Understanding EUR Profiles
End-use reservation (EUR), also known as intended use or product allocation, refers to the assignment of a blend lot or a block to one or more end products. This product allocation is used for planning and for supply-and-demand analysis. EURs also drive accounting transactions by enabling the system to track assets by product, brand, or product family.
EURs can represent products, product blends, or product families. For example, part of a blend lot could be intended for producing a high-end wine, whereas the remaining lot quantity goes into the production of a wine of lesser quality. You can assign lot and blocks to an EUR as a percentage or as fixed volume. If you assign a fixed volume, the total volume that you allocate to the fixed EURs does not change, but the percentage of the balance EUR changes as a result of gains and losses in bulk material. You must always allocate a lot or block fully to one or more EURs.
When setting up EUR information, you can ensure product consistency by defining an EUR profile. The EUR profile represents an information set that consists of an EUR definition, as well as specifications, protocols, and planning criteria that you associate with the EUR. You set up an EUR profile by wine status. The following diagram displays the components of an EUR profile:
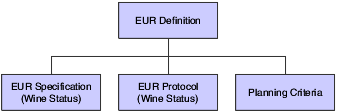
When you define profiles for sub-EURs, the sub-EUR inherits all the components of the parent EUR profile, including specifications. During validation, the system validates the sub-EUR against the specifications that you defined for the sub-EUR and against the specifications that the sub-EUR inherits from the parent EUR profile.
An EUR profile also includes product specifications that you use to validate actual operation values against target values that you define for an EUR. In addition, you can attach protocols based on wine status that provide additional details for the EUR, such as instructions, notes, and operating procedures.
You can create a new EUR profile by using the copy function that copies the EUR definition along with all associated specifications, protocols, and planning information. You can also copy EUR profiles to a version, for example for a particular year. You can run the EUR Profile Versions report (R31B071) periodically to create snapshots of existing EUR profiles. For example, you might want to copy all EUR profiles to a version at the end of a year. After creating an EUR profile version, you can no longer revise the data in this version, but you can continue to revise the current EUR profile.
You can run a report on current profiles by running the EUR Profile report (R31B07). You can use this report to print planning and specification information for an EUR by wine status.