Before you Begin
Learn how to use a GIT repository with your semantic model. Using a Git repository provides version control and multiple user development of semantic models.
This tutorial shows you how to open the Semantic Model Markup Language (SMML) editor to review and make changes to a semantic model.
Background
This tutorial describes how to build governed semantic models using the Semantic Modeler.
You can use Git repositories with Oracle Analytics to enable concurrent semantic modeler development.
A semantic model is comprised of a set of JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) files. When you create and develop a semantic model locally, the model's JSON files are stored in Oracle Cloud. To make the semantic model's JSON files available for other development team members, the semantic model's owner creates a Git repository, initializes it with HTTPS or SSH, and uploads the semantic model's JSON files to the repository. Each developer creates a semantic model and uses HTTPS or SSH to connect to and clone the semantic model's JSON files to their Git repository.
You can use the SMML editor to view and change the JSON SMML schema file of an object in your semantic model. If you are viewing or editing an invalid file, syntax and semantic errors are marked on the relevant line of text.
This is the fifth tutorial in the Create a Semantic Model series. Do the tutorials in the order listed:
- Create the Physical Database, Physical Tables, and Physical Joins
- Create the Business Model, Logical Tables, and Logical Joins
- Create the Subject Areas and Presentation Tables
- Test, Deploy, and Validate a Semantic Model
- Examine Semantic Model Markup Language (SMML) and Integrate Semantic Model With a Git Repository
- Manage Logical Table Sources
- Create Logical Dimensions
- Create Calculated, Level-Based, and Share Measures
- Create Ragged and Skipped Level Hierarchies
- Create Parent-Child Hierarchies
- Create Aggregate Tables
- Create Time Series Measures
- Create Initialization Blocks and Variables
What Do You Need?
- Access to Oracle Analytics Cloud
- Access to DV Content Author, BI Data Model Author, or a BI Service Administrator role
- Access to the Sample Sales Semantic Model
- Access to a Git Repository using your Github account
Examine the Semantic Model Markup Language
This section shows you how to review JSON objects in a semantic model. You can makes changes to the object definitions using the Semantic Model Markup Language (SMML) editor.
Begin with step 3 if you're continuing this tutorial directly after completing the steps in Test, Deploy, and Validate a Semantic Model tutorial.
- If you closed your semantic model, sign in to Oracle Analytics Cloud using one of DV Content Author, BI Data Model Author or service administrator credentials. On the Home page, click the Navigator
 , and then click Semantic Models.
, and then click Semantic Models. - In the Semantic Models page, select Sample Sales, click Actions menu
 , and then select Open.
, and then select Open. - In the Sample Sales semantic model, click the Physical Layer
 . Expand MySampleSalesDatabase and expand BISAMPLE.
. Expand MySampleSalesDatabase and expand BISAMPLE. - Right-click SAMP_PRODUCTS_D, and select Open in SMML Editor.
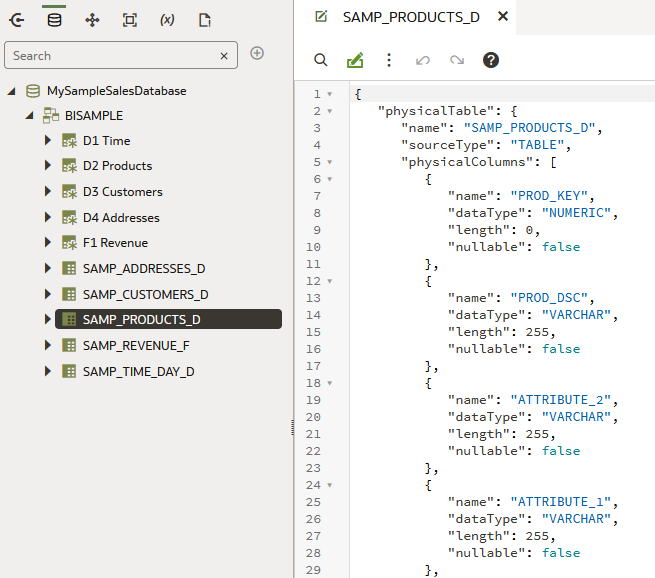
Description of the illustration smml_editor_samp_prods.png
Open Your Git Repository
In this section, you use your Git repository to store your semantic model. You must use the personal access token you generated in Github to access your Git repository from Oracle Analytics Cloud Semantic Modeler.
- Sign in to GitHub using the URL to your repository.
- Click Repositories and open the repository to use with your semantic model.
Back Up Your Semantic Model
In this section, you create an archive of your semantic model as a backup.
- If you closed your semantic model, sign in to Oracle Analytics Cloud with your BI Data Model Author application role or service administrator credentials. On the Home page, click the Navigator
 , and then click Semantic Models.
, and then click Semantic Models. - In the Semantic Models page, select Sample Sales, click Actions menu
 , and then select Open.
, and then select Open. - In the Sample Sales semantic model, click the Page Menu
 , and select Export.
