Before You Begin
This 15-minute tutorial shows you how to create datasets that contain multiple tables for use in analyses.
Background
You can create a dataset that uses tables from different connections and schemas. Oracle Analytics uses the relationships defined between these tables to create the joins in your dataset. If you're creating a dataset from multiple connections and schemas, you define the joins between tables in Oracle Analytics. When relationships aren't defined between tables, you can define them in Oracle Analytics.
You can use tables from relational sources including data from relational databases, data sources that are based on ODBC/JDBC connections such as SaaS data sources, and Oracle Service Cloud.
When defining your dataset, add the tables that form the base for your analysis first such as Sales, Customers, and products, and then add other related tables. The most detailed table is possibly a fact table with measures if you are adding tables from a data source.
This is the first tutorial in the Prepare and Analyze Datasets series in Oracle Analytics. Read the tutorials in the order listed.
- Create a Multiple Table Dataset
- Blend Datasets
What Do You Need?
- Access to Oracle Analytics
- Ability to connect a relational data source such as Oracle Autonomous AI Lakehouse or Oracle AI Database
- Access to the Oracle sample SH schema to perform the steps in this tutorial, see Installing Sample Schemas
Create a Dataset
In this section, you create a dataset using tables from an Oracle Database. You must have an existing Oracle Database or Oracle Autonomous AI Lakehouse connection and the details required to create a connection to a supported data source.
This example uses the SH schema from an Oracle Database connection. The steps in this tutorial are all related to using the tables in the SH schema.
- Sign in to Oracle Analytics.
- On the Home page, click Create, and then click Dataset.
- In Create Dataset, select the Oracle Database connection to use as the source.
- In the Connections panel, expand Schemas, and then expand the SH schema.
- Under the SH schema, select the SALES table and drag it to the Join diagram.
A data preview shows the columns and data in the SALES table.

Description of the illustration sh_sales_table.png - Under the SH schema, hold down the Ctrl key, select the following tables, and then drag them to the Join Diagram.
- CHANNELS
- CUSTOMERS
- PRODUCTS
- PROMOTIONS
- TIMES
- In Connections
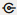 under the SH schema, select COUNTRIES and drag it on top of CUSTOMERS.
under the SH schema, select COUNTRIES and drag it on top of CUSTOMERS. - Right-click SALES and select Preserve Grain.
Oracle Analytics automatically creates the joins between the tables using the relationships defined in the schema.

Description of the illustration sales_joins.png
Apply Changes to Tables in the Dataset
In the Join Diagram, you can select individual tables, apply transformations or enrichments in the selected table's data columns, change table names, and edit the table definition. In the CHANNEL_TOTAL_ID column, you can see that the values are the same for each row. You can remove columns from the tables in the dataset that you don't need for your analyses.
- In the Join Diagram
 , click the CHANNELS tab.
, click the CHANNELS tab. - In the CHANNEL_CLASS_ID column, click Measure
 and click Attribute.
and click Attribute. 
Description of the illustration channel_transform.png - Click Edit Definition.
- In CHANNELS under Selections, click CHANNEL_TOTAL_ID, click Remove Selected, and then click OK.
- Click the CUSTOMERS tab. Click Measure
 in the CUST_YEAR_OF_BIRTH column, and then click Attribute.
in the CUST_YEAR_OF_BIRTH column, and then click Attribute. - In the Join Diagram
 , right-click PROMOTIONS, and then select Edit Definition.
, right-click PROMOTIONS, and then select Edit Definition. - In Table Name, enter
CAMPAIGNSto replace PROMOTIONS, and then click OK. - Click Join Diagram
 to see the table name change.
to see the table name change. 
Description of the illustration promo_to_campaigns.png - Click Save. In Save Dataset As, enter
Sales_Historyin Name, and then click OK.
Visualize the Sales_History Dataset
- Click Create Workbook. Close the Insights panel.
- In the Data
 panel, expand the SALES and PRODUCTS folders.
panel, expand the SALES and PRODUCTS folders. - Hold down the Ctrl key, select QUANTITY_SOLD and AMOUNT_SOLD from SALES, and select PROD_SUBCATEGORY from PRODUCTS. Right-click, select Pick Visualization, and then select Pivot
 .
. - Right-click AMOUNT_SOLD in Values, select Sort By and then select High to Low. Click OK.

Description of the illustration sales_hist_pivot.png - Click Save. In Save Workbook, enter a Name and click Save.
Learn More
Create a Dataset with Multiple Tables in Oracle Analytics
F33695-06
February 2026
Learn how to create a dataset that contains multiple tables from a relational data source.
This software and related documentation are provided under a license agreement containing restrictions on use and disclosure and are protected by intellectual property laws. Except as expressly permitted in your license agreement or allowed by law, you may not use, copy, reproduce, translate, broadcast, modify, license, transmit, distribute, exhibit, perform, publish, or display any part, in any form, or by any means. Reverse engineering, disassembly, or decompilation of this software, unless required by law for interoperability, is prohibited.
If this is software or related documentation that is delivered to the U.S. Government or anyone licensing it on behalf of the U.S. Government, then the following notice is applicable:
U.S. GOVERNMENT END USERS: Oracle programs (including any operating system, integrated software, any programs embedded, installed or activated on delivered hardware, and modifications of such programs) and Oracle computer documentation or other Oracle data delivered to or accessed by U.S. Government end users are "commercial computer software" or "commercial computer software documentation" pursuant to the applicable Federal Acquisition Regulation and agency-specific supplemental regulations. As such, the use, reproduction, duplication, release, display, disclosure, modification, preparation of derivative works, and/or adaptation of i) Oracle programs (including any operating system, integrated software, any programs embedded, installed or activated on delivered hardware, and modifications of such programs), ii) Oracle computer documentation and/or iii) other Oracle data, is subject to the rights and limitations specified in the license contained in the applicable contract. The terms governing the U.S. Government's use of Oracle cloud services are defined by the applicable contract for such services. No other rights are granted to the U.S. Government.
This software or hardware is developed for general use in a variety of information management applications. It is not developed or intended for use in any inherently dangerous applications, including applications that may create a risk of personal injury. If you use this software or hardware in dangerous applications, then you shall be responsible to take all appropriate fail-safe, backup, redundancy, and other measures to ensure its safe use. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates disclaim any liability for any damages caused by use of this software or hardware in dangerous applications.
Oracle and Java are registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Intel and Intel Inside are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation. All SPARC trademarks are used under license and are trademarks or registered trademarks of SPARC International, Inc. AMD, Epyc, and the AMD logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices. UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
This software or hardware and documentation may provide access to or information about content, products, and services from third parties. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates are not responsible for and expressly disclaim all warranties of any kind with respect to third-party content, products, and services unless otherwise set forth in an applicable agreement between you and Oracle. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates will not be responsible for any loss, costs, or damages incurred due to your access to or use of third-party content, products, or services, except as set forth in an applicable agreement between you and Oracle.