The Data Load Page
Use the Data Load page to make more data available to your Oracle Autonomous Database. You can load data from files or databases, from links to external databases or cloud storage files, or from a live feed of data from cloud storage.
From the Data Load page, you can also explore the data in your autonomous database and manage your cloud storage locations.
Note:
If you do not see the Data Load card then your database user is missing the required DWROLE role.
To reach the Data Load page, click Data Load in the Database Actions page, or click the Selector![]() icon and select Data Load from the Data Studio menu in the navigation pane.
icon and select Data Load from the Data Studio menu in the navigation pane.
To load or create links to data or create live table feeds, on the Data Load page, select a combination of an operation and a data source location. The following table lists the operations and the source locations that support those operations.
| Operation | Source Location | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Load data |
Local file Database Cloud storage |
Load data from files on your local device, from remote databases, or from cloud storage into tables in your Oracle Autonomous Database. |
|
Link data |
Database Cloud storage |
Create external tables or views in your Oracle Autonomous Database that link to data in cloud storage or remote databases. Changes to the source data automatically appear in the target objects. |
|
Feed data |
Cloud storage |
Set up a feed of data from a cloud storage bucket into a table. Changes to the source data load into the target table as scheduled or on demand. |
- Data Load Jobs: View and check your data load jobs.
- Connections: Manage your cloud storage links, Data Catalog links and Share Providers.
The following topics describe these actions.
- Checking Data Load Jobs
You can check an existing data load job and retrieve the data load job later when required. - Data Studio Preferences
This topic explains the Data Studio Preferences setting in the Load Data page. - Managing Connections
Connections that are established from the Data Studio to the cloud, catalogs and shares are listed on this page. - Loading Data
You can load data from files on your local device, from remote databases, or from cloud storage buckets from directories and share providers. - Linking Data
You can link to data in remote databases or in cloud storage buckets. - Feeding Data
You can run a live table feed on demand, on a schedule, or as the result of a notification.
Parent topic: The Data Load Page
Checking Data Load Jobs
You can check an existing data load job and retrieve the data load job later when required.
The Data Load Job page displays the data load history in your Oracle Autonomous Database. On the Data Load Page, in the Explore and Connect section, select Data Load Jobs.
The Data Load Job page contains the Search for Data Load Jobs field, a list of Data load job cards. You can enter the data load job you are looking for in the field or click one of the data load jobs from the list.
The Data Load Jobs page consists of:
-
Search for Data Load Jobs field
You can click the field and type or search for the name of the data load job you are looking for.
-
Toolbar
The toolbar consists of the following buttons:
-
Sort By
To select sorting values, click the Sort By button to open the list of options. Then click the Ascending or Descending icon next to one or more of the sorting values. For example, if you select the Ascending icon next to Entity name and the Descending icon next to Entity type, the entities will be sorted in alphabetical order by entity name and then in reverse alphabetical order by entity type.
Click Reset in the list to clear the choices in the list.
The sorting values you choose are listed next to the Sort by label beneath the toolbar. Click the X icon on a sorting value to remove it.
-
Page size
By default, up to 25 entities are displayed on the page. If you want more entities on a page, select a number from this list.
-
Previous and Next
If the search results are displayed on multiple pages, click these buttons to navigate through the pages.
-
Refresh
Click to refresh the data load jobs shown on the page, based on the current search field.
-
-
Filters panel
Select one or more filter values to limit the data load jobs shown on the page. Only those entities that match the filter values are shown. The filter criteria are based on the schemas and how data is loaded or linked. That is, the items returned by a search are filtered by these filter settings. Selecting all or none of the options shows all entities.
-
Display Area
The area beneath the Search for Data Load Jobs field displays the data load job carts returned by a search and that match the filter criteria set in the Filters panel. It displays list of carts which represents a list of previously run data load jobs
You can view details about the job, re-run the Data Load job, Rename the Data Load Job and Delete the Data Load Job.
View Details about the Data Load Job
To view details about the existing data load job, click Action and select View Details in the card for the load job. Selecting View Details displays details like Lineage, Impact and Log details of the data load job.
For details on Lineage, Impact and Log details, see Viewing Entity Details.