, and select Export. - In Export, keep Sample Sales as the archive name, select Archive File (.zip), and then click Export.
- In Opening Sample Sales.zip, click Save and click OK.
- Use the default download location or selection another location, and click Save.
Initialize Git Integration
In this section, you specify your profile name, Git user name, and your personal access token in the Semantic Modeler to initialize Git.
- In the Sample Sales semantic model, click Toggle Git Panel
 , and then click Start.
, and then click Start. - In Initialize Git, paste your Git repository URL in to Git Repository URL, and then click Continue.
- Select your Git profile, or select New Profile. Enter a Profile Name, your Git user name, and your personal access token in Password.
- Click Initialize Git.
Initialize adds the semantic model files to your Git repository.
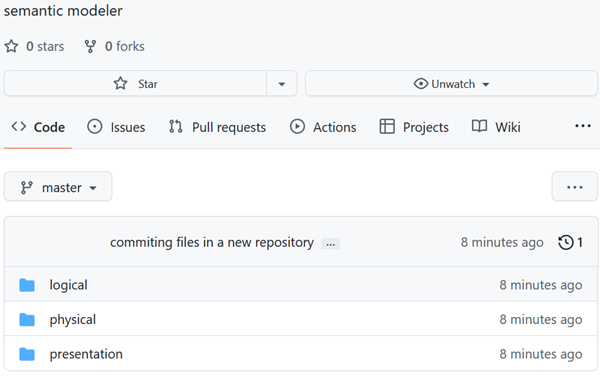
Description of the illustration initialize_adds_sm_2repo.png
Review the Git Integration
In this section, you look at the semantic modeler content added to your Git repository.
- In your Git repository, click the repository name, and then click View code.
- Click the physical folder, click the MySampleSalesDatabaseDatabase folder, and then click the BISAMPLE schema folder to view the contents.
The BISAMPLE folder contains the JSON definitions for the physical layer's tables.
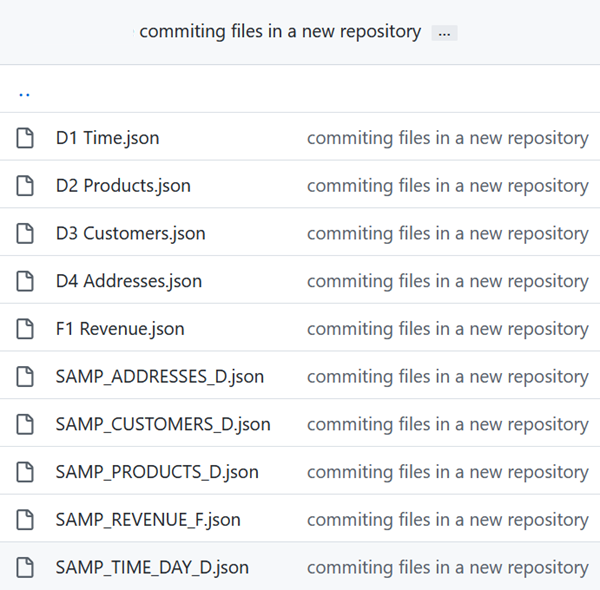
Description of the illustration bisample_folder_contents.png - Click the SAMP_PRODUCTS_D.json object to see the definition of the object in the semantic model.

Description of the illustration samp_prods_json.png
Change the Semantic Model
In this section, you add a description in SAMP_PRODUCTS_D to demonstrate changes to the semantic model and how those changes are tracked in Git.
- In the Physical Layer
 , double-click SAMP_PRODUCTS_D. Click the General tab.
, double-click SAMP_PRODUCTS_D. Click the General tab. - In Description, enter
Test product description to show semantic model changes and Git.Click Save .
.The Git panel shows the status of the changes in the semantic model.
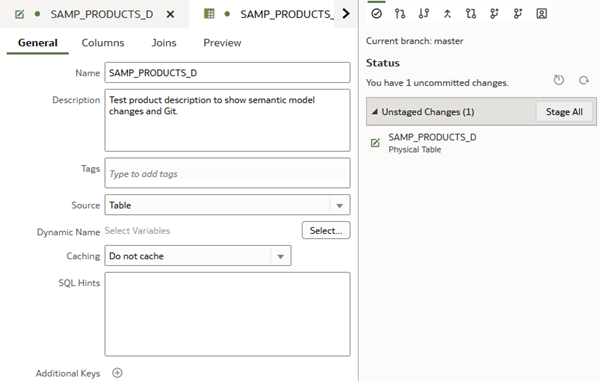
Description of the illustration git_status.png - In the Git panel, right-click SAMP_PRODUCTS_D and select View Diffs.
