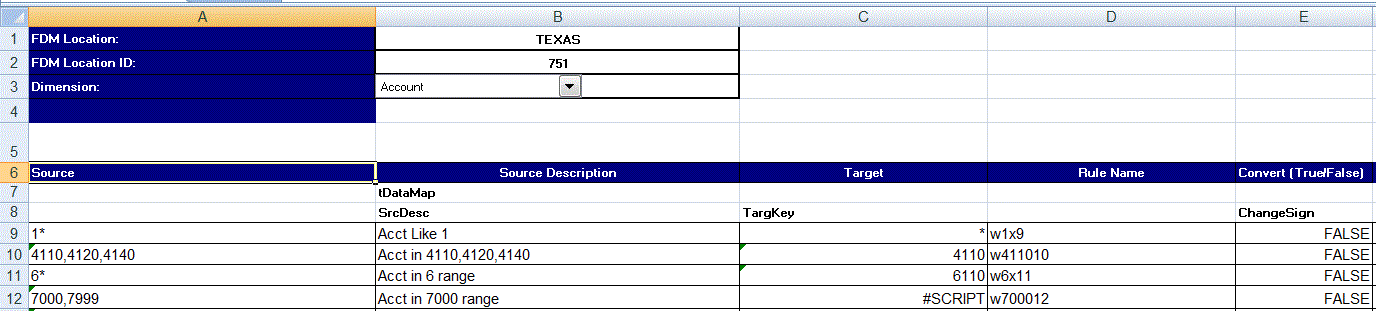
Downloading an Excel Template (Mapping Template)
In Data Load Mapping using the import feature, you can select and import an Excel mapping, and specify whether to merge or replace the mappings. Excel mapping templates with correct formatting are included in the EPM_ORACLE_HOME/products/FinancialDataQuality/templates directory.
The mapping template also includes a macro script that pulls Oracle Hyperion Financial Management dimensions directly from the target application to which you are connecting.
You must upload the Excel template to the Data Management server, and then pick the excel file as the file to load in the data load rule, or when prompted by the system if the file name is left blank. The system determines if the file being processed is an Excel file, and then reads the required formatting to load the file.
When working with a mapping template in Excel:
-
Do not have any blank lines in the map template.
-
You can insert lines in the template, but you must keep new lines in the designated area.
-
Each template supports a single dimension.
To download an Excel template: