Accessing the Oracle Autonomous AI Lakehouse
Create a database in the Oracle Autonomous AI Lakehouse
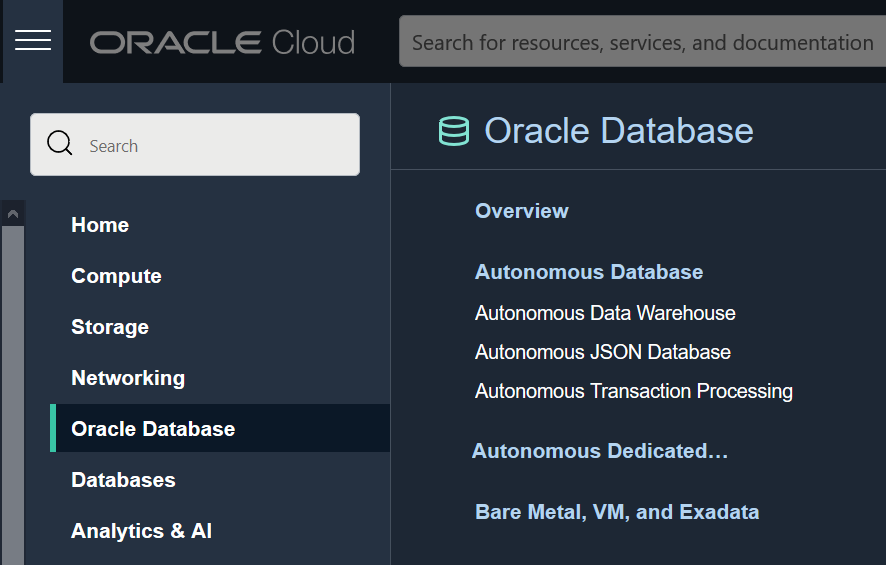
- Select Oracle AI Database from the menu on the left side of the display.
- Select Autonomous AI
Database.
- In Applied Filters, select the Compartment to create the database.
- Select Create Autonomous AI Database.
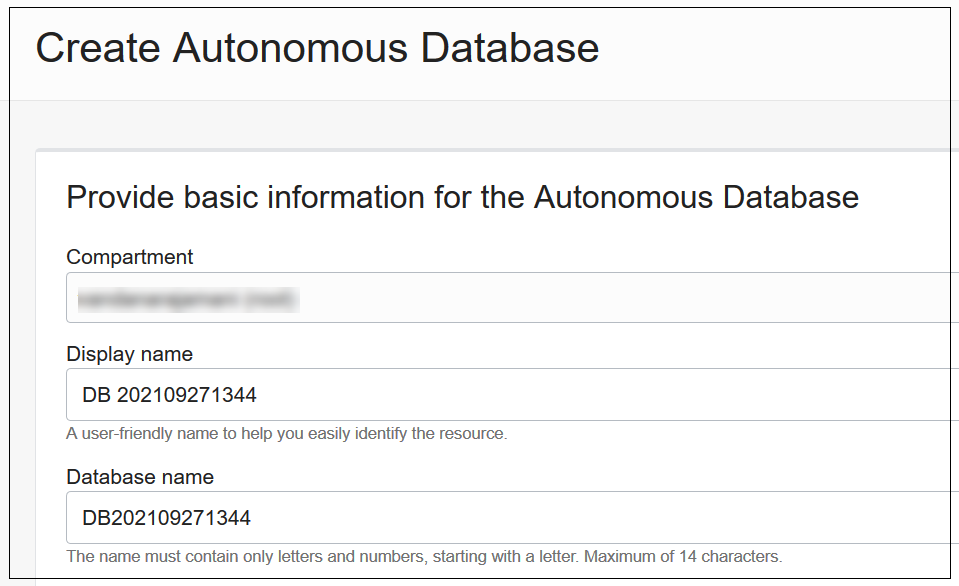
- Enter the Basic Information for the Autonomous AI
Database; for example,
- Compartment: enter the compartment name selected above.
- Display name: the name to display
on the console; for example,
NoSqlToAdwDb. - Database name: the name to use when
connecting to the database; for example,
NoSqlToAdwDb(cannot be more than 30 characters).