Rerun Data Load Job
After viewing details about the selected data load or data link job whose sources are from cloud storage, you can re-run the selected previously run data load job. The previous files and folders processed in that job will be loaded in the cart with all your settings unchanged from the last run. On the left side of the page is a navigator pane, where you choose the cloud store connection and the folders or files containing the data that were previously run. The previously used cloud storage details are already present in the navigator pane. Select additional files or folders from the navigator pane and drop them in the Data Load Cart area. To change the cloud storage connection and the folders and files containing the data, see Managing Connections
Once you have added the data sources to the data load cart, click the Start icon in the data load cart menu bar. When the data load job completes, the Load Cloud Object page displays the results of the job. At the top of the page, a status message shows the number of items for which the load has completed over the number of items in the job and the total time elapsed for the job. If any previously loaded or linked files and folders are no longer present in the cloud location, an error message reports the problem. You can view the list of unavailable files and folders, which will not be loading into the cart for processing.
Click the Cancel icon to cancel re-running the selected job.
Note:
The Rerun Data Load Job option is visible for data jobs with Load and Link data options for Object storage.
Rename Data Load Job
To rename existing name of data load job cart, select the Rename Data Load Job option. The data load job names are system generated. This option enables you to rename the job to be more descriptive. This makes it easier to search the next time you want to re-run the data load job.
Delete Data Load Job
Select the Delete Data Load Job option to remove the previously run job from the Data load Job page. This will also remove the log files and the error logs generated when attempting to run the data load job.
Parent topic: The Data Load Page
Data Studio Preferences
This topic explains the Data Studio Preferences setting in the Load Data page.
This setting in the Load Data page enables you to select this data during the load. This setting sets a variety of general preferences and defines the data you can load.
To set the Data Studio Preferences:
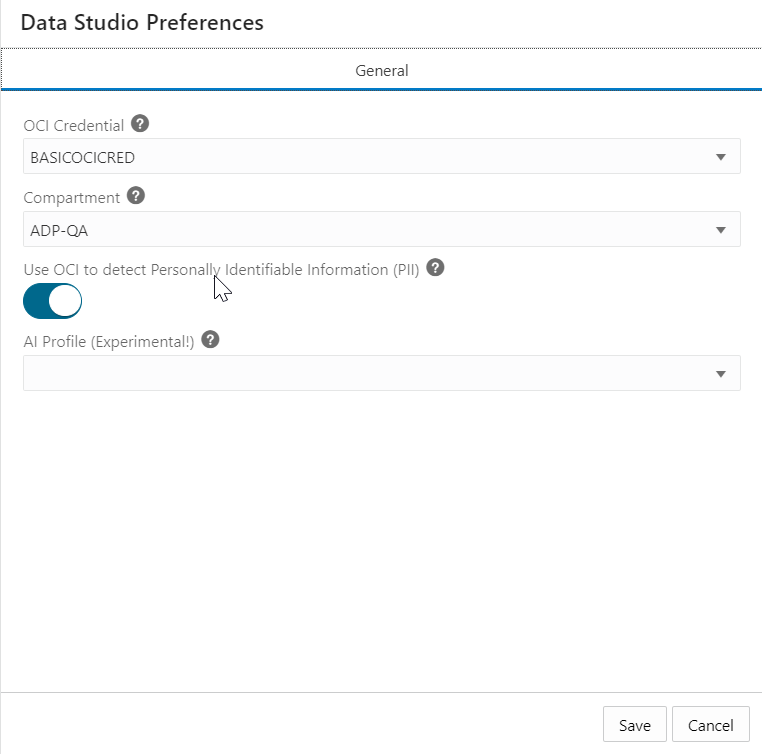
- Select the Data Studio Preferences icon
in the top-right corner of the data load page to view the Data Studio Preferences wizard and access this feature. - In the General tab of the Data Studio Preferences screen, select the OCI Credential from the drop-down. See Create Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Native Credentials to refer to the steps you need to follow to establish cloud storage connection from Data Studio to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Object service. You will use this credential to access various OCI services such as OCI languages, Identity, and storage Buckets. The Data Load tool uses the OCI Credential to list compartments, call the OCI Language PII API, list buckets for data load from cloud Store, and list buckets when creating a Cloud Storage Link.
- Select your root compartment from the Compartment drop-down which lists the buckets in the Object Storage compartment.
- Select Use OCI to detect Personally Identifiable Information (PII) to warn you about loading private and sensitive data such as your name, date of birth, social security number, and email address.
