About Security for Oracle SOA Suite on Marketplace Instances
Security in the cloud is a shared responsibility between you and Oracle. In a shared, multitenant compute environment, Oracle is responsible for the security of the underlying cloud infrastructure (such as data center facilities, hardware, and software) and you are responsible for securing your workloads and configuring your services (such as compute, network, storage, and database) securely.
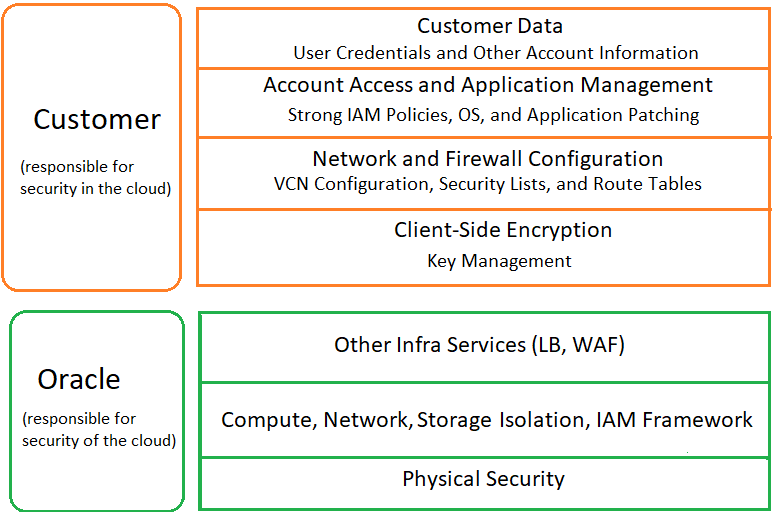
The following principles are fundamental to using any application securely:
- Keep patches up-to-date. This includes all product patches that are applicable. For more information, see About Managing Patches for Instances Provisioned With Earlier Releases and Patches Installed By Release.
- Limit privileges as much as possible. Users should be given only the access necessary to perform their work. User privileges should be reviewed periodically to determine relevance to current work requirements.
- Monitor system activity. Establish who should access which system components, and how often, and monitor those components.
- Learn about and use the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure security features.
- Use secure best practices. For more information, see Security Best Practices in the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure documentation.
- Keep up-to-date on security information. Oracle regularly issues security-related patch updates and security alerts. Install all security patches as soon as possible. See the Critical Patch Updates and Security Alerts website.
- If you’re creating a Linux instance, then try to determine how many users you expect to access the instance and plan for a separate SSH key pair for each user.
- Keep your SSH keys secure. Lay down policies to ensure that the keys aren’t lost or compromised when employees leave the organization or move to other departments. If you lose your private key, then you can’t access your instances. For business continuity, ensure that the SSH keys of at least two IT system administrators are added to your instances.
- If you need to edit the
~/.ssh/authorized_keysfile of a user on your instance, then before you make any changes to the file, start a secondsshsession and ensure that it remains connected while you edit theauthorized_keysfile. This secondsshsession serves as a backup. If theauthorized_keysfile gets corrupted or you inadvertently make changes that result in your getting locked out of the instance, then you can use the backupsshsession to fix or revert the changes. Before closing the backupsshsession, test the changes you made in theauthorized_keysfile by logging in with the new or updated SSH key. - Ensure instance isolation by creating security lists and adding instances to the appropriate security lists. For more information, see Configure Security Lists.
- To monitor network traffic on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, enable VCN flow logs. For more information, see VCN Flow Logs in the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure documentation.
- WebLogic Server includes a set of demonstration private keys, digital certificates, and trusted certificate authorities that are for development only. Oracle highly recommends that you use third-party Certificate Authority (CA) signed certificates in a production environment.