Overview of Configuring Digital Assistant
Your project users access Oracle Digital Assistant (ODA) with a specific user role. So you can assign the user roles to them, such as administrator, developer, and business user.
You must train your digital assistant, configure channels, and associate them with your digital assistant. Once you set up your digital assistant, you can test it to check whether it's working correctly on your desktop and mobile devices.
Oracle Digital Assistant Architecture
The ODA platform supports the development of the digital assistants and individual skill chatbots. This diagram illustrates the architecture of ODA.
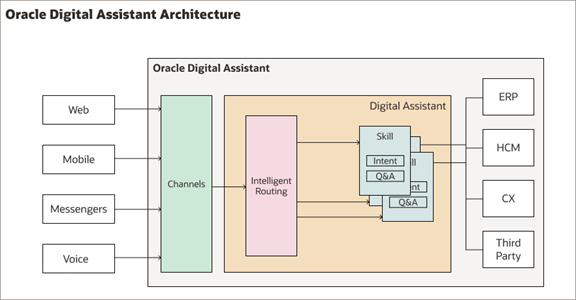
The ODA platform includes the tools to create and configure the various components involved in the architecture of ODA.
- Digital assistants, which are AI-driven interfaces (commonly known as chatbots) that help users accomplish a variety of tasks in natural language conversations. It’s the central chatbots that coordinate the user interaction with one or more skill chatbots, by using intelligent routing.
- Skill chatbots, which are individual chatbots that are focused on specific types of tasks, such as tracking inventory, submitting time cards, and creating expense reports. It uses natural language processing to resolve user intent and extract information from the message sent through conversational channels. You can add skills to the digital assistants or deploy them to a channel on their own.
- Channels, which are the connectors that bind a digital assistant or an individual skill chatbot to messaging services, such as Facebook, WeChat, mobile, or web. A single digital assistant or skill can have several channels configured for it so that it can run on different services simultaneously.
- Skill Store, which offers a range of pre-packaged skills and digital assistants. Chatbot developers and administrators add pre-built skill chatbots to their digital assistants, including SaaS service skill chatbots for ERP, CX, and HCM.