Architecture
Learn about the architecture of the DR solution for the integration feature.
The DR architecture for Integrations consists of two Oracle Integration instances in two different cloud regions, which are accessed using a single custom endpoint (URL).
Optionally, you can use an OCI Domain Name System (DNS) zone to resolve the custom endpoint name. If you always want to run Oracle Integration in the primary region (that is, you fail over and then fail back as soon as possible to the primary region), then set up the OCI DNS zone in the secondary region to minimize downtime. Otherwise, if you fail over from the primary to the secondary region and stay there even after the primary region resumes operation, you may increase your chances of downtime if the entire primary region in which your OCI DNS zone is located fails. In Oracle Integration, you typically want to fail back as soon as possible to keep your data in the primary region.
Customer-managed custom endpoint URLs are a feature provided by Oracle Integration that allow you to define a custom URL in a domain that you manage. You can use these URLs as the entry point to the Oracle Integration instances. For example, prod-integration.mycompany.com. For more information about configuring customer-managed custom endpoints, see Configure a Customer-Managed Custom Endpoint in Provisioning and Administering Oracle Integration 3.
The two Oracle Integration instances in the architecture are designated as primary and secondary, and both the instances run concurrently; however, only one of the instances receives traffic. Initially, it’s the primary instance that receives the traffic flow. When this instance becomes unavailable, the DNS record is updated to route the traffic to the secondary instance. The following image shows this architecture in detail for a scenario using connectivity agents:
Note:
Customer-managed custom endpoint support is provided for the runtime URL (oic.mycompany.com in the
architecture diagram below), but not for the design-time URL. To log in to Oracle Integration at design time, you must use the URL
provided during service instance provisioning.
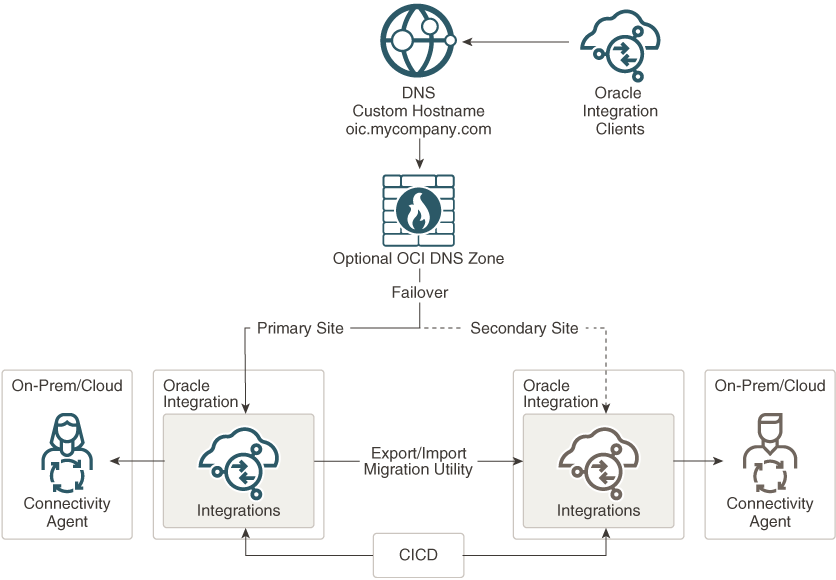
You must update the DNS record at your DNS provider to switch between instances. Optionally, you can implement an OCI DNS zone to manage the subdomain related to the Oracle Integration custom hostname. The OCI DNS zone can reflect changes to the CNAME much faster.
In this setup, you must synchronize the Oracle Integration metadata at both the sites using continuous integration and continuous deployment (CICD).