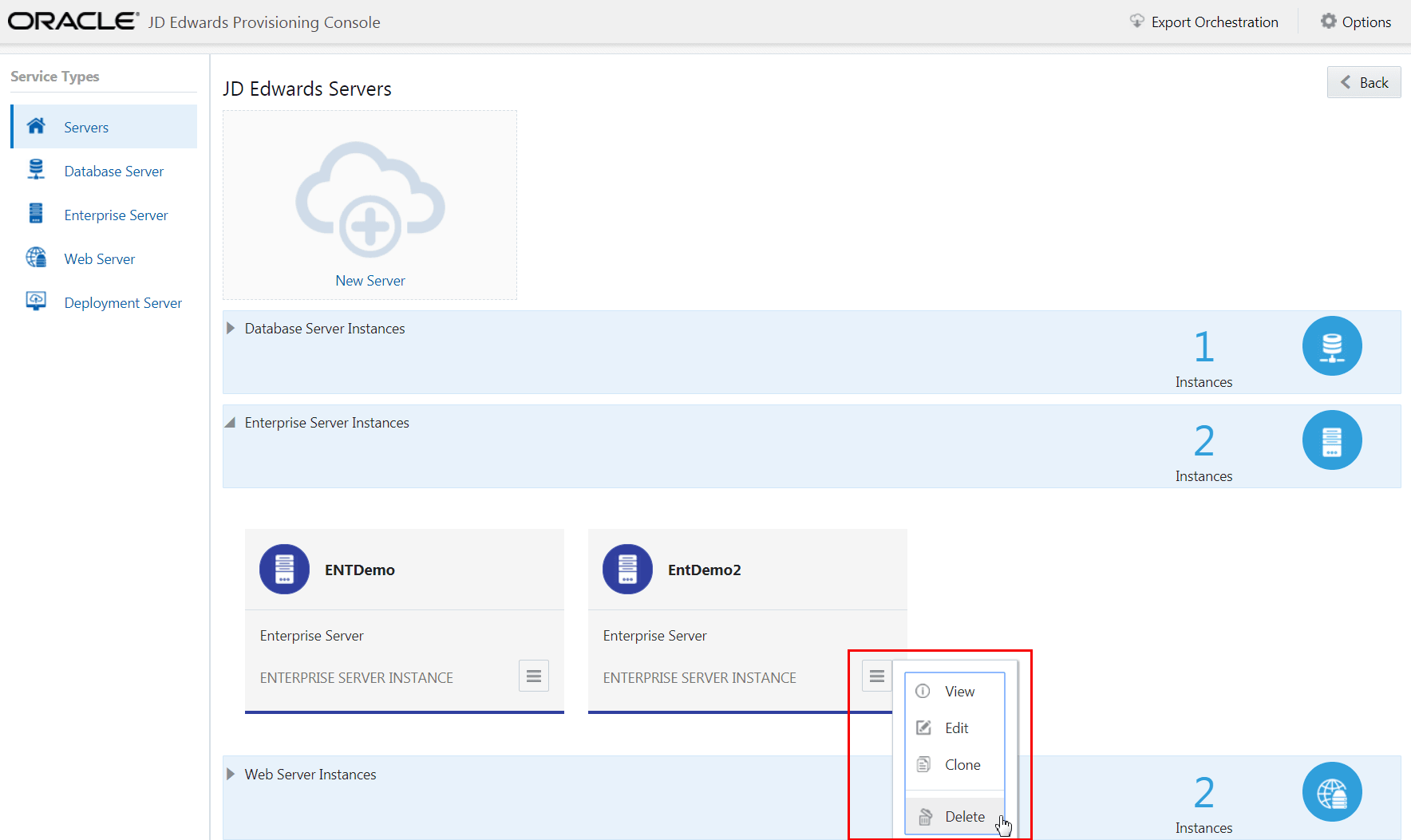
- To delete the instance, use the Application Options menu to select Delete.
Web Server
The instance type for Web Servers can be any of the server types available from the Type drop-down list; however, you must have at least one HTML Server configured prior to creating an associated AIS instance.
You can define any number of Web Server instances.
To add or modify a Web Server instance:
- Select the service type for the Web Server.
