Enhance Natural Language Prompts Using Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)
Select AI with RAG augments your natural language prompt by retrieving content from your specified vector store using semantic similarity search. This reduces hallucinations by using your specific and up-to-date content and provides more relevant natural language responses to your prompts.
Select AI automates the Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) process. This technique retrieves data from enterprise sources using AI vector search and augments user prompts for your specified large language model (LLM). By leveraging information from enterprise data stores, RAG reduces hallucinations and generates grounded responses.
RAG uses AI vector search on a vector index to find semantically similar data for the specified question. Vector store processes vector embeddings, which are mathematical representations of various data points like text, images, and audio. These embeddings capture the meaning of the data, enabling efficient processing and analysis. For more details on vector embeddings and AI vector search, see Overview of AI Vector Search.
Select AI integrates with AI vector search available in Oracle Autonomous AI Database 26ai for similarity search using vector embeddings.
Benefits of Select AI RAG
Simplify querying, enhance response accuracy with current data, and gain transparency by reviewing sources used by the LLM.
-
Simplify data querying and increase response accuracy: Enable users to query enterprise data using natural language and provide LLMs with detailed context from enterprise data to generate more accurate and relevant responses, reducing instances of LLM hallucinations.
-
Up-to-date information: Provide LLMs access to current enterprise information using vector stores, eliminating the need for costly, time-consuming fine-tuning of LLMs trained on static data sets.
-
Seamless integration: Integrate with Oracle AI Vector Search for streamlined data handling and enhanced performance.
-
Automated data orchestration: Automate orchestration steps with a fully managed Vector Index pipeline, ensuring efficient processing of new data.
-
Understandable contextual results: Has access and retrieves the sources used by the LLM from vector stores, ensuring transparency and confidence in results. Views and extracts data in natural language text or JSON format for easier integration and application development.
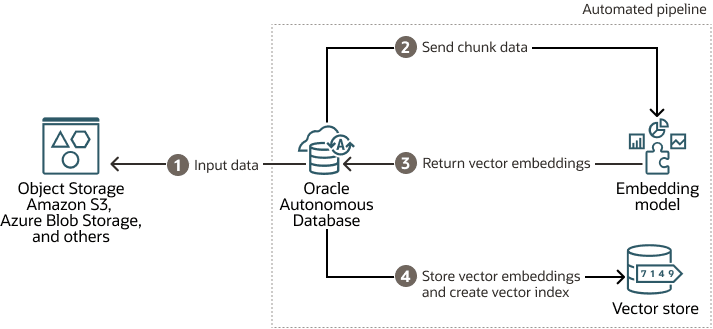
Build your Vector Store
Select AI automatically processes documents to chunks, generates embeddings, stores them in the specified vector store, and updates the vector index as new data arrives.
- Input: Data is initially stored in an Object Storage.
- Oracle Autonomous Database retrieves the input data or the document, chunks it and sends the chunks to an embedding model.
- The embedding model processes the chunk data and returns vector embeddings.
- The vector embeddings are then stored in a vector store for use with RAG. As content is added, the vector index is automatically updated.
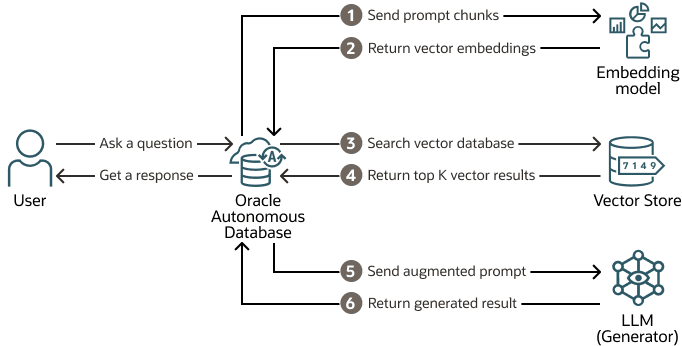
RAG retrieves relevant pieces of information from the enterprise database to answer a user's question. This information is provided to the specified large language model along with the user prompt. Select AI uses this additional enterprise information to enhance the prompt, improving the LLM's response. RAG can enhance response quality with update-to-date enterprise information from the vector store.
-
Input: User asks a question (specifies a prompt) using Select AI
narrateaction. -
Select AI generates vector embeddings of the prompt using the embedding model specified in the AI profile.
-
The vector search index uses the vector embedding of the question to find matching content from the customer's enterprise data (searching the vector store) which has been indexed.
- The vector search returns top K texts similar to the input to your Autonomous AI Database instance.
- Autonomous AI Database then sends these top K query results with user question to the LLM.
- The LLM returns its response to your Autonomous AI Database instance.
- Autonomous AI Database Select AI provides the response to the user.
Use DBMS_CLOUD_AI to Create and Manage Vector Indexes
Use the DBMS_CLOUD_AI package
to create and manage vector indexes and configure vector database JSON parameters.
Note:
If you do not want table data or vector search documents to be sent to an LLM, a user with administrator privileges can disable such access for all users of the given database. This, in effect, disables the narrate action for RAG.
You can configure AI profiles for providers listed in through the DBMS_CLOUD_AI package.
See Also:
-
Create a vector index: CREATE_VECTOR_INDEX Procedure.
-
Manage vector index profiles and other AI profiles: Summary of DBMS_CLOUD_AI Subprograms.
-
Query vector index views: DBMS_CLOUD_AI Views.
Use In-database Transformer Models
Select AI RAG enables you to use pretrained ONNX transformer models that are imported into your database in Oracle Database 23ai instance for generating embedding vectors from document chunks and user prompts.
Note:
You must import a pretrained ONNX-format transformer model into Oracle Database 23ai instance to use Select AI RAG with imported in-database transformer model. You can also use other transformer models from supported AI providers.See Example: Select AI with In-database Transformer Models to explore the feature.
Example: Set Up and Use Select AI with RAG
This example guides you through setting up credentials, configuring network access, and creating a vector index for integrating OCI Generative AI vector store cloud services with OpenAI using Oracle Autonomous AI Database.
The setup concludes with creating an AI profile that uses the vector
index to enhance LLM responses. Finally, this example uses the Select AI
narrate action, which returns a response that has been enhanced
using information from the specified vector database.
The following example demonstrates building and querying vector index in Oracle Database 23ai.
--Grants EXECUTE privilege to ADB_USER
GRANT EXECUTE on DBMS_CLOUD_AI to ADB_USER;
--Grants EXECUTE privilege DBMS_CLOUD_PIPELINE to ADB_USER
GRANT EXECUTE on DBMS_CLOUD_PIPELINE to ADB_USER;
-- Create the OpenAI credential
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD.CREATE_CREDENTIAL(
credential_name => 'OPENAI_CRED',
username => 'OPENAI_CRED',
password => '<your_api_key>'
);
END;
/
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
-- Append the OpenAI endpoint
BEGIN
DBMS_NETWORK_ACL_ADMIN.APPEND_HOST_ACE(
host => 'api.openai.com',
ace => xs$ace_type(privilege_list => xs$name_list('http'),
principal_name => 'ADB_USER',
principal_type => xs_acl.ptype_db)
);
END;
/
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
-- Create the object store credential
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD.CREATE_CREDENTIAL(
credential_name => 'OCI_CRED',
username => '<your_username>',
password => '<OCI_profile_password>'
);
END;
/
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
-- Create the profile with the vector index.
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD_AI.CREATE_PROFILE(
profile_name =>'OPENAI_ORACLE',
attributes =>'{"provider": "openai",
"credential_name": "OPENAI_CRED",
"vector_index_name": "MY_INDEX",
"temperature": 0.2,
"max_tokens": 4096,
"model": "gpt-3.5-turbo-1106"
}');
END;
/
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
-- Set profile
EXEC DBMS_CLOUD_AI.SET_PROFILE('OPENAI_ORACLE');
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
-- create a vector index with the vector store name, object store location and
-- object store credential
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD_AI.CREATE_VECTOR_INDEX(
index_name => 'MY_INDEX',
attributes => '{"vector_db_provider": "oracle",
"location": "https://swiftobjectstorage.us-phoenix-1.oraclecloud.com/v1/my_namespace/my_bucket/my_data_folder",
"object_storage_credential_name": "OCI_CRED",
"profile_name": "OPENAI_ORACLE",
"vector_dimension": 1536,
"vector_distance_metric": "cosine",
"chunk_overlap":128,
"chunk_size":1024
}');
END;
/
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
-- After the vector index is populated, we can now query the index.
-- Set profile
EXEC DBMS_CLOUD_AI.SET_PROFILE('OPENAI_ORACLE');
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
-- Select AI answers the question with the knowledge available in the vector database.
set pages 1000
set linesize 150
SELECT AI narrate how can I deploy an oracle machine learning model;
RESPONSE
To deploy an Oracle Machine Learning model, you would first build your model within the Oracle database. Once your in-database models are built, they become immediately available for use, for instance, through a SQL query using the prediction operators built into the SQL language.