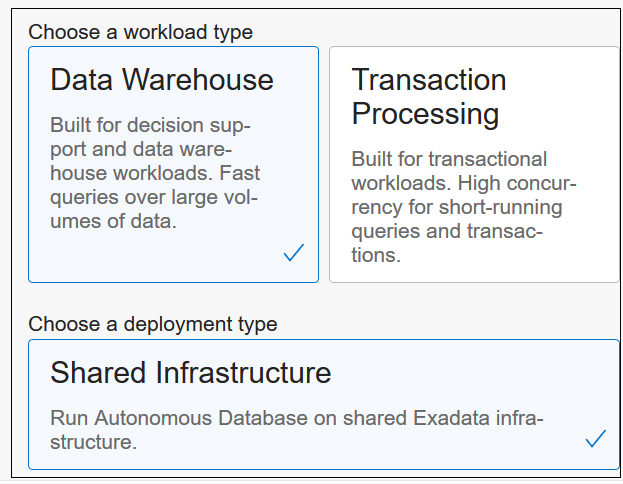
- Select the Lakehouse
workload type.
- Use the default configuration for the
database.
- Set a Password under Administrator
credentials creation.
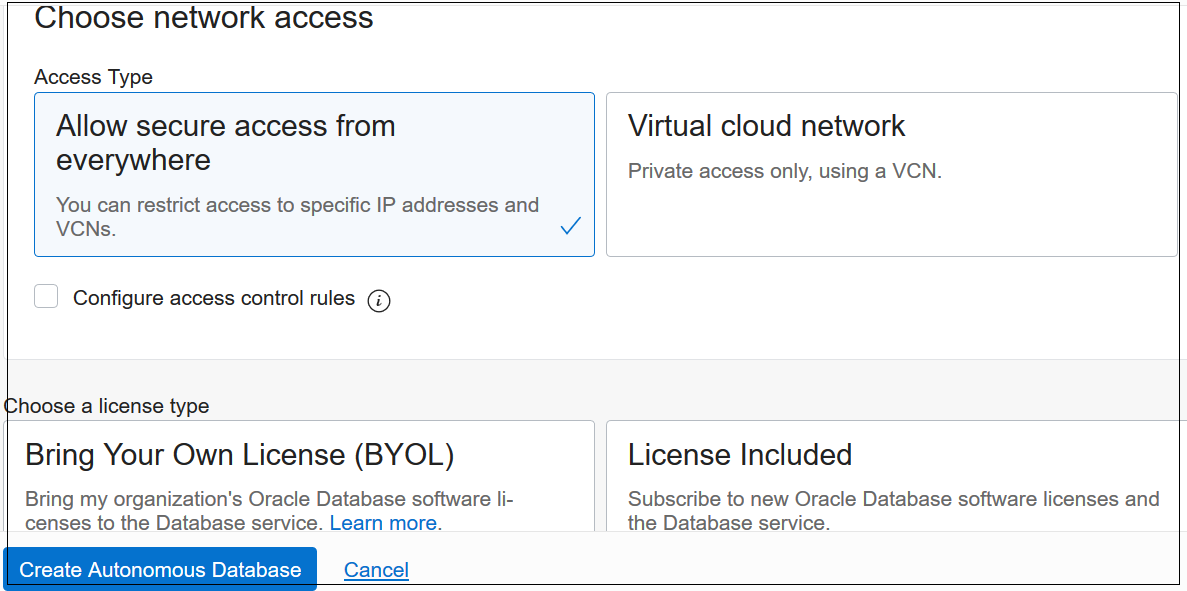
- Select Secure access from
everywhere for Access
Type.
- Select the appropriate license type. If you have
your own license, then enable Bring Your Own
License (BYOL).
- Select Create.
Related Topics
Install credentials needed for a secure database connection
Connections to the database you created in the Oracle Autonomous AI Lakehouse must be secure. For the Oracle NoSQL Database Analytics Integrator to connect securely to the Oracle Autonomous AI Lakehouse database, the utility uses the credentials contained in an Oracle Wallet.
- Select Oracle AI Database from the menu on the left side of the display.
- Select Autonomous AI
Database.