- To create a new Web Server, click the New Server icon and then the Web Server icon and complete the required fields.
-
To view an existing Web Server, click View from the Application Options menu. To modify the instance configuration, select the Edit option from the action tab. You will need enter the values for your installation for each of these Web Server types:
- HTML Server (Dedicated HTML Server for AIS)
- Application Interface Services (AIS) Server
- Standard JAS Server
Important:Because multiple Web Server instances can run on the same WebLogic Server, you must specify a different port for each instance.
Important:For a description of each HTML server type (Dedicated for AIS or Standard), refer to the Fundamentals section of this Learning Path.
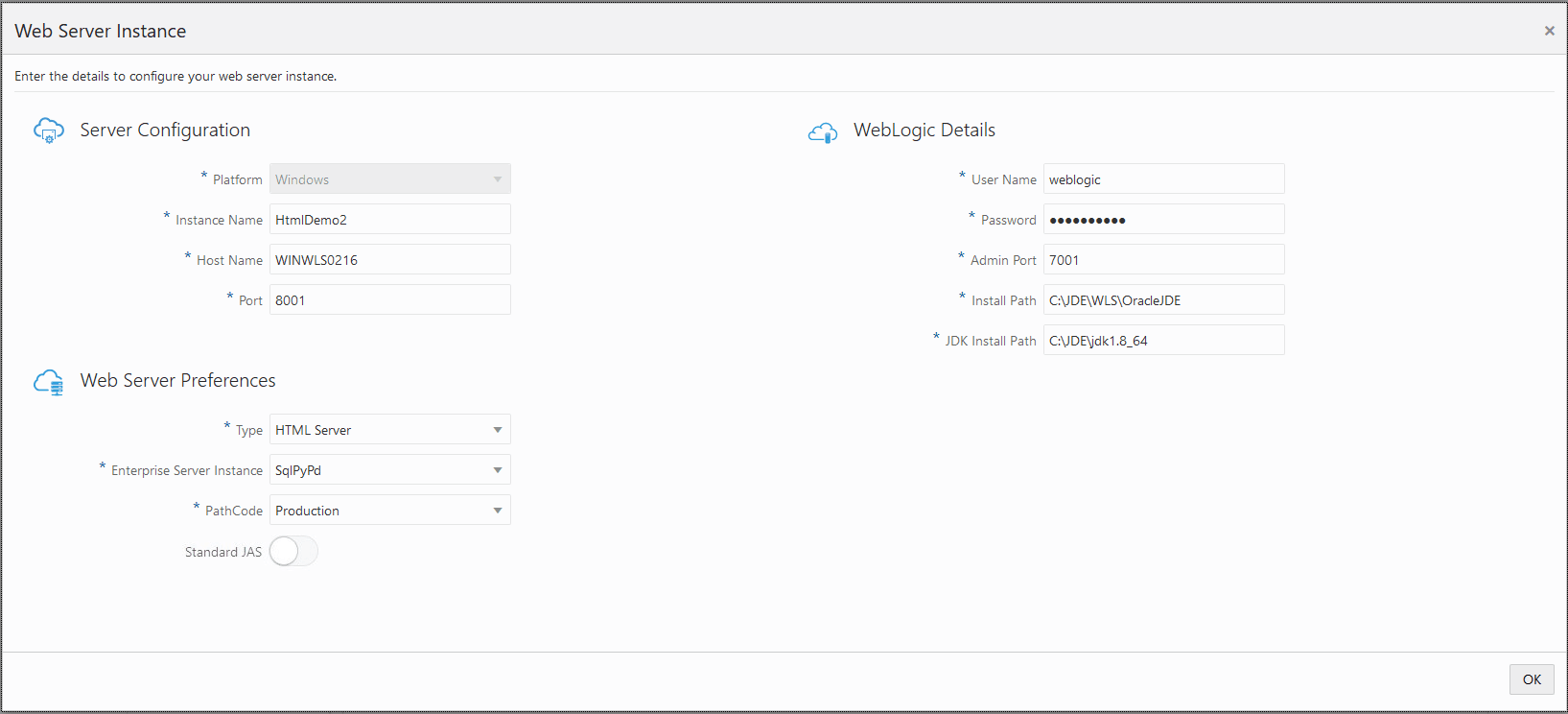
On the JD Edwards HTML Server page, complete these fields to create and configure the HTML Server instance.