The model scoring, like model building, occurs directly in the database, eliminating the need for a separate engine or environment within which the model and corresponding algorithm code operate. You can also use models from a different schema (user account) if the appropriate permissions are in place.
Sources:
- Manage-your-models-with-Oracle-Machine-Learning-on-Autonomous-Database.txt (https://objectstorage.../v1/my_namespace/my_bucket/my_data_folder/Manage-your-models-with-Oracle-Machine-Learning-on-Autonomous-Database.txt)
- Develop-and-deploy-machine-learning-models-using-Oracle-Autonomous-Database-Machine-Learning-and-APEX.txt (https://objectstorage.../v1/my_namespace/my_bucket/my_data_folder/Develop-and-deploy-machine-learning-models-using-Oracle-Autonomous-Database-Machine-Learning-and-APEX.txt)
Example: Select AI with In-database Transformer Models
This example demonstrates how you can import a pretrained transformer model that is stored in Oracle object storage into your Oracle Database 23ai instance and then use the imported in-database model in Select AI profile to generate vector embeddings for document chunks and user prompts.
-
your pretrained model imported in your Oracle Database 23ai instance.
-
optionally, access to Oracle object storage.
Review the steps in Import Pretrained Models in ONNX Format for Vector Generation Within the Database and the blog Pre-built Embedding Generation model for Oracle AI Database 26ai to import a pretrained transformer model into your database.
The following example shows how to import a pretained transformer model from Oracle object storage into your database and then view the imported model.
- Create a Directory object, or use an existing directory object
CREATE OR REPLACE DIRECTORY ONNX_DIR AS 'onnx_model';
-- Object storage bucket
VAR location_uri VARCHAR2(4000);
EXEC :location_uri := 'https://adwc4pm.objectstorage.us-ashburn-1.oci.customer-oci.com/p/eLddQappgBJ7jNi6Guz9m9LOtYe2u8LWY19GfgU8flFK4N9YgP4kTlrE9Px3pE12/n/adwc4pm/b/OML-Resources/o/';
-- Model file name
VAR file_name VARCHAR2(512);
EXEC :file_name := 'all_MiniLM_L12_v2.onnx';
-- Download ONNX model from object storage into the directory object
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD.GET_OBJECT(
credential_name => NULL,
directory_name => 'ONNX_DIR',
object_uri => :location_uri || :file_name);
END;
/
-- Load the ONNX model into the database
BEGIN
DBMS_VECTOR.LOAD_ONNX_MODEL(
directory => 'ONNX_DIR',
file_name => :file_name,
model_name => 'MY_ONNX_MODEL');
END;
/
-- Verify
SELECT model_name, algorithm, mining_function
FROM user_mining_models
WHERE model_name='MY_ONNX_MODEL';These examples illustrate how to use in-database transformer models within a Select AI profile. One profile is configured only for generating vector embeddings, while the other supports both Select AI actions and vector index creation.
Review Requirements to Configure DBMS_CLOUD_AI Package to complete the prerequisites.
The following is an example for generating vector embeddings only:
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD_AI.CREATE_PROFILE(
profile_name => 'EMBEDDING_PROFILE',
attributes => '{"provider" : "database",
"embedding_model": "MY_ONNX_MODEL"}'
);
END;
/The following is an example for general Select AI actions and vector index generation where you can specify a supported AI provider. This example uses OCI Gen AI profile and credentials. See for list of supported providers. However, if you want to use in-database transformer model for generating vector embeddings, then use "database: <MY_ONNX_MODEL>" in embedding_model attribute:
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD.CREATE_CREDENTIAL(
credential_name => 'GENAI_CRED',
user_ocid => 'ocid1.user.oc1..aaaa...',
tenancy_ocid => 'ocid1.tenancy.oc1..aaaa...',
private_key => '<your_api_key>',
fingerprint => '<your_fingerprint>'
);
END;
/
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD_AI.CREATE_PROFILE(
profile_name => 'OCI_GENAI',
attributes => '{"provider": "oci",
"model": "meta.llama-3.3-70b-instruct",
"credential_name": "GENAI_CRED",
"vector_index_name": "MY_INDEX",
"embedding_model": "database: MY_ONNX_MODEL"}'
);
END;
/This example demonstrates
how to use Select AI with an in-database transformer model if another schema owner
owns the model. Specify schema_name.object_name as the fully
qualified name of the model in embedding_model attribute. If the
current user is the schema owner or owns the model, you can omit the schema
name.