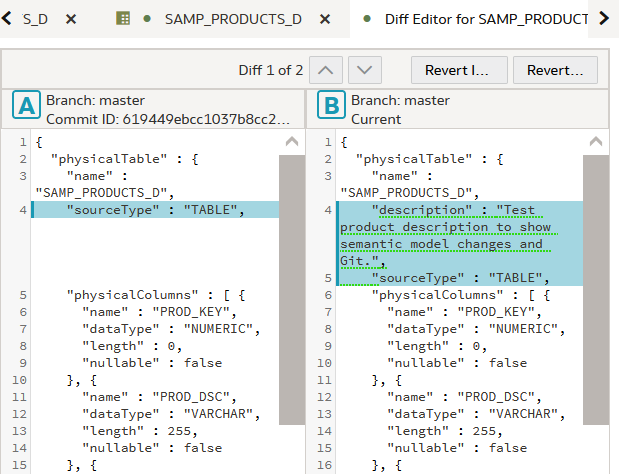
Description of the illustration view_diffs.png - Close the Diff Editor.
- In the Git panel, click Stage All in Unstaged Changes. In the commit description field, enter a description of the changes and click Commit.
- In the Git panel, click Push
 , and then click Push.
, and then click Push. The message, "Push successful" appears when the changes are added to your Git repository.
- In your Git repository, click the Physical folder, click MySampleSalesDatabase, click BISAMPLE, and then click SAMP_PRODUCTS_D.json to view the changes made in the semantic model.
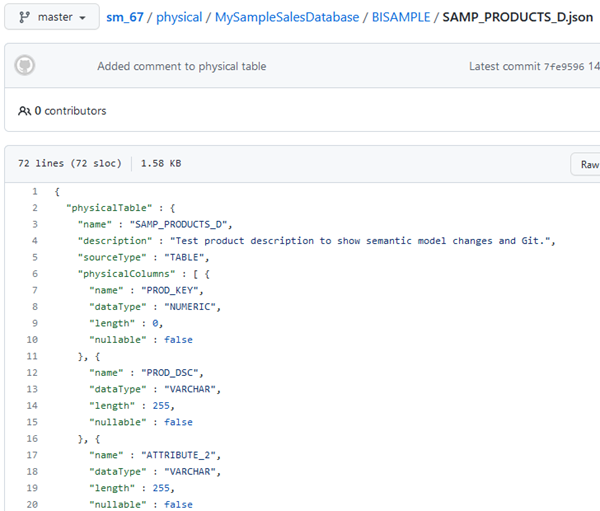
Description of the illustration changes_in_git.png
Next Steps
Learn More
Examine Semantic Model Markup Language (SMML) and Integrate Semantic Model With a Git Repository
F57936-05
November 2023
Copyright © 2023, Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Learn how to use a Git repository with Oracle Analytics Semantic Modeler.
This software and related documentation are provided under a license agreement containing restrictions on use and disclosure and are protected by intellectual property laws. Except as expressly permitted in your license agreement or allowed by law, you may not use, copy, reproduce, translate, broadcast, modify, license, transmit, distribute, exhibit, perform, publish, or display any part, in any form, or by any means. Reverse engineering, disassembly, or decompilation of this software, unless required by law for interoperability, is prohibited.
If this is software or related documentation that is delivered to the U.S. Government or anyone licensing it on behalf of the U.S. Government, then the following notice is applicable:
U.S. GOVERNMENT END USERS: Oracle programs (including any operating system, integrated software, any programs embedded, installed or activated on delivered hardware, and modifications of such programs) and Oracle computer documentation or other Oracle data delivered to or accessed by U.S. Government end users are "commercial computer software" or "commercial computer software documentation" pursuant to the applicable Federal Acquisition Regulation and agency-specific supplemental regulations. As such, the use, reproduction, duplication, release, display, disclosure, modification, preparation of derivative works, and/or adaptation of i) Oracle programs (including any operating system, integrated software, any programs embedded, installed or activated on delivered hardware, and modifications of such programs), ii) Oracle computer documentation and/or iii) other Oracle data, is subject to the rights and limitations specified in the license contained in the applicable contract. The terms governing the U.S. Government's use of Oracle cloud services are defined by the applicable contract for such services. No other rights are granted to the U.S. Government.
This software or hardware is developed for general use in a variety of information management applications. It is not developed or intended for use in any inherently dangerous applications, including applications that may create a risk of personal injury. If you use this software or hardware in dangerous applications, then you shall be responsible to take all appropriate fail-safe, backup, redundancy, and other measures to ensure its safe use. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates disclaim any liability for any damages caused by use of this software or hardware in dangerous applications.
Oracle and Java are registered trademarks of Oracle and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Intel and Intel Inside are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation. All SPARC trademarks are used under license and are trademarks or registered trademarks of SPARC International, Inc. AMD, Epyc, and the AMD logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices. UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
This software or hardware and documentation may provide access to or information about content, products, and services from third parties. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates are not responsible for and expressly disclaim all warranties of any kind with respect to third-party content, products, and services unless otherwise set forth in an applicable agreement between you and Oracle. Oracle Corporation and its affiliates will not be responsible for any loss, costs, or damages incurred due to your access to or use of third-party content, products, or services, except as set forth in an applicable agreement between you and Oracle.