Server Configuration
-
Platform
This field is disabled and it is automatically populated as Windows.
-
Instance Name
Create the instance name of the HTML Server instance.
-
Host Name
Enter the host name.
Tip:To determine a currently set host name, refer to the section "Retrieve a Host Name" of this Learning Path.
-
Port
Enter a unique (available) port number for this server that will use an SSL connection. This port number must be between 1024 and 65535. This port number is used by HTTPS to create a container and deploy the web component. For the port number you enter here, ensure that the port for one less <ensure that the port number that is one less> is also available. That is, if you specify port 8081, you must also ensure that port 8080 is available.
Important:For each SSL port that you open in the firewall, you must also open a companion port for non-SSL access that is required for the Server Manager. The companion port must have a numeric value that is one less than the value specified for the SSL port. For example, if you specify a port value of 8081 for SSL in the firewall, you must also open a port one less than that value; in this case you must open port 8080. Refer to the subsection "Enable Inbound Ports in the Firewall" of the OBE "Performing Common Setup for All Microsoft Windows Servers" in this Learning Path.
Web Server Preferences
-
PathCode
Create the instance name of the HTML Server instance.
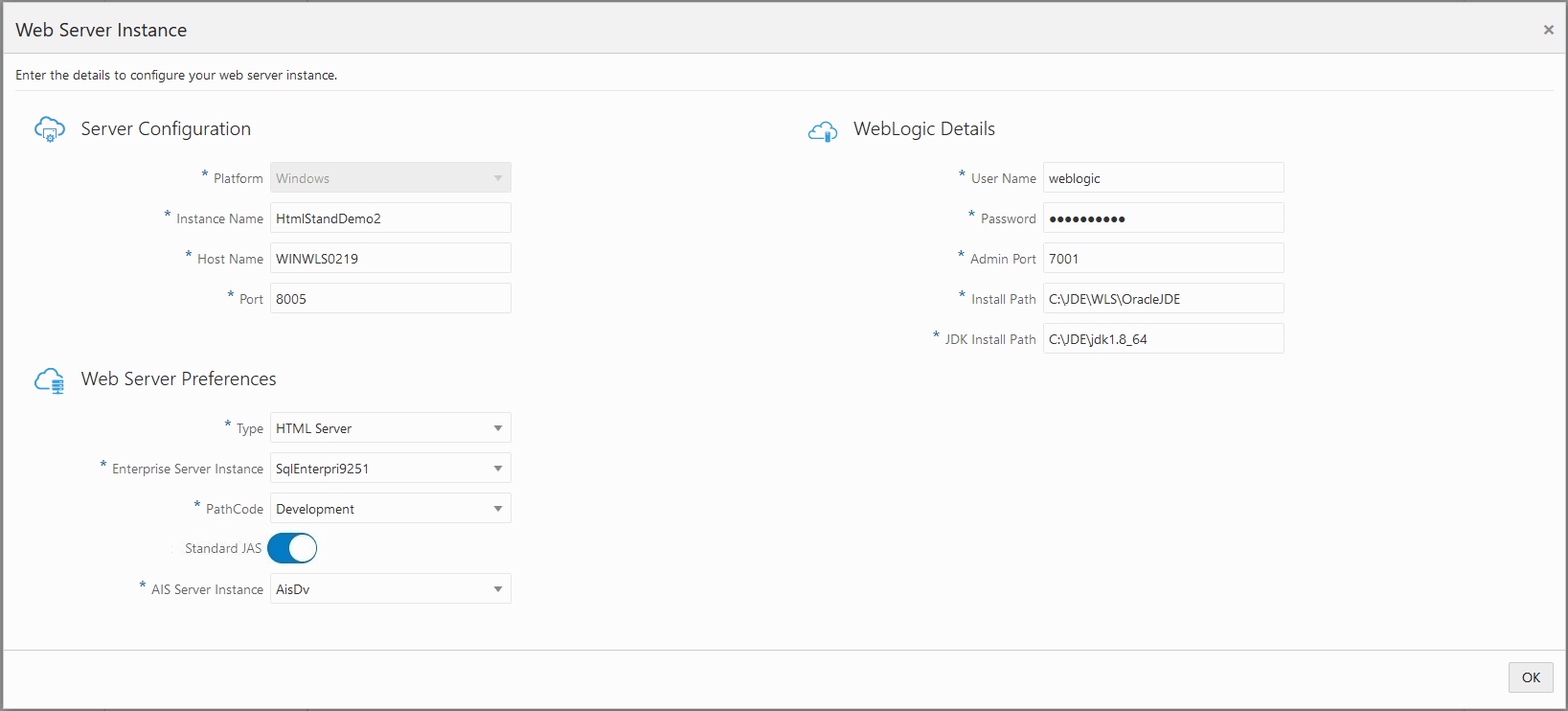
WebLogic Details
-
User Name
Enter the user name.