CREATE ANY MINING MODELsystem privilegeSELECT ANY MINING MODELsystem privilegeSELECT MINING MODELobject privilege on the specific model
To grant a system privilege, you must either have been
granted the system privilege with the ADMIN OPTION or have been
granted the GRANT ANY PRIVILEGE system privilege.
See System Privileges for Oracle Machine Learning for SQL to review the privileges.
The
following statements allow ADB_USER1 to score data and view model
details in any schema as long as SELECT access has been granted to
the data. However, ADB_USER1 can only create models in the
ADB_USER1 schema.
GRANT CREATE MINING MODEL TO ADB_USER1;
GRANT SELECT ANY MINING MODEL TO ADB_USER1;
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD_AI.CREATE_PROFILE(
profile_name => 'OCI_GENAI',
attributes => '{"provider": "oci",
"credential_name": "GENAI_CRED",
"vector_index_name": "MY_INDEX",
"embedding_model": "database: ADB_USER1.MY_ONNX_MODEL"}'
);
END;
/The following example shows how you can specify case sensitive model object name:
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD_AI.CREATE_PROFILE(
profile_name => 'OCI_GENAI',
attributes => '{"provider": "oci",
"credential_name": "GENAI_CRED",
"model": "meta.llama-3.3-70b-instruct",
"vector_index_name": "MY_INDEX",
"embedding_model": "database: \"adb_user1\".\"my_model\""}'
);
END;
/These examples demonstrate end-to-end steps for using in-database transformer model with Select AI RAG. One profile uses database as the provider exclusively created for generating embedding vectors while the other profile uses oci as the provider created for Select AI actions as well as vector index.
Review Requirements to Configure DBMS_CLOUD_AI Package to complete the prerequisites.
--Grant create any directory privilege to the user
GRANT CREATE ANY DIRECTORY to ADB_USER;
- Create a Directory object, or use an existing directory object
CREATE OR REPLACE DIRECTORY ONNX_DIR AS 'onnx_model';
-- Object storage bucket
VAR location_uri VARCHAR2(4000);
EXEC :location_uri := 'https://adwc4pm.objectstorage.us-ashburn-1.oci.customer-oci.com/p/eLddQappgBJ7jNi6Guz9m9LOtYe2u8LWY19GfgU8flFK4N9YgP4kTlrE9Px3pE12/n/adwc4pm/b/OML-Resources/o/';
-- Model file name
VAR file_name VARCHAR2(512);
EXEC :file_name := 'all_MiniLM_L12_v2.onnx';
-- Download ONNX model from object storage into the directory object
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD.GET_OBJECT(
credential_name => NULL,
directory_name => 'ONNX_DIR',
object_uri => :location_uri || :file_name);
END;
/
-- Load the ONNX model into the database
BEGIN
DBMS_VECTOR.LOAD_ONNX_MODEL(
directory => 'ONNX_DIR',
file_name => :file_name,
model_name => 'MY_ONNX_MODEL');
END;
/
-- Verify
SELECT model_name, algorithm, mining_function
FROM user_mining_models
WHERE model_name='MY_ONNX_MODEL';
--Administrator grants EXECUTE privilege to ADB_USER
GRANT EXECUTE on DBMS_CLOUD_AI to ADB_USER;
--Administrator grants EXECUTE privilege DBMS_CLOUD_PIPELINE to ADB_USER
GRANT EXECUTE on DBMS_CLOUD_PIPELINE to ADB_USER;
-- Create the object store credential
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD.CREATE_CREDENTIAL(
credential_name => 'OCI_CRED',
username => '<your_username>',
password => '<OCI_profile_password>'
);
END;
/
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
-- Create the profile with Oracle Database.
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD_AI.CREATE_PROFILE(
profile_name =>'EMBEDDING_PROFILE',
attributes =>'{"provider": "database",
"embedding_model": "MY_ONNX_MODEL"
}');
END;
/
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
-- Set profile
EXEC DBMS_CLOUD_AI.SET_PROFILE('EMBEDDING_PROFILE');
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
This example uses oci as the
provider.
