Building Blocks of Schema Creation
The foundation of a data scripting program begins with either the source table or the data warehouse tables in a module.
- Source: Existing data structures with predefined schemas.
- Module: Organized grouping of warehouse tables that assist in analyzing one or more related business processes.
Import Source or Warehouse Tables
Run these commands to import the source table and module.
IMPORT SOURCE SALES // Import a source table
IMPORT MODULE [FA_GL, FA_AP] // Import a single or list of modulesSource tables are read-only definitions that serve as foundational building blocks for data transformations. Modules can be imported and their underlying tables can be used directly in the code.
Dataset Definitions
Datasets are the primary constructs in Data Augmentation Scripts. There are two ways to define data sets: Data sets can inherit their schema directly from a source table or a derived table.
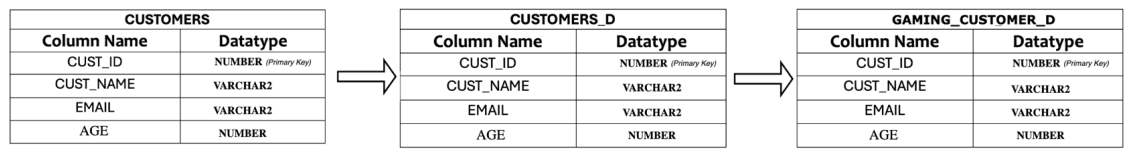
IMPORT SOURCE CUSTOMERS
DEFINE DATASET CUSTOMERS_D
ROWSOURCE CUSTOMERS;
THIS = CUSTOMERS[CUST_ID];
THIS = CUSTOMERS[CUST_NAME];
THIS = CUSTOMERS[EMAIL];
THIS = CUSTOMERS[AGE];
PRIMARYKEY[CUST_ID];
END
DEFINE DATASET GAMING_CUSTOMER_D
ROWSOURCE CUSTOMERS_D WHERE CUSTOMERS_D.AGE BETWEEN 13 AND 35;
THIS = CUSTOMERS_D[CUST_ID];
THIS = CUSTOMERS_D[CUST_NAME];
THIS = CUSTOMERS_D[EMAIL];
THIS = CUSTOMERS_D[AGE];
PRIMARYKEY[CUST_ID];
END
These are the key characteristics of a dataset directly inheriting the schema:
- Automatically inherits and preserves the source table’s schema
- Eliminates the need for any explicit column definitions .
You can also rewrite the code as:
IMPORT SOURCE CUSTOMERS
DEFINE DATASET CUSTOMERS_D FROM CUSTOMERS[CUST_ID,CUST_NAME,EMAIL,AGE] END
DEFINE DATASET GAMING_CUSTOMER_D
ROWSOURCE CUSTOMERS_D WHERE CUSTOMERS_D.AGE BETWEEN 13 AND 35;
THIS = CUSTOMERS_D[CUST_ID,CUST_NAME,EMAIL,AGE];
PRIMARYKEY[CUST_ID];
END
An error is displayed if a column that's not present in the corresponding table is referenced.
GENDER that's not in the CUSTOMERS table.THIS = CUSTOMERS_D[CUST_ID,CUST_NAME,EMAIL,GENDER];An error that GENDER is not present in the table CUSTOMERS is displayed.
You can also define dataset schemas using the Custom Schema Definition feature.
DEFINE SCHEMA DW_PROJECT_D_SCHEMA
[
PROJECT_ID NUMBER(38,0) PRIMARYKEY,
PROJECT_NUMBER VARCHAR2(32),
START_DATE DATE NOT NULL,
COMPLETION_DATE DATE
]
END
DEFINE DATASET DW_PROJECT_D
SCHEMA DW_PROJECT_D_SCHEMA;
ROWSOURCE PROJECTS;
THIS[PROJECT_ID] = PROJECTS[PROJECT_ID, PROJECT_NUMBER];
END
For more information about the data types that Data Augmentation Scripts supports, see Data Types.