- Select AI Profile (Experimental) from the drop-down to use this AI profile for facilitating and configuring the translation of natural language prompts to SQL statements. If you have Select AI set up using either OpenAI or Cohere, you can enhance your data by loading small reference data tables that are generated by large language models. Try out the suggested prompts, or come up with your own to generate data to load into the autonomous database.
- Click Save to save the current preferences once all the settings are complete.
Parent topic: The Data Load Page
Managing Connections
Connections that are established from the Data Studio to the cloud, catalogs and shares are listed on this page.
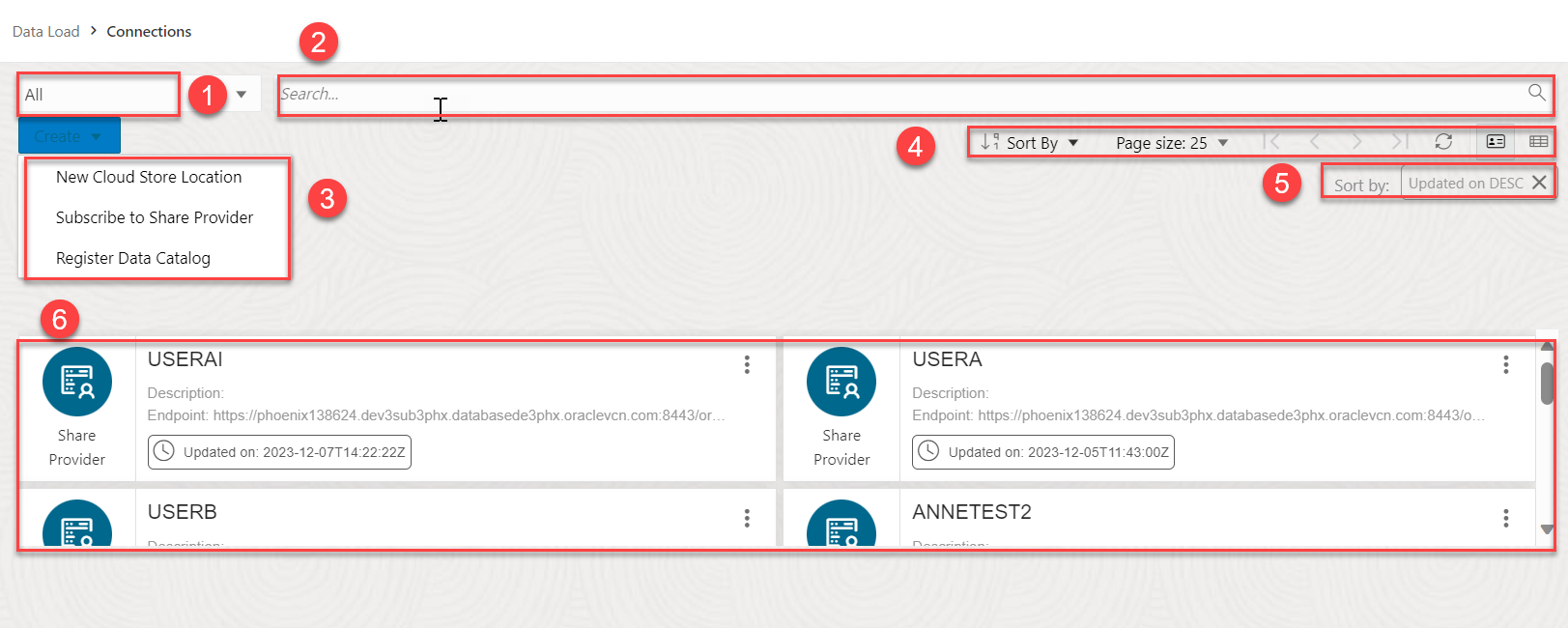
The Connections page contains the Search for entities such as Cloud Storage Links, Data Catalog Links, and Share Providers, and a list of entity cards. You can enter the entity you are looking for in the field or click one of the entity card from the list. You can register the cloud store you want to use from this page. You can also register data catalogs and subscribe to a share provider.
- Entity Selector: You can Use the drop-down lists to select the entity from which the connection is created. You can select from Cloud Storage Links, Data Catalog Links, Share Provider or all.
- Search field: Searches for entities in the field by name. The search functionality is not case-sensitive, retrieves all matching entries, and does not require the use of wild card characters.