--Grant create any directory privilege to the user
GRANT CREATE ANY DIRECTORY to ADB_USER;
- Create a Directory object, or use an existing directory object
CREATE OR REPLACE DIRECTORY ONNX_DIR AS 'onnx_model';
-- Object storage bucket
VAR location_uri VARCHAR2(4000);
EXEC :location_uri := 'https://adwc4pm.objectstorage.us-ashburn-1.oci.customer-oci.com/p/eLddQappgBJ7jNi6Guz9m9LOtYe2u8LWY19GfgU8flFK4N9YgP4kTlrE9Px3pE12/n/adwc4pm/b/OML-Resources/o/';
-- Model file name
VAR file_name VARCHAR2(512);
EXEC :file_name := 'all_MiniLM_L12_v2.onnx';
-- Download ONNX model from object storage into the directory object
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD.GET_OBJECT(
credential_name => NULL,
directory_name => 'ONNX_DIR',
object_uri => :location_uri || :file_name);
END;
/
-- Load the ONNX model into the database
BEGIN
DBMS_VECTOR.LOAD_ONNX_MODEL(
directory => 'ONNX_DIR',
file_name => :file_name,
model_name => 'MY_ONNX_MODEL');
END;
/
-- Verify
SELECT model_name, algorithm, mining_function
FROM user_mining_models
WHERE model_name='MY_ONNX_MODEL';
–-Administrator Grants EXECUTE privilege to ADB_USER
GRANT EXECUTE on DBMS_CLOUD_AI to ADB_USER;
--Administrator Grants EXECUTE privilege DBMS_CLOUD_PIPELINE to ADB_USER
GRANT EXECUTE on DBMS_CLOUD_PIPELINE to ADB_USER;
-- Create the object store credential
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD.CREATE_CREDENTIAL(
credential_name => 'OCI_CRED',
username => '<your_username>',
password => '<OCI_profile_password>'
);
END;
/
--Create GenAI credentials
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD.CREATE_CREDENTIAL(
credential_name => 'GENAI_CRED',
user_ocid => 'ocid1.user.oc1..aaaa...',
tenancy_ocid => 'ocid1.tenancy.oc1..aaaa...',
private_key => '<your_api_key>',
fingerprint => '<your_fingerprint>'
);
END;
/
--Create OCI AI profile
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD_AI.CREATE_PROFILE(
profile_name => 'OCI_GENAI',
attributes => '{"provider": "oci",
"model": "meta.llama-3.3-70b-instruct",
"credential_name": "GENAI_CRED",
"vector_index_name": "MY_INDEX",
"embedding_model": "database: MY_ONNX_MODEL"}'
);
END;
/
-- Set profile
EXEC DBMS_CLOUD_AI.SET_PROFILE('OCI_GENAI');
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
-- create a vector index with the vector store name, object store location and
-- object store credential
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD_AI.CREATE_VECTOR_INDEX(
index_name => 'MY_INDEX',
attributes => '{"vector_db_provider": "oracle",
"location": "https://swiftobjectstorage.us-phoenix-1.oraclecloud.com/v1/my_namespace/my_bucket/my_data_folder",
"object_storage_credential_name": "OCI_CRED",
"profile_name": "OCI_GENAI",
"vector_dimension": 384,
"vector_distance_metric": "cosine",
"chunk_overlap":128,
"chunk_size":1024
}');
END;
/
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
-- Set profile
EXEC DBMS_CLOUD_AI.SET_PROFILE('OCI_GENAI');
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
-- Select AI answers the question with the knowledge available in the vector database.
set pages 1000
set linesize 150
SELECT AI narrate how can I deploy an oracle machine learning model;
RESPONSE
To deploy an Oracle Machine Learning model, you would first build your model within the Oracle database. Once your in-database models are
built, they become immediately available for use, for instance, through a SQL query using the prediction operators built into the SQL
language.
The model scoring, like model building, occurs directly in the database, eliminating the need for a separate engine or environment within
which the model and corresponding algorithm code operate. You can also use models from a different schema (user account) if the appropriate
permissions are in place.
Sources:
- Manage-your-models-with-Oracle-Machine-Learning-on-Autonomous-Database.txt (https://objectstorage.../v1/my_namespace/my_bucket/
my_data_folder/Manage-your-models-with-Oracle-Machine-Learning-on-Autonomous-Database.txt)
- Develop-and-deploy-machine-learning-models-using-Oracle-Autonomous-Database-Machine-Learning-and-APEX.txt
(https://objectstorage.../v1/my_namespace/my_bucket/my_data_folder/Develop-and-deploy-machine-learning-models-using-Oracle-Autonomous-
Database-Machine-Learning-and-APEX.txt)For information about Oracle's commitment to accessibility, visit the Oracle Accessibility Program website at http://www.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=acc&id=docacc.
Access to Oracle Support
Oracle customer access to and use of Oracle support services will be pursuant to the terms and conditions specified in their Oracle order for the applicable services.