Information Enrichment
Overview
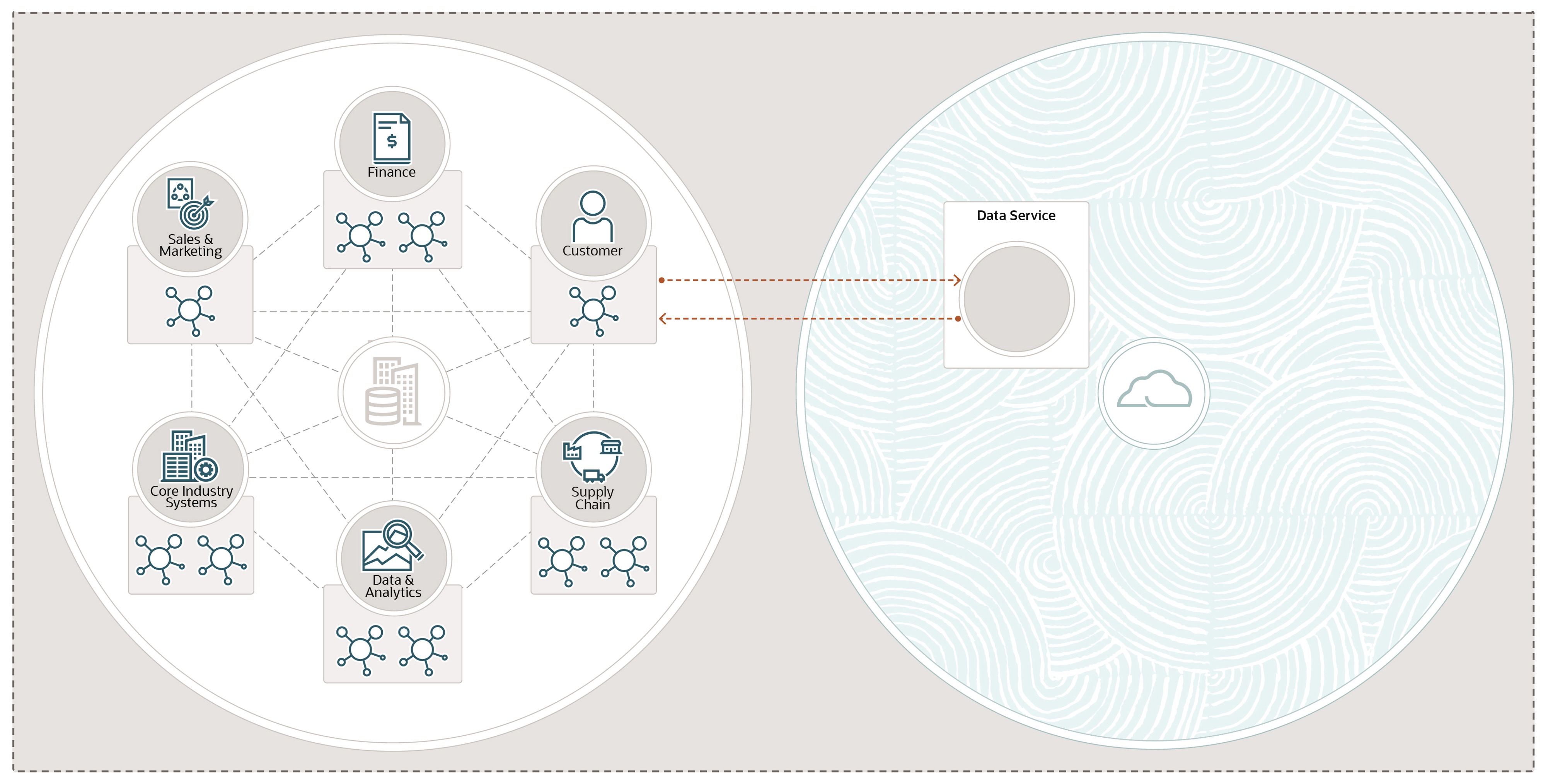
Information enrichment, in a general sense, is when a dataset is enhanced - usually by combining it with another related dataset. In a cloud context, bringing together the data sets is done in the public cloud. A second more recent extension to this concept is that a dataset can be enhanced through data science - i.e. taking the original dataset and adding information to that dataset by applying a machine-learning or artificial-intelligence algorithm.
In both cases, the most common pattern is for the enhanced data to be returned to the originating system, or passed on to another system which can then provide a higher-value service based on the enhanced data.
Use
The breadth of use of this type of use of cloud is already vast and still growing. Marketing teams have enhanced customer data through the use of external demographic data for 25 years, and telecoms companies have built highly effective churn models for a similar time.
What is new in the public cloud is that the substantial resources that some of these calculations require can now be done as a significantly lower cost on commodity-priced cloud infrastructure. In addition, the speed at which infrastructure can be set up and ready to use has decreased from many months when attempted on-premises to just a few hours in the public cloud.
Perhaps the final remaining challenge is the transfer of data into the public cloud. While some datasets that can benefit from this approach are small, many are very large. Data transfer still has to obey the laws of physics, and so internet-based transfer of large data sets is often not feasible. Oracle provides a physical data transfer service for these challenges.
In addition to customer information, financial information is also a common area where information enrichment can be highly valuable. For example, financial stress testing, physics simulation, molecular modeling and genetics are also common.
Most of these capabilities only require a simplistic batch interface for smaller data sets, and these are often file based. For security and privacy, data is typically anonymized.
Use Cases
- Credit Scoring : Credit scoring is a long established third-party service that can be considered to be part of hybrid cloud
- Customer Segmentation & Propensity : Uploading customer data to a data analytics service where customers can be segmented or assess for product propensity to buy
- Company Information Services Uploading customer data to a data enrichment service that enhances the data with additional attributes
- High-performance computing Complex mathematical calculations for simulation, data analysis, data science, machine learning and artificial intelligence.