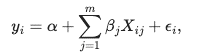Spatial Diagnostics Using OLS
The first step in spatial modeling is to do some spatial diagnostics, such as analyzing multicollinearity, normal distribution bias, spatial heterogeneity, and spatial dependence. You can do this using the Ordinary Least Squre (OLS) model.
The OLS algorithm fits a line that minimizes the Mean Squared Error (MSE) from the training set to predict new values. The formula of the ordinary linear regression is given as shown:
In the preceding formula:α is the intercept or
constant parameter, β is a vector of parameters that give us
information about to what extent each variable is related to the target variable
y and εi represents the
error. The goal when training an OLS model is to estimate the parameters
α and β to predict values of
y for new values of X.
The OLSRegressor class in Spatial AI adds the
spatial_weights_definition parameter in the general OLS model,
which allows you to get spatial statistics after training the model. These statistics
help identify the presence of spatial dependence or spatial heterogeneity and determine
if another algorithm is required. So OLSRegressor intends to help user
diagnose the data to see if there are any special spatial relationships, which in turn
helps decide which spatial regression algorithm to use for the specific task. See Metrics for Spatial Regression for more information on the statistics.
The following table describes the main methods of the
OLSRegressor class.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
fit |
Trains the OLS model from the given training data and
obtains spatial statistics if the
spatial_weights_definition parameter is
specified.
|
predict |
Uses the trained parameters to estimate the target variable of the given data. |
fit_predict |
Calls the fit and
predict methods sequentially with the training
data.
|
score |
The R-squared statistic for the given data. |
See the OLSRegressor class in Python API Reference for Oracle Spatial AI for more information.
The following example uses the block_groups
and creates an OLS model defining the
SpatialDataFramespatial_weights_definition parameter. After training the model, it
calls the predict and score methods. Finally, the
program prints a summary of the model containing the spatial statistics.
from oraclesai.preprocessing import spatial_train_test_split
from oraclesai.regression import OLSRegressor
from oraclesai.weights import KNNWeightsDefinition
# Define the training and test set.
X = block_groups[["MEDIAN_INCOME", "MEAN_AGE", "HOUSE_VALUE", "INTERNET", "geometry"]]
X_train, X_test, _, _, _, _ = spatial_train_test_split(X, y="MEDIAN_INCOME", test_size=0.2)
# Create the OLSRegressor defining the spatial_weights
spatial_ols_model = OLSRegressor(KNNWeightsDefinition(k=10))
# Train the model and specify the target variable
spatial_ols_model.fit(X_train, "MEDIAN_INCOME")
# Print the predictions of the test set
ols_predictions_test = spatial_ols_model.predict(X_test.drop(["MEDIAN_INCOME"])).flatten()
print(f"\n>> predictions (X_test):\n {ols_predictions_test[:10]}")
# Print the R-squared score of the test set
ols_r2_score = spatial_ols_model.score(X_test, y="MEDIAN_INCOME")
print(f"\n>> r2_score (X_test):\n {ols_r2_score}")
# Prints a summary of the model
print(spatial_ols_model.summary)The program output includes the following:
- The
predictmethod returns the estimated values of the target variable over the test set. - The
scoremethod returns the R-squared metric of the model from the test set. - The
summaryproperty provides multiple statistics and the parameters associated with each explanatory variable. Also, it includes spatial statistics based on thespatial_weights_definitionparameter.
>> predictions (X_test):
[84333.95556955 88819.9988673 52445.40662329 66192.50638257
66613.63752196 53802.16810985 65151.54020825 29424.26087764
37296.49147829 85676.22038382]
>> r2_score (X_test):
0.6009367861353069
REGRESSION
----------
SUMMARY OF OUTPUT: ORDINARY LEAST SQUARES
-----------------------------------------
Data set : unknown
Weights matrix : unknown
Dependent Variable : dep_var Number of Observations: 2750
Mean dependent var : 70051.6531 Number of Variables : 4
S.D. dependent var : 40235.8666 Degrees of Freedom : 2746
R-squared : 0.6385
Adjusted R-squared : 0.6381
Sum squared residual:1608810557754.003 F-statistic : 1616.7374
Sigma-square :585874201.658 Prob(F-statistic) : 0
S.E. of regression : 24204.838 Log likelihood : -31659.426
Sigma-square ML :585022021.001 Akaike info criterion : 63326.852
S.E of regression ML: 24187.2285 Schwarz criterion : 63350.529
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Variable Coefficient Std.Error t-Statistic Probability
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
CONSTANT -61472.5132881 3718.3646558 -16.5321368 0.0000000
MEAN_AGE 798.8367637 94.5268152 8.4509011 0.0000000
HOUSE_VALUE 0.0558167 0.0014696 37.9805274 0.0000000
INTERNET 85961.1765144 3867.7192944 22.2252883 0.0000000
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
REGRESSION DIAGNOSTICS
MULTICOLLINEARITY CONDITION NUMBER 20.388
TEST ON NORMALITY OF ERRORS
TEST DF VALUE PROB
Jarque-Bera 2 955.683 0.0000
DIAGNOSTICS FOR HETEROSKEDASTICITY
RANDOM COEFFICIENTS
TEST DF VALUE PROB
Breusch-Pagan test 3 1198.122 0.0000
Koenker-Bassett test 3 526.447 0.0000
DIAGNOSTICS FOR SPATIAL DEPENDENCE
TEST MI/DF VALUE PROB
Moran's I (error) 0.2395 29.493 0.0000
Lagrange Multiplier (lag) 1 426.035 0.0000
Robust LM (lag) 1 4.674 0.0306
Lagrange Multiplier (error) 1 854.940 0.0000
Robust LM (error) 1 433.579 0.0000
Lagrange Multiplier (SARMA) 2 859.614 0.0000
================================ END OF REPORT =====================================