Build a Data Model from Google BigQuery Data Source
You build a data model for your Google BigQuery database so that you can deploy it to visualize data in a BigQuery project.
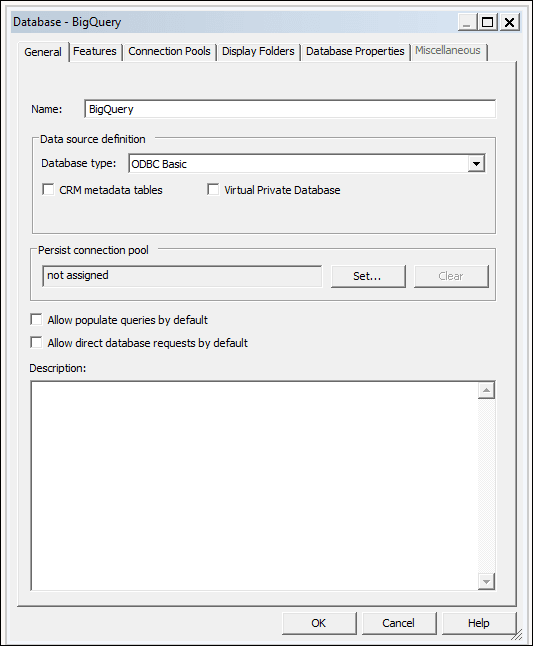
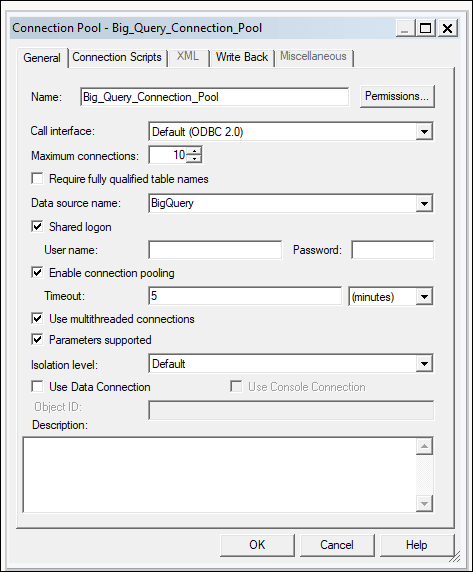
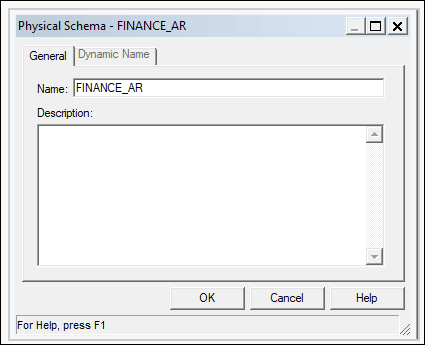
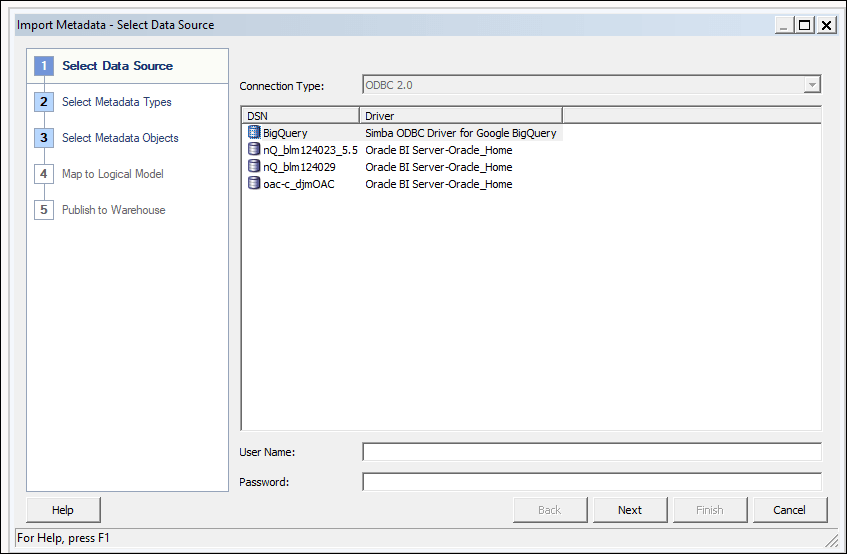
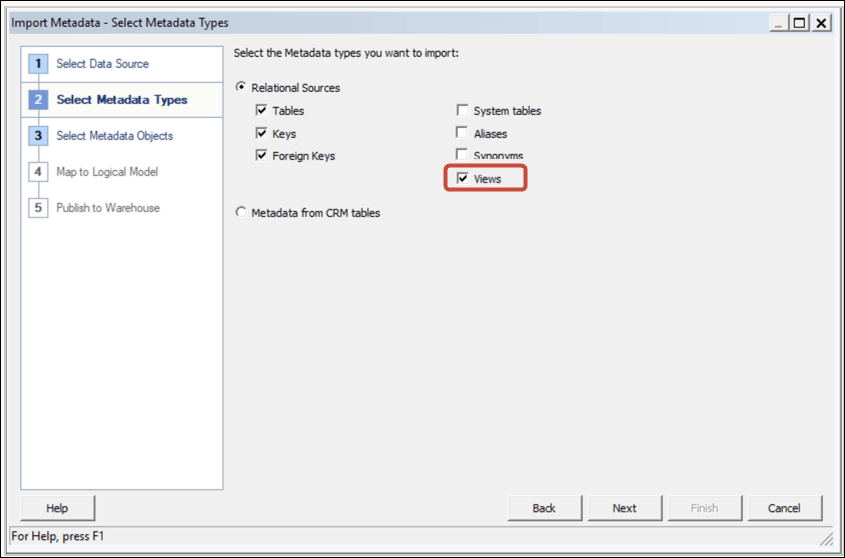
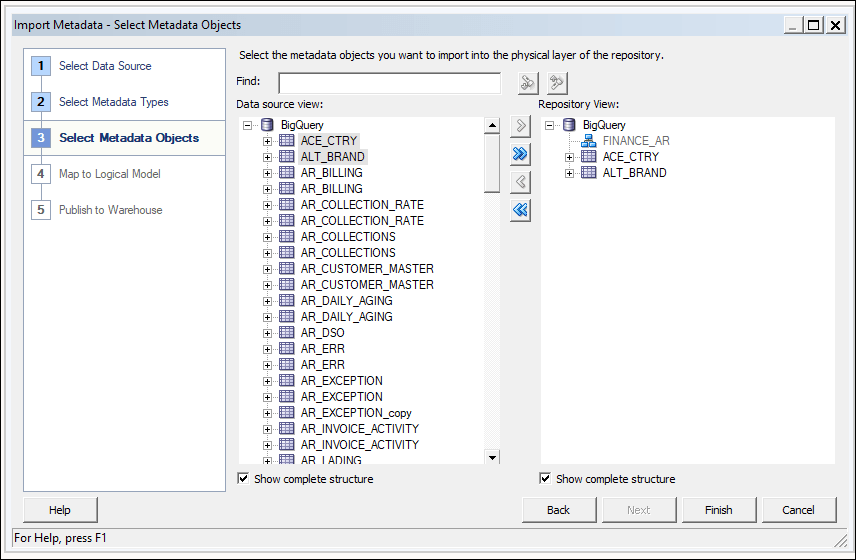
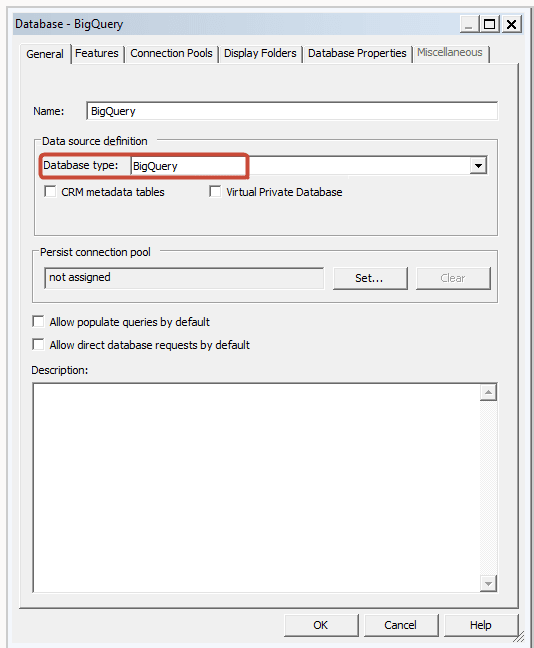
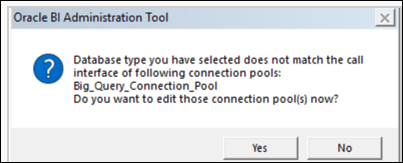