-
Password
Enter the WebLogic password.
-
Admin Port
Enter the admin port number.
-
Install Path
Enter the installation path of the WebLogic instance.
-
JDK Install Path
Enter the JDK installation path.
Important:Each HTML Server can only support one pathcode. If you want additional HTML instances to support additional pathcodes, you should use the Advanced mode of the Provisioning Console. Refer to the section "Orchestrating the Advanced Deployment Plan Using the Microsoft SQL Server" of this Learning Path.
-
- Click the Next button. The system validates the inputs. If the validation is successful, the JD Edwards AIS Server page is displayed.
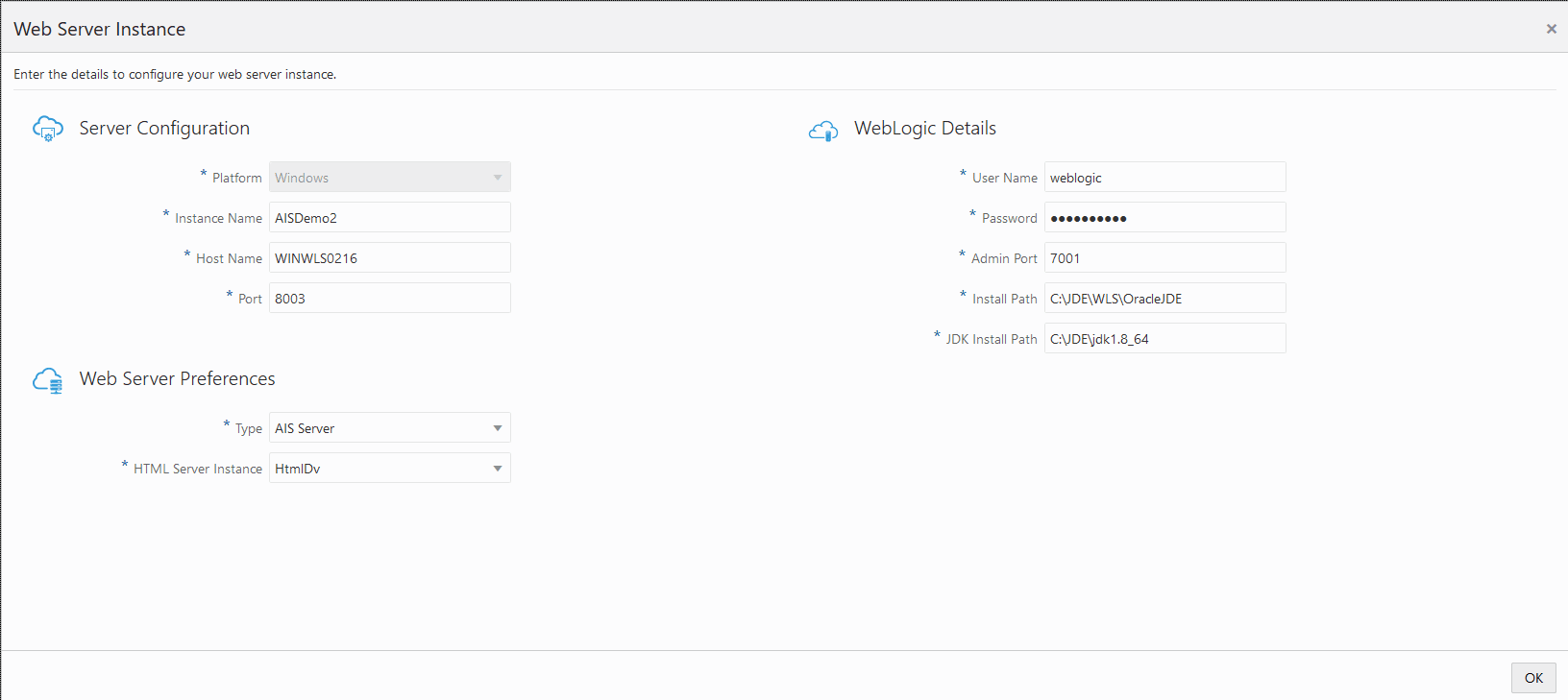
On the JD Edwards AIS Server, complete these fields to configure your AIS Server instance.