-
Create drop-down: The options available in the Create drop-down are:
- New Cloud Store Location: Before you can load data from a cloud store, you must establish a connection to the cloud store you want to use. You can select cloud store location from the cloud store locations field. A cloud storage link is a connection to a bucket in a cloud store. You can view the existing cloud storage links and add new ones. Refer to the Create Cloud Store Location to add a cloud store location.
- Subscribe to a Share Provider: Upload the JSON profile file and create a share provider description To subscribe, you need to use the information contained in the uploaded JSON profile you received from the share provider. From the Consume Share feature of the Data Share tool, you upload the JSON profile and follow the subscribe wizard. Refer to the Subscribe to a Share Provider for more details.
- Register Data Catalogs: You can create a connection by registering a data source as a data asset in your data catalog. You can view, delete and rename the data catalogs. Refer to the Register Data Catalog chapter.
-
The toolbar consists of the following buttons:
-
Sort By
To select sorting values, click the Sort By button to open the list of options. Then click the Ascending or Descending icon next to one or more of the sorting values. For example, if you select the Ascending icon next to Entity name and the Descending icon next to Entity type, the entities will be sorted in alphabetical order by entity name and then in reverse alphabetical order by entity type.
Click Reset in the list to clear the choices in the list.
-
Page size
By default, up to 25 entities are displayed on the page. If you want more entities on a page, select a number from this list.
-
Previous and Next
If the search results are displayed on multiple pages, click these buttons to navigate through the pages.
-
Refresh
Click to refresh the data load jobs shown on the page, based on the current search field.
-
-
The sorting values you choose are listed next to the Sort by label beneath the toolbar. Click the X icon on a sorting value to remove it.
- Display area: The area below the Create drop-down field displays the entity carts returned by a search.
-
To view details about the existing entities, click Actions.
-
For a Share Provider, refer to the View Share Provider Entity detail.
- For a Cloud Storage Link, click Actions to Rename, Edit, and Delete the link.
The procedure for creating a credential varies depending on the cloud storage provider. If your source files reside in a cloud store provided by one of the following, see the example for that provider.
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI), see Create an OCI Cloud Store Location.
- Amazon S3, or you are calling an AWS API, see Create an Amazon S3 Cloud Store Location.
- Microsoft Azure Blob Storage or you are calling an Azure API, see Create an Microsoft Azure Cloud Store Location.
- Google Cloud Storage, see Create a Google Cloud Store Location.
- Other (Swift compatible) cloud storage, see Create an Other (Swift Compatible) Cloud Store Location.
- OCI cloud storage by using native OCI credentials, see Create an OCI Cloud storage location using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Signing Keys.
Note:
This method is suggested if you need to use the OCI REST APIs. You need to use the Native OCI credentials if you want to use the OCI REST APIs. To create an OCI cloud storage location using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Signing Keys, you must first Table 3-*.
Create an OCI Cloud Store Location
- On the Connections page, click Create and select Create New Cloud Store Location. This opens the Add Cloud Store Location wizard.
- In the Storage Settings tab of the Add Cloud Store Location box, enter a name for the cloud storage link. For example:
My_Cloud_Store - (Optional) In the Description field, enter a description for the link. For example:
My cloud storage link. - Click Select Credential and Create Credential to create a credential. This opens a Create Credential wizard.
In the Credentials section, select Cloud Username and Password.
- From the Cloud Store drop-down list, select Oracle.
- Enter a name in the Credential Name field. The name must conform to Oracle object naming conventions, which do not allow spaces or hyphens. For example:
my_credential - For an OCI cloud store, in the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure User Name field, enter your OCI user name. For example:
myUsername - For an OCI cloud store, in the Auth Token field, enter your auth token. For example:
LPB>Ktk(1M1SD+a]+r - In the Bucket URI field, enter the URI and bucket for your OCI instance bucket.
- To get the URI and bucket, go to the bucket in the Object Storage compartment in your Oracle Cloud Instance.
- In the Objects group, click the Actions (three vertical dots) icon for a file in the bucket, then click View Object Details.