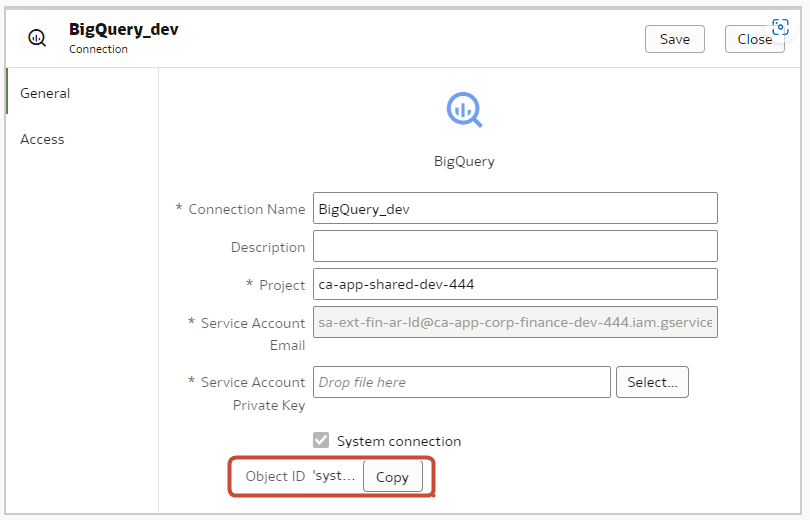
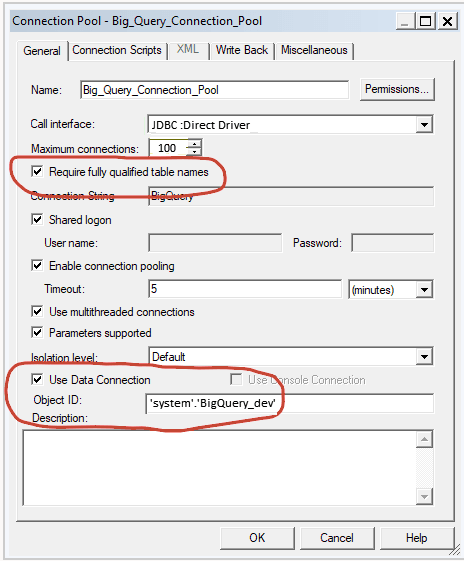
To build a data model, you need permissions in the BigQuery key. If the BigQuery key grants access to the dataset level, simply perform Import Metadata using the BigQuery ODBC driver by following the steps below. If the BigQuery key grants access to only specific tables or views, follow the steps below to create a physical schema.
Model the metadata in the repository and upload the repository file (RPD) to Oracle Analytics.