AGGREGATION ONLY Dataset
AGGREGATIONONLY datasets are tables that contain summarized data in a single row.
The following rules are for creating
AGGREGATIONONLY datasets:
- The dataset must always be
VERSIONEDand have only one row. - All column assignments must use aggregate functions.
- No Primary Key declaration is required.
- The dataset is treated as a regular dataset and not as aggregation-only dataset if
GROUPBYis specified.
Follow these rules for using
AGGREGATIONONLY datasets as input in ROWSOURCE:
- Only
CROSS-JOINis allowed withAGGREGATIONONLYtables inROWSOURCE. - If a dataset is created using only an AGGREGATIONONLY dataset in ROWSOURCE, then the derived table must also be marked as
AGGREGATIONONLYdataset. SEToperations aren't supported directly onAGGREGATIONONLYdatasets.REFRESH ON CHANGES INaren't allowed onAGGREGATIONONLYtables.
Example:
IMPORT SOURCE SALES
// Single column assignment
DEFINE AGGREGATIONONLY DATASET DW_SALES_AGG
ROWSOURCE SALES;
THIS[AVG_SALES_AMT] = AVG(SALES[AMOUNT_SOLD]);
END
// Multiple column assignments
DEFINE AGGREGATIONONLY DATASET DW_SALES_AGG1
ROWSOURCE SALES;
THIS[AVG_SALES_AMT] = AVG(SALES[AMOUNT_SOLD]);
THIS[SUM_SALES_AMT] = SUM(SALES[AMOUNT_SOLD]);
THIS[MIN_SALES_AMT] = MIN(SALES[AMOUNT_SOLD]);
THIS[MAX_SALES_AMT] = MAX(SALES[AMOUNT_SOLD]);
END
// Derived from another AGGREGATIONONLY dataset
DEFINE AGGREGATIONONLY DATASET DW_SALES_AGG2
ROWSOURCE DW_SALES_AGG2;
THIS = DW_SALES_AGG2 [AVG_SALES_AMT];;
END
The following output is derived: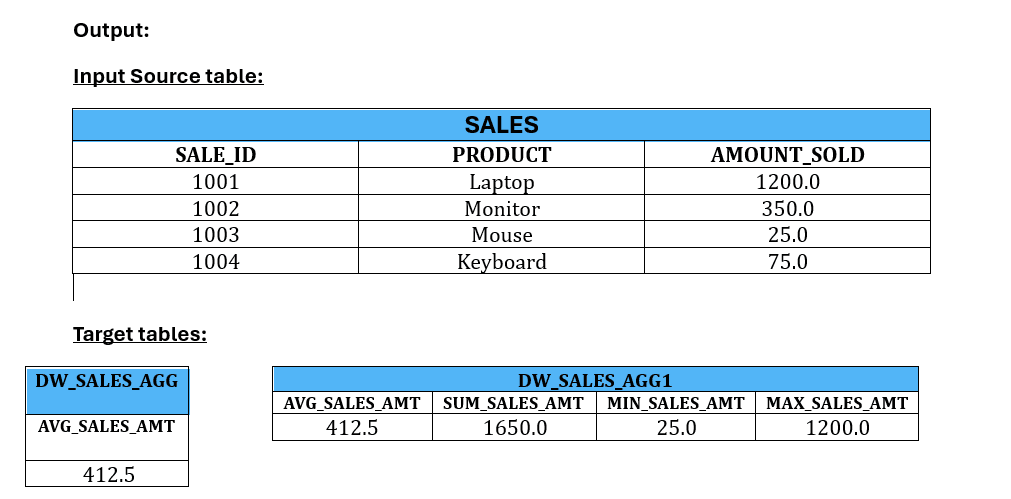
Description of the illustration dasrg-aggregation-only.png
DW_SALES_AGG2 is the same as DW_SALES_AGG1.