About Check Consistency
Use the Check Consistency feature to validate a semantic model object or the entire semantic model. Check Consistency locates and helps you fix issues that cause query generation to fail at runtime.
Check Consistency provides the following types of messages:
- Errors - These messages describe errors that you must fix. Use the information in the message to correct the inconsistency, then run the Check Consistency again to confirm that you've fixed the error.
- Warnings - These messages indicate conditions that you might need to fix. For example, a warning message about a missing display key in a logical hierarchy level. Other messages warn of inconsistent values, or feature table changes that don't match the defaults.
For examples of error and warning messages, see Common Consistency Check Messages.
If the standard consistency checks don't meet your model's unique validation requirements, you can create custom consistency check rules specific to your model. See About Custom Consistency Check Rules.
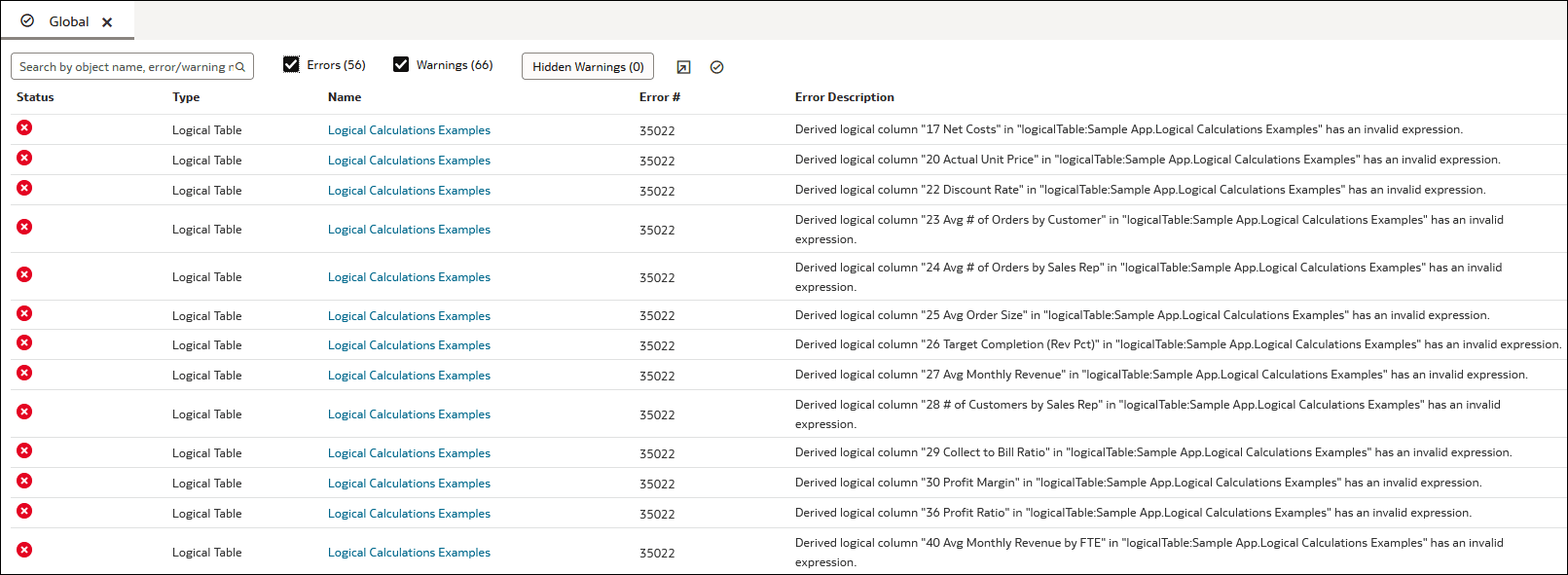
The consistency check results display in a tab and contains information that you can use to understand, navigate to, and fix the objects listed in the report. Each error or a warning is identified by its name and object type (for example, Logical Table or Initialization Block).
In the consistency check results, you can search for objects in the list by name, error message number, and so on. And you can choose to hide specific warnings from the list for all the semantic models you work with. See Hide Warnings in Check Consistency Results.
Description of the illustration consistency_checker_hide_warn.png
Passing the consistency check doesn't guarantee that a semantic model is constructed correctly, but it does rule out many common problems.
The consistency check doesn't check the validity of objects outside the metadata using the connection. It only checks the consistency of the metadata and not the mapping to the physical objects outside the metadata. If the connection isn't working or objects were deleted in the database, the consistency check doesn't report these errors.
If you use lookup tables to store localized field names with multilingual schemas, the consistency check rules are relaxed for the lookup tables.
Sometimes when you check the semantic model's consistency after an Oracle Analytics upgrade, you might see errors that weren't included in previous consistency checks.
You can create custom consistency checks specific to your organization's specific model development standards. You create and run custom consistency checks from the Custom Rules tab. See About Custom Consistency Check Rules.