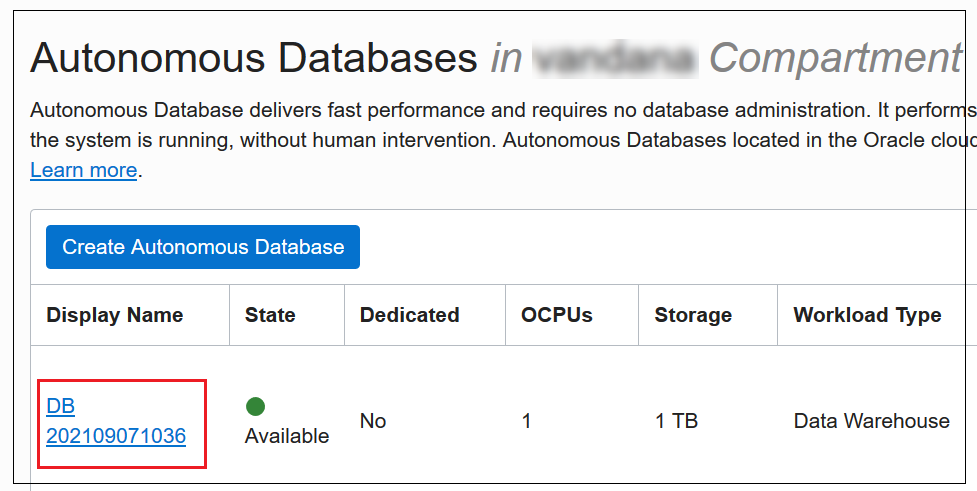
- In Applied Filters, select the Compartment in which the database is located.
- Select the link with the display name you entered when creating the database.
- Select Database Connection.
- Select Download wallet and enter the administrative password set during database creation.
- Save the file (zip) to a safe location.
- The network configuration files (
tnsnames.oraandsqlnet.ora) needed to connect to the database. - The auto-open SSO wallet file,
cwallet.sso. - The PKCS12 file,
ewallet.p12which is protected by the wallet password you provided when you downloaded the zip file via the Oracle Cloud Console. - The Java keystore and trustore files,
keystore.jksandtruststore.jks;protected by the wallet password. - The file
ojdbc.properties, which specifies the wallet-related Java system property required for connecting to the database via JDBC. - A
READMEfile containing wallet expiration information.
After obtaining the wallet zip file, make note of the password and store the wallet in any environment from where you will be connecting to the database. Additionally, to use the Oracle NoSQL Database Analytics Integrator, the extracted contents of the wallet zip file must be installed in the environment where you will be running the utility. For example, if you are running the utility from an Oracle Cloud Compute Instance, you should extract the contents of the zip file in any directory on that instance. Then use the path to that directory as the value of the parameter databaseWallet in the database section of the utility’s configuration file.
Enable the Resource Principal Credential or Store/Enable the User's Object Storage AUTH_TOKEN in the Oracle Autonomous AI Lakehouse Database
After retrieving data from the desired NoSQL Cloud Service table and writing that data to Parquet files in Object Storage, the Oracle NoSQL Database Analytics Integrator uses subprograms from the Oracle PL/SQL DBMS_CLOUD package to retrieve the Parquet files from Object Storage. It then loads the data contained in those files to a table in the database you created in the Oracle Autonomous AI Lakehouse.
- Select Oracle AI Database from the menu on the left side of the display.
- Select Autonomous AI
Database.
- In Applied Filters, select the Compartment in which the database is located.
- Select the link with the display name you entered
when creating the database.
- Under Database actions, select SQL.
-
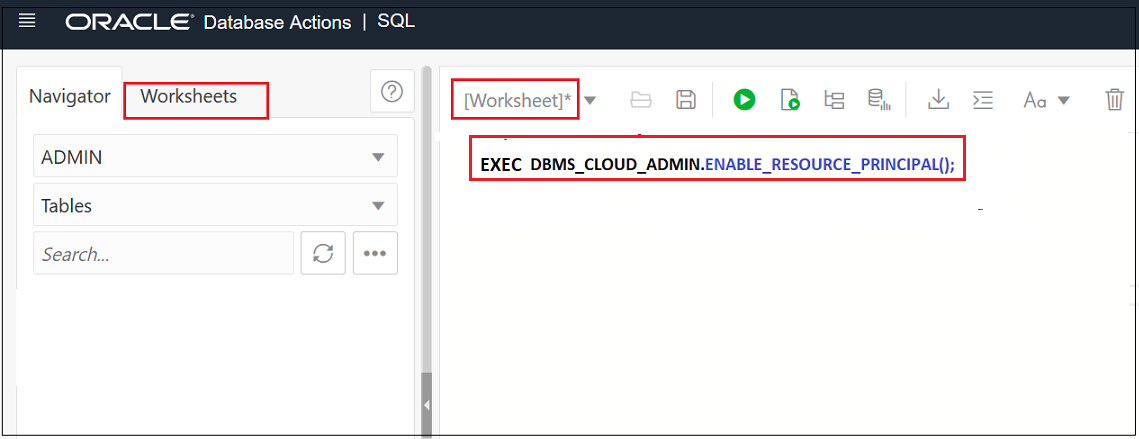
From the window labeled [Worksheet]*, if you wish to authenticate the Oracle Autonomous AI Lakehouse database with Object Storage using the Resource Principal, then execute the following procedure.