- Copy all of the URL Path (URI) except for the file name. Be sure to include the trailing slash. For example, for the file
https://objectstorage.us-phoenix-1.oraclecloud.com/n/myoci/b/my_bucket/o/MyFile.csv, select the following:https://objectstorage.us-phoenix-1.oraclecloud.com/n/myoci/b/my_bucket/o/ - Paste the string into the URI + Bucket field.
- Click Next.
The dialog box progresses to the Cloud Data tab. This tab lists the objects available on this cloud storage location in the display area.
Note:
The display area is blank when we create a new cloud storage location. - Click Create create the cloud storage location.
Create an Amazon S3 Cloud Store Location
- On the Connections page, click Create and select Create New Cloud Store Location. This opens the Add Cloud Store Location wizard.
- In the Storage Settings tab of the Add Cloud Store Location box, enter a name for the cloud storage link. For example:
My_Cloud_Store - (Optional) In the Description field, enter a description for the link. For example:
My cloud storage link. - Click Select Credential and Create Credential to create a credential. This opens a Create Credential wizard.
In the Credentials section, select Cloud Username and Password.
- From the Cloud Store drop-down list, select Oracle.
- Enter a name in the Credential Name field. The name must conform to Oracle object naming conventions, which do not allow spaces or hyphens. For example:
my_credential - From the Cloud Store drop-down list, select Amazon S3.
- Enter a name in the Credential Name field. The name must conform to Oracle object naming conventions, which do not allow spaces or hyphens. For example:
my_credential - In the AWS Access Key ID field, enter your AWS access key ID. For example:myAccessKeyID
- In the AWS Secret Access Key field, enter your AWS secret access key. For information on AWS access keys, see Managing access keys for IAM users.
- In the Bucket URI field, enter the URI and bucket for your Amazon S3 bucket. For example:
https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/adwc/my_bucket - Click Next.
The dialog box progresses to the Cloud Data tab. This tab lists the objects available on this cloud storage location in the display area.
Note:
The display area is blank when we create a new cloud storage location. - Click Create create the cloud storage location.
Create an Microsoft Azure Cloud Store Location
- On the Connections page, click Create and select Create New Cloud Store Location. This opens the Add Cloud Store Location wizard.
- In the Storage Settings tab of the Add Cloud Store Location box, enter a name for the cloud storage link. For example:
My_Cloud_Store - (Optional) In the Description field, enter a description for the link. For example:
My cloud storage link. - Click Select Credential and Create Credential to create a credential. This opens a Create Credential wizard.
In the Credentials section, select Cloud Username and Password.
- From the Cloud Store drop-down list, select Microsoft Azure.
- Enter a name in the Credential Name field. The name must conform to Oracle object naming conventions, which do not allow spaces or hyphens. For example:
my_credential - In the Azure Storage Account Name field, enter the name of your Azure storage account. For example:
AZURE_KEY123... - In the Azure Storage Account Access Key field, enter your Azure access key.
For information on Azure storage accounts, see Create a storage account.
- In the Bucket URI field, enter the URI and bucket for your Microsoft Azure bucket. For example:
https://objectstore.microsoft.com/my_bucket - Click Next.
The dialog box progresses to the Cloud Data tab. This tab lists the objects available on this cloud storage location in the display area.
Note:
The display area is blank when we create a new cloud storage location. - Click Create to create the cloud storage location.
Create a Google Cloud Store Location
- On the Connections page, click Create and select Create New Cloud Store Location. This opens the Add Cloud Store Location wizard.
- In the Storage Settings tab of the Add Cloud Store Location box, enter a name for the cloud storage link. For example:
My_Cloud_Store - (Optional) In the Description field, enter a description for the link. For example:
My cloud storage link. - Click Select Credential and Create Credential to create a credential. This opens a Create Credential wizard.
In the Credentials section, select Cloud Username and Password.
- Enter a name in the Credential Name field. The name must conform to Oracle object naming conventions, which do not allow spaces or hyphens. For example:
my_credential - From the Cloud Store drop-down list, select Google.
- In the HMAC Access Key field, enter your HMAC access ID. For example:
GOOGTS1C3LPB3KTKSDMB2BFD - In the HMAC Access Secret field, enter your HMAC secret. For information on HMAC keys, see HMAC Keys.
- In the Storage Settings tab of the Add Cloud Store dialog box, enter a name for the cloud storage link. For example:
My_Cloud_Store - (Optional) In the Description field, enter a description for the link. For example:
My cloud storage link. - In the Bucket URI field, enter the bucket and URI for your Google bucket. For example:
https://my_bucket.storage.googleapis.com - Click Next.
