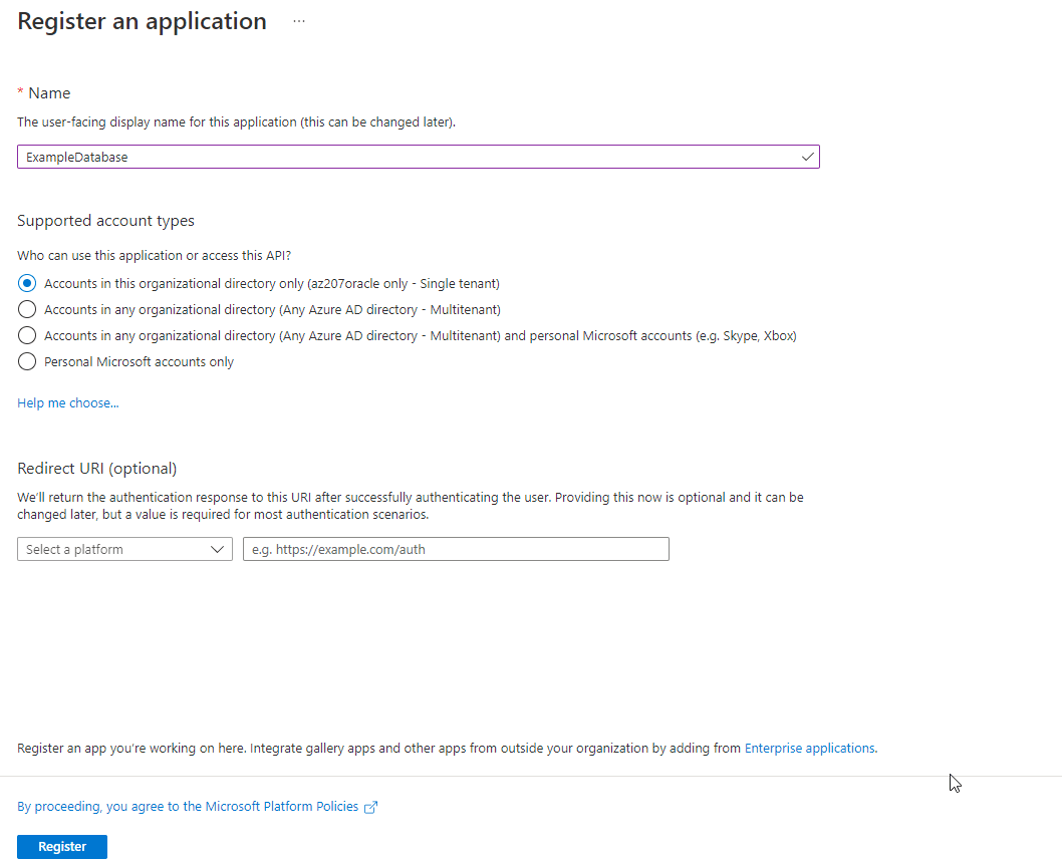
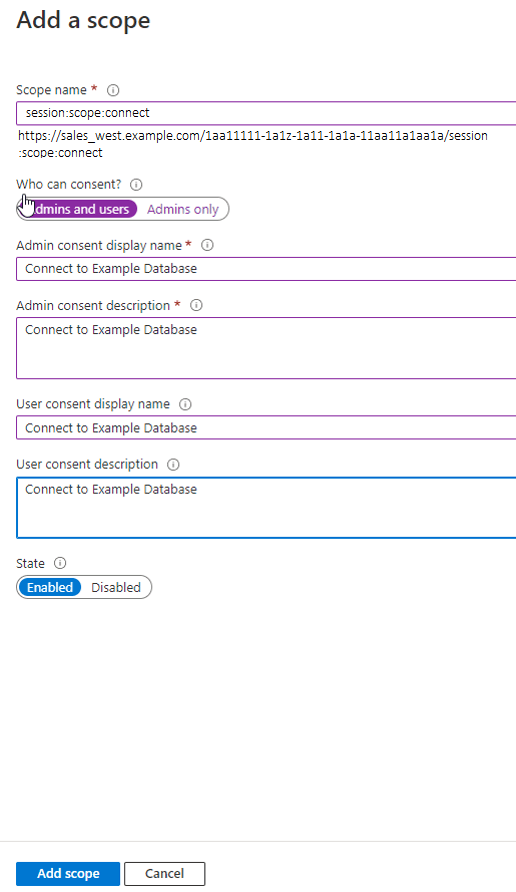
Registering the Oracle Database Instance with a Microsoft Azure AD Tenancy
A user with Azure AD administrator privileges uses Microsoft Azure AD to register the Oracle Database instance with the Microsoft Azure AD tenancy.
After you complete these steps, you are ready to add one or more Azure app roles, and then perform the mappings of Oracle schemas and roles.