EXEC DBMS_CLOUD_ADMIN.ENABLE_RESOURCE_PRINCIPAL();Alternatively, if you wish to perform the authentication using the AUTH_TOKEN that either the system administrator provided to you or you generated yourself, then execute the procedure,
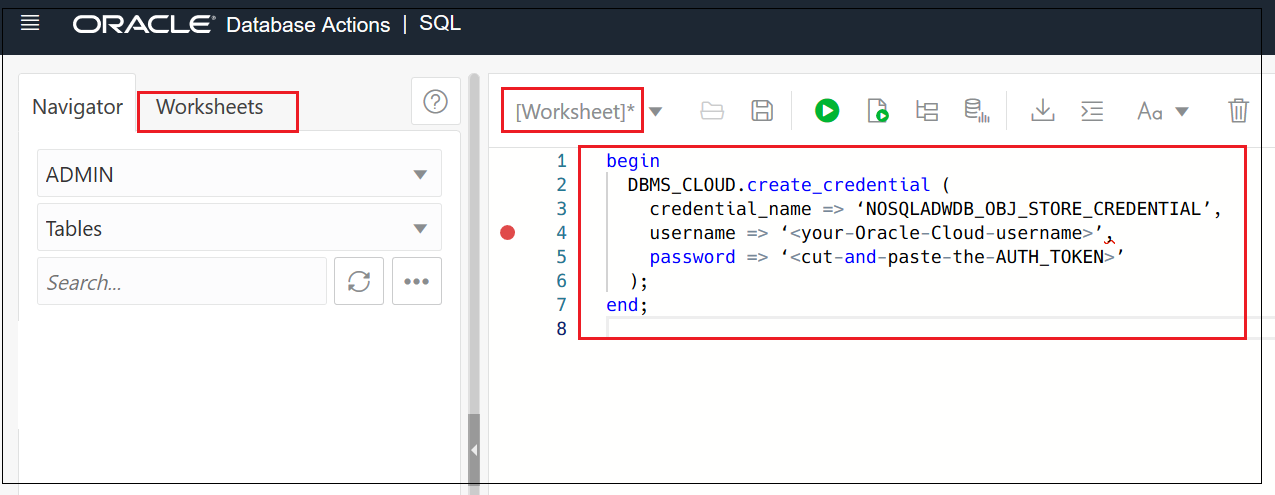
BEGIN DBMS_CLOUD.CREATE_CREDENTIAL ( credential_name => 'NOSQLADWDB_OBJ_STORE_CREDENTIAL', username => '<your-Oracle-Cloud-username>', password => '<cut-and-paste-the-AUTH_TOKEN>' ); END;
DBMS_CLOUD_ADMIN.ENABLE_RESOURCE_PRINCIPAL
procedure enables the OCI Resource Principal (named
OCI$RESOURCE_PRINCIPAL) for use by the Oracle
Autonomous AI Lakehouse database when authenticating with an OCI resource
such as Object Storage. The DBMS_CLOUD.CREATE_CREDENTIAL
procedure encrypts the specified AUTH_TOKEN credential and stores it in a
table in the database named adwc_user. Whichever procedure
you employ, that procedure needs to be executed only once; after which the
same credential name can be specified for all transfers from Object Storage
to the Oracle Autonomous AI Lakehouse database.
Note:
When the Oracle Autonomous AI Lakehouse database uses the OCI Resource Principal to authenticate with Object Storage, the name of the credential isOCI$RESOURCE_PRINCIPAL. Alternatively, when
using the AUTH_TOKEN to authenticate with Object Storage, the name
of the credential is the value you specify for the
credential_name parameter in the
DBMS_CLOUD.CREATE_CREDENTIAL procedure. But
note that the value shown above
(NOSQLADWDB_OBJ_STORE_CREDENTIAL) is only
an example. You can use any name you wish. Thus, the
dbmsCredentialName parameter in the
configuration file should contain either the value
OCI$RESOURCE_PRINCIPAL, or the name you
specify here for the credential_name parameter;
depending on the authentication mechanism you choose to employ for
authenticating the Oracle Autonomous AI Lakehouse database with
Object Storage.