Server Configuration-
Platform
This field is disabled and it is automatically populated as Windows.
-
Instance Name
Create an instance name for the WebLogic Server.
-
Host Name
Enter the Host Name.
Tip: To determine a currently set host name, refer to the section "Retrieve a Host Name" of this Learning Path. -
Port
Enter a unique (available) port number for this server that will use a <an>SSL connection. This port number must be between 1024 and 65535. This port number is used by HTTPS to create a container and deploy the web component. For the port numberyou enter here, ensure that the port number that is one less is also available. This is, if you specify port 8081, you must also ensure that port 8080 is available.
Important:For each SSL port that you open in the firewall, you must also open a companion port for non-SSL access required for the Server Manager. The companion port must have a numeric value that is one less than the value specified for the SSL port. For example, if you specify a port value of 8081 for SSL in the firewall, you must also open a port one less than that value; in this case you must open port 8080. Refer to the subsection "Enable Inbound Ports in the Firewall" of the OBE "Performing Common Setup for All Microsoft Windows Servers" in this Learning Path.
WebLogic Details
-
User Name
Enter the user name.
-
Password
Enter the WebLogic password.
-
Admin Port
Enter the admin port number.
-
Install Path
Enter the installation path of the WebLogic instance.
-
JDK Install Path
Enter the JDK installation path.
-
- Click the Finish button.
- Verify that the Web Server instances you modified or added are displayed in the
JD Edwards Servers window.
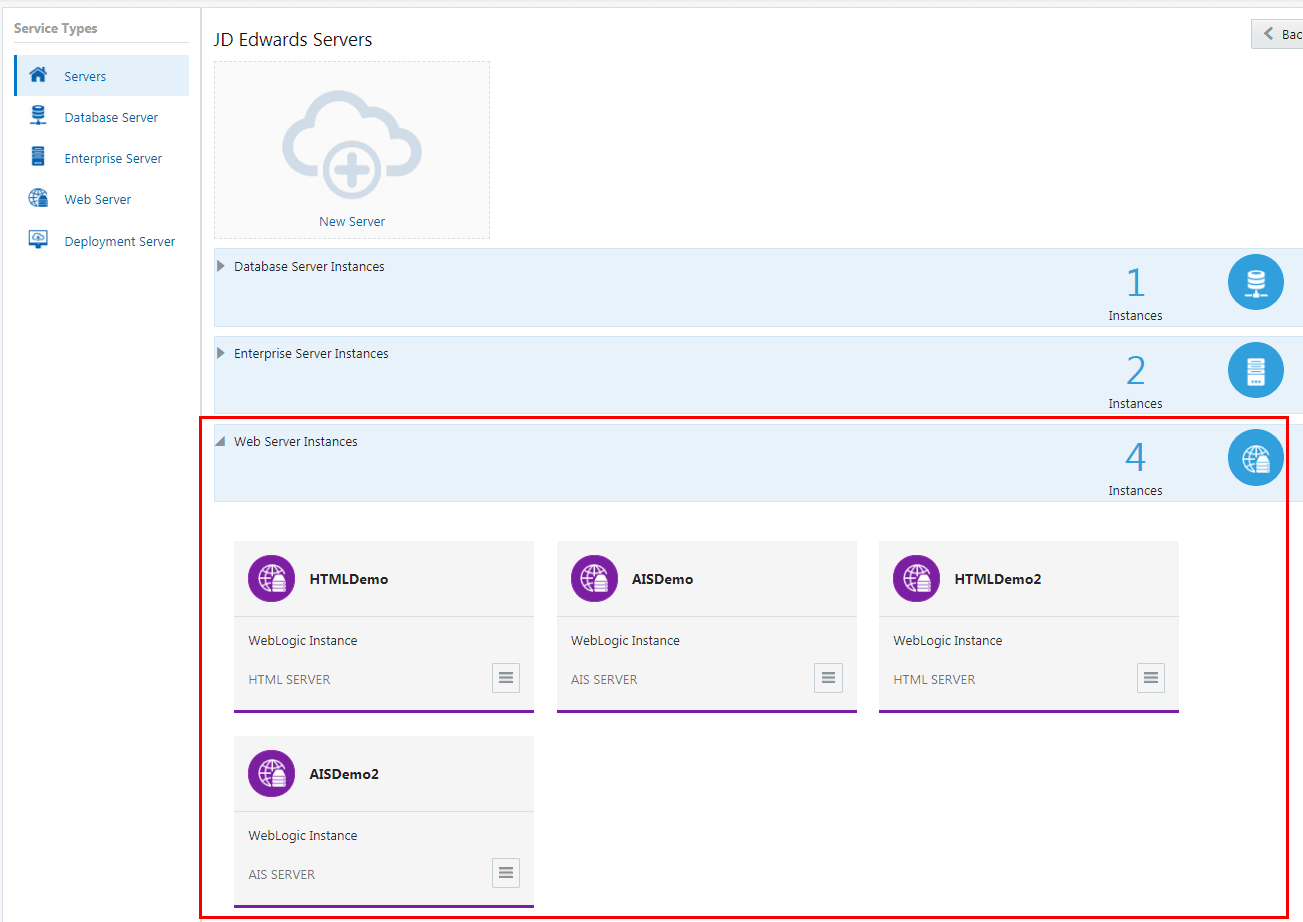
- To delete any web instance, use the Application Options menu to select Delete.
Deployment Server
You can use only one Deployment Server per deployment. If you attempt to add more
than one Deployment Server, the Provisioning Console displays an error
message.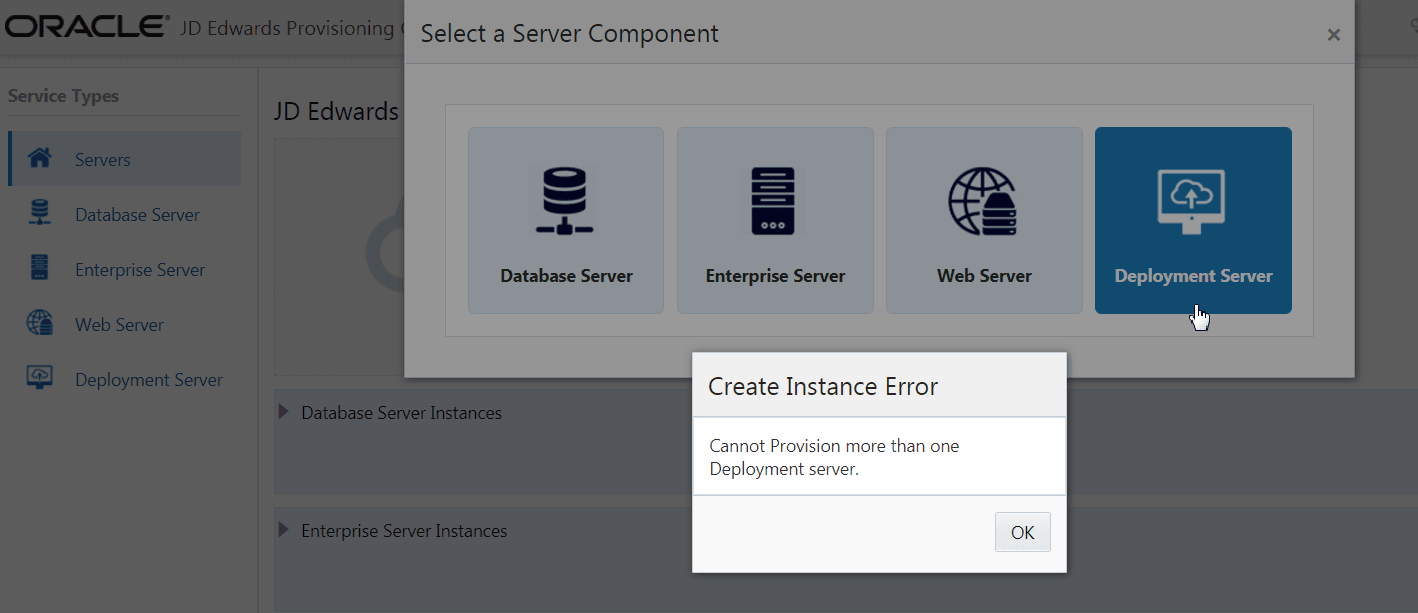
To modify the Deployment Server instance:
- On the JD Edwards Servers section, click the existing Deployment Server
instance, click the Application Options icon of an existing instance, and
select Edit.