The dialog box progresses to the Cloud Data tab. This tab lists the objects available on this cloud storage location in the display area.
Note:
The display area is blank when we create a new cloud storage location. - Click Create to create the cloud storage location.
Create an Other (Swift Compatible) Cloud Store Location
- On the Connections page, click Create and select Create New Cloud Store Location. This opens the Add Cloud Store Location wizard.
- In the Storage Settings tab of the Add Cloud Store Location box, enter a name for the cloud storage link. For example:
My_Cloud_Store - (Optional) In the Description field, enter a description for the link. For example:
My cloud storage link. - Click Select Credential and Create Credential to create a credential. This opens a Create Credential wizard.
In the Credentials section, select Cloud Username and Password.
Note:
If you have the user OCID, tenancy OCID, private key and fingerprint, select Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Signing Keys and refer to the Create an OCI Cloud storage location using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Signing Keys section of this topic. - From the Cloud Store drop-down list, select Other (Swift Compatible).
- Enter a name in the Credential Name field. The name must conform to Oracle object naming conventions, which do not allow spaces or hyphens. For example:
my_credential - In the Access User Name field, enter your access user name. For example:
OTHER_KEY123... - In the Access Key field, enter your access key.
- In the Bucket URI field, enter the URI and bucket for your cloud store bucket. For example:
https://someswiftcompatibleprovider.com/my_bucket - Click Next.The dialog box progresses to the Cloud Data tab. This tab lists the objects available on this cloud storage location in the display area. The display area is blank when we create a new cloud storage location.
- Click Create to create the cloud storage location.
Create an OCI Cloud storage location using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Signing Keys
To create an OCI Cloud storage location using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Signing Keys:
- On the Connections page, click Create and select Create New Cloud Store Location. This opens the Add Cloud Store Location wizard.
- In the Storage Settings tab of the Add Cloud Store Location box, enter a name for the cloud storage link. For example:
My_Cloud_Store - (Optional) In the Description field, enter a description for the link. For example:
My cloud storage link. - Click Select Credential and Create Credential to create a credential. This opens a Create Credential wizard.
If you have the user OCID, tenancy OCID, private key and fingerprint, select Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Signing Keys.
Note:
If you only have a username and password select Cloud Username and Password in this step and refer to the Create an Other (Swift Compatible) Cloud Store Location section of this topic. -
Specify the following information about your OCI account:
Credential Name: Specify a name to identify the credentials. See Create an OCI Credential Object to enter the Credential name to specify the credential name.
-
Fingerprint: The fingerprint of the RSA key pair. See Create an OCI Credential Object to enter the Credential name to enter the fingerprint.
-
Private Key: The unencrypted private key in the RSA key pair. This should not be encrypted by using any passphrase. See Create an OCI Credential Object to enter the Credential name to enter the private key.
-
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Tenancy: The OCID of the tenant. See Where to Get the Tenancy's OCID and User's OCID for details on obtaining the Tenancy's OCID.
-
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure User Name: The OCID of the user. See Where to Get the Tenancy's OCID and User's OCID for details on obtaining the User's OCID.
- Select Create Credential.
- n the Bucket URI field, enter the URI and bucket for your cloud store bucket. For example:
https://objectstorage.<region>.oraclecloud.com/<namespace>/b/<bucket>/. - Click Next.
-
The dialog box progresses to the Cloud Data tab. This tab lists the objects available on this cloud storage location in the display area.
Note:
The display area is blank when we create a new cloud storage location. - Click Create.
You will receive a notification that the cloud storage location is created successfully.
- Create Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Native Credentials
To establish cloud storage connection from Data Studio to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Object storage service, you must configure the cloud storage location with your OCI authentication details. You can create Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Native Credentials by using the CREATE_CREDENTIAL procedure of DBMS_CLOUD package. - Register Data Catalog
You can register data catalogs you want to use with registering the data catalog.
Parent topic: The Data Load Page
Create Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Native Credentials
To establish cloud storage connection from Data Studio to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Object storage service, you must configure the cloud storage location with your OCI authentication details. You can create Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Native Credentials by using the CREATE_CREDENTIAL procedure of DBMS_CLOUD package.