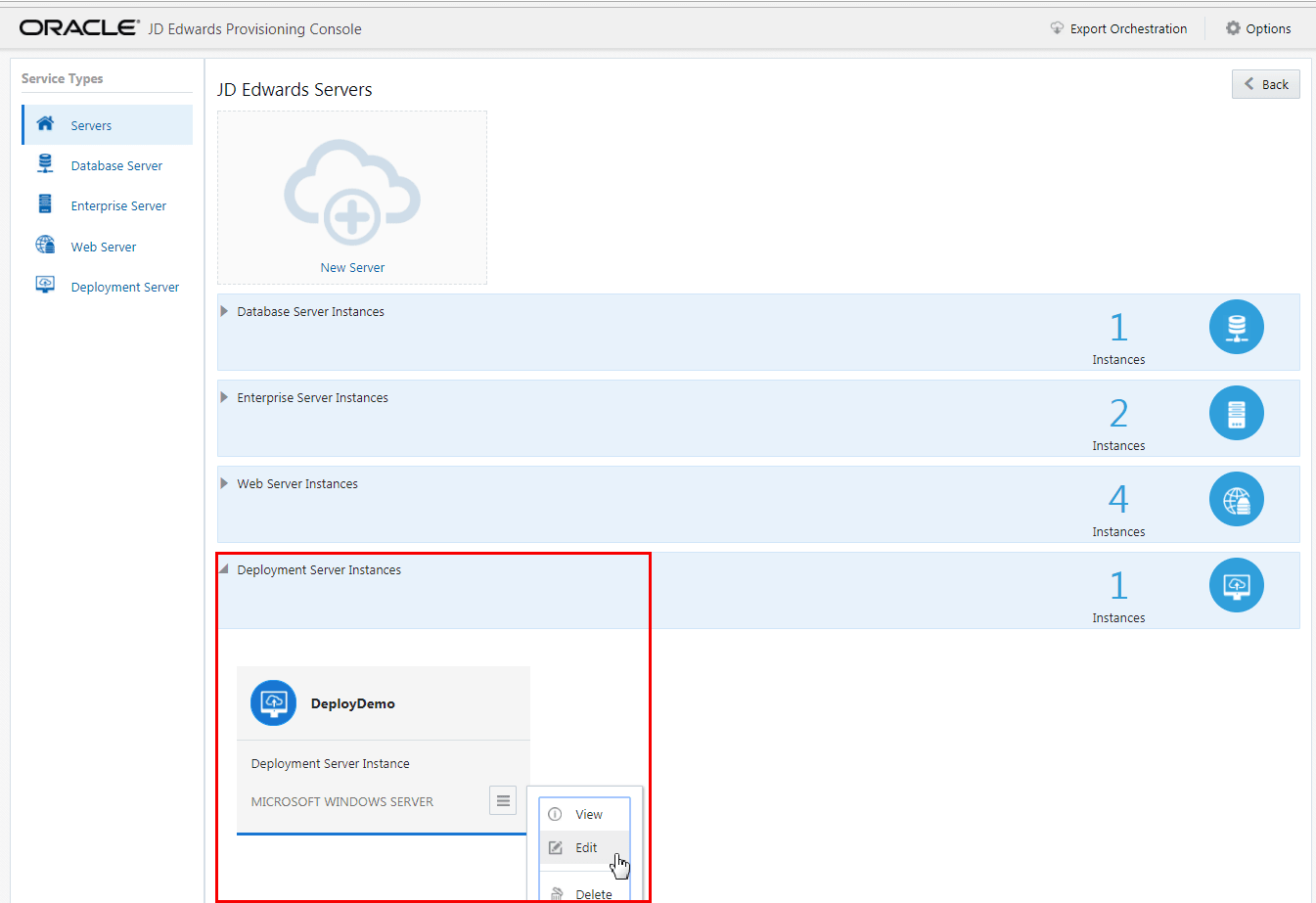
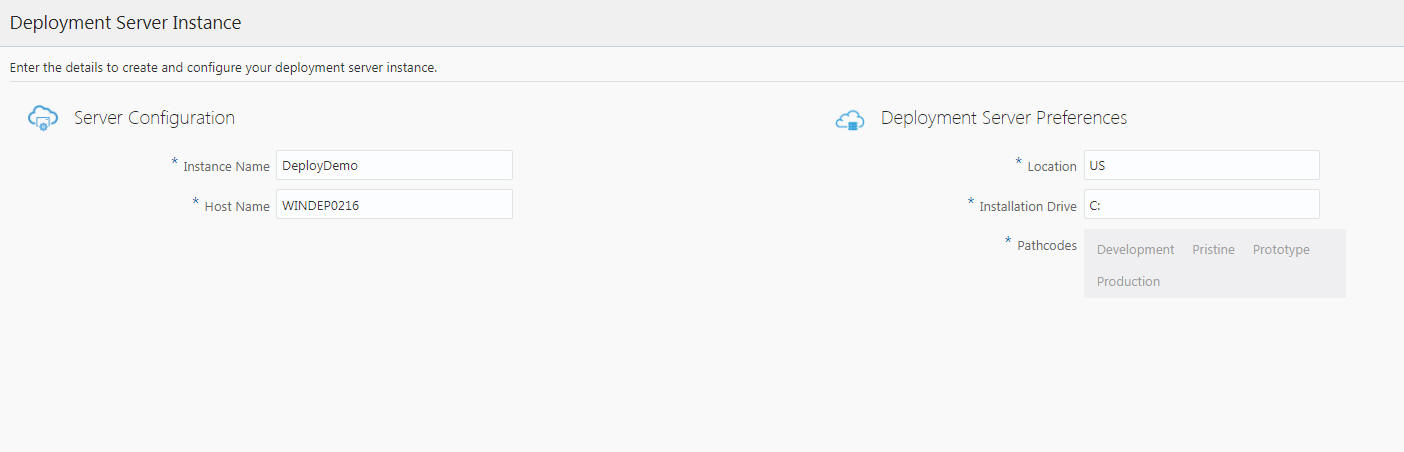
On the JD Edwards Deployment Server, complete these fields to create and configure your Deployment Server instance.
Server Configuration
-
Instance Name
Create an instance name for the Deployment Server instance. The condition to set the Service Name is displayed in the tooltip when you click the field.
-
Host Name
Enter the host name.
Tip: To determine a currently set host name, refer to the section "Retrieve a Host Name" of this Learning Path.
Deployment Server Preferences
-
Location
Enter the location.
This value is the base location for your JD Edwards EnterpriseOne machines. For example, typical values might be a city name (such as Denver or Austin), a geographical region name (such as US or India), or a general location name (such as Corporate).
-
Installation Drive
Enter the drive for the installation.
-
Pathcodes
This field is automatically populated.
-
- Click the Finish button. A success message is displayed.
- Verify that the Deployment Server instance you modified is displayed in the JD Edwards Servers window.
- You can select the Delete option in the Application Options menu to
delete the Deployment Server instance. After you delete the existing Deployment
Server instance, you can click the New Server icon, and then select
Deployment Server from the Select a Component page to add a new Deployment
Server instance.Note:
To deploy an orchestration, refer to the section "Deploying an Orchestration" of this Learning Path.