Create an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Credential Object
To access Object Storage, you must have credentials that you can create via the CREATE_CREDENTIAL procedure of DBMS_CLOUD package. DBMS_CLOUD supports creation of credential objects that contains OCI native authentication. The DBMS_CLOUD procedure stores cloud service credentials in Autonomous Database.
The DBMS_CLOUD.CREATE_CREDENTIAL procedure is overloaded with the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure-related parameters, including: user_ocid, tenancy_ocid, private_key, and fingerprint. This is for using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Signing Keys authentication.
Let us create an OCI native authentication credential when creating an object store credential object. In the OCI native authentication, the DBMS_CLOUD.CREATE_CREDENTIAL procedure includes the following parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
The |
|
|
Specifies the user's OCID. See Where to Get the Tenancy's OCID and User's OCID for details on obtaining the User's OCID. |
|
|
Specifies the tenancy's OCID. See Where to Get the Tenancy's OCID and User's OCID for details on obtaining the Tenancy's OCID. |
|
|
Specifies the generated private key. Private keys generated with a passphrase are not supported. You need to generate the private key without a passphrase. See How to Generate an API Signing Key for details on generating a key pair in PEM format. |
|
|
Specifies a fingerprint. After a generated public key is uploaded to the user's account the fingerprint is displayed in the console. Use the displayed fingerprint for this argument. See How to Get the Key's Fingerprint and How to Generate an API Signing Key for more details. |
Here is the syntax of the DBMS_CLOUD.CREATE_CREDENTIAL procedure:
DBMS_CLOUD.CREATE_CREDENTIAL (
credential_name IN VARCHAR2,
user_ocid IN VARCHAR2,
tenancy_ocid IN VARCHAR2,
private_key IN VARCHAR2,
fingerprint IN VARCHAR2);Once you obtain all the necessary inputs and generate your private key, here is a sample of your CREATE_CREDENTIAL procedure:
BEGIN DBMS_CLOUD.CREATE_CREDENTIAL ( credential_name =>
'OCI_NATIVE_CRED', user_ocid =>
'ocid1.user.oc1..aaaaaaaatfn77fe3fxux3o5lego7glqjejrzjsqsrs64f4jsjrhbsk5qzndq', tenancy_ocid =>
'ocid1.tenancy.oc1..aaaaaaaapwkfqz3upqklvmelbm3j77nn3y7uqmlsod75rea5zmtmbl574ve6a', private_key =>
'MIIEogIBAAKCAQEAsbNPOYEkxM5h0DF+qXmie6ddo95BhlSMSIxRRSO1JEMPeSta0C7WEg7g8SOSzhIroCkgOqDzkcyXnk4BlOdn5Wm/BYpdAtTXk0sln2DH/GCH7l9P8xC9cvFtacXkQPMAXIBDv/zwG1kZQ7Hvl7Vet2UwwuhCsesFgZZrAHkv4cqqE3uF5p/qHfzZHoevdq4EAV6dZK4Iv9upACgQH5zf9IvGt2PgQnuEFrOm0ctzW0v9JVRjKnaAYgAbqa23j8tKapgPuREkfSZv2UMgF7Z7ojYMJEuzGseNULsXn6N8qcvr4fhuKtOD4t6vbIonMPIm7Z/a6tPaISUFv5ASYzYEUwIDAQABAoIBACaHnIv5ZoGNxkOgF7ijeQmatoELdeWse2ZXll+JaINeTwKU1fIB1cTAmSFv9yrbYb4ubKCJuYZJeC6I92rT6gEiNpr670Pn5n43cwblszcTryWOYQVxAcLkejbPA7jZd6CW5xm/vEgRv5qgADVCzDCzrij0t1Fghicc+EJ4BFvOetnzEuSidnFoO7K3tHGbPgA+DPN5qrO/8NmrBebqezGkOuOVkOA64mp467DQUhpAvsy23RjBQ9iTuRktDB4g9cOdOVFouTZTnevN6JmDxufu9Lov2yvVMkUC2YKd+RrTAE8cvRrn1A7XKkH+323hNC59726jT57JvZ+ricRixSECgYEA508e/alxHUIAU9J/uq98nJY/6+GpI9OCZDkEdBexNpKeDq2dfAo9pEjFKYjH8ERj9quA7vhHEwFL33wk2D24XdZl6vq0tZADNSzOtTrtSqHykvzcnc7nXv2fBWAPIN59s9/oEKIOdkMis9fps1mFPFiN8ro4ydUWuR7B2nM2FWkCgYEAxKs/zOIbrzVLhEVgSH2NJVjQs24S8W+99uLQK2Y06R59L0Sa90QHNCDjB1MaKLanAahP30l0am0SB450kEiUD6BtuNHH8EIxGL4vX/SYeE/AF6tw3DqcOYbLPpN4CxIITF0PLCRoHKxARMZLCJBTMGpxdmTNGyQAPWXNSrYEKFsCgYBp0sHr7TxJ1WtO7gvvvd91yCugYBJAyMBr18YY0soJnJRhRL67A/hlk8FYGjLW0oMlVBtduQrTQBGVQjedEsepbrAcC+zm7+b3yfMb6MStE2BmLPdF32XtCH1bOTJSqFe8FmEWUv3ozxguTUam/fq9vAndFaNre2i08sRfi7wfmQKBgBrzcNHN5odTIV8l9rTYZ8BHdIoyOmxVqM2tdWONJREROYyBtU7PRsFxBEubqskLhsVmYFO0CD0RZ1gbwIOJPqkJjh+2t9SH7Zx7a5iV7QZJS5WeFLMUEv+YbYAjnXK+dOnPQtkhOblQwCEY3Hsblj7Xz7o=', fingerprint =>
'4f:0c:d6:b7:f2:43:3c:08:df:62:e3:b2:27:2e:3c:7a');END;/
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.You can now retrieve the new credentials with the following query:
SELECT owner, credential_name FROM dba_credentials WHERE credential_name LIKE '%NATIVE%'; OWNER CREDENTIAL_NAME----- ---------------
ADMIN OCI_NATIVE_CREDParent topic: Managing Connections
Register Data Catalog
You can register data catalogs you want to use with registering the data catalog.
To register a data catalog you need to specify the details of the credentials you want to register your data source. A credential object manages a data catalog instance. In OCI native authentication, the DBMS_CLOUD.CREATE_CREDENTIAL procedure includes these parameters: credential_name, user_ocid, tenancy_ocid, private_key, and fingerprint.
See REF DBMS_DCAT Package to refer to the procedures to add custom parameters such as region and data catalog ID to the Data Catalog. The Data Catalog ID is a unique Oracle cloud Identifier for data catalog instance and region is the data catalog region.
- Select Cloud Locations under Data Load to register the data catalog.
- Click Register Data Catalog. This opens a Register Data Catalog wizard.
- In the Catalog Settings tab, specify the following details:
- Catalog Name:
Test. Enter a name of your choice. - Description: Specify a description. This is an optional field.
- Under Data Catalog details, select a Credential option.
- If you click Select Credential, specify the following information.
- Credential for Data Catalog Connection: Select a value from the drop-down. The drop-down lists the values of credentials you create.
- Region:
us-ashburn-1. Enter the region name from the DBMS_DCAT package. - Data Catalog ID:
ocid1.datacatalog.oc1.iad.amaaaaaa7ratcziayxh7uzll24cp3uwzsugfj7qlubak77toiehidpsqsygq.Enter the data catalog ID from the DBMS_DCAT package.
- If you select Create Credentials, specify the following information:
- Credential Name: Specify a name to identify the credentials. See Create an OCI Credential Object to enter the Credential name to specify the credential name.
- Fingerprint: The fingerprint of the RSA key pair. See Create an OCI Credential Object to enter the Credential name to enter the fingerprint.
- Private Key: The unencrypted private key in the RSA key pair. This should not be encrypted by using any passphrase.
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Tenancy: The OCID of the tenant.
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure User Name: The OCID of the user.
- Region:
us-ashburn-1. Enter the region name from the DBMS_DCAT package. - Data Catalog ID:
ocid1.datacatalog.oc1.iad.amaaaaaa7ratcziayxh7uzll24cp3uwzsugfj7qlubak77toiehidpsqsygq.Enter the data catalog ID from the DBMS_DCAT package.
- Catalog Name:
- Select Next to progress to the Register Assets tab where you need to select the source of data catalogs assets you create.
- Select Create.
After successful registering of the data catalog, you can view the data catalog entity in the list of entities in the Manage Cloud Store page.
Parent topic: Managing Connections