Multiperiod Accounting
Multiperiod accounting enables you to create accounting entries across more than one accounting period for a single accounting event. The functionality is primarily used to defer the recognition of revenue or prepaid expense across multiple accounting periods.
You can:
-
Determine how to distribute the amount across accounting periods.
-
Specify a prepaid expense or deferral account.
-
Preview multiperiod journal entries before creating and posting final entries:
-
Submit the Create Multiperiod Accounting process in Draft mode.
-
Review the multiperiod journal entries in the Create Multiperiod Accounting Execution Report.
Note: You can only preview multiperiod journal entries for a single accounting period. -
Multiperiod Accounting Process Flow
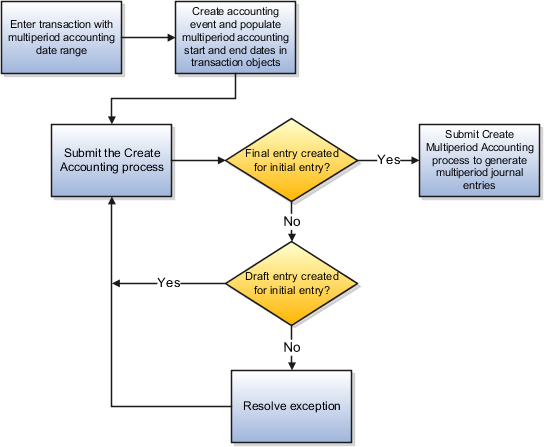
This figure illustrates the multiperiod accounting process flow.
-
Enter transaction with multiperiod accounting date range.
-
Create accounting event. Populate multiperiod accounting Start and End dates in transaction objects.
-
Submit the Create Accounting process.
-
Final entry created for initial entry? Yes
-
Submit Create Accounting process to generate multiperiod journal entries
-
-
Final entry created for initial entry? No
-
Draft entry created for initial entry? Yes
-
Resolve exception.
-
-
Draft entry created for initial entry? No
-
Submit the Create Multiperiod Accounting process to generate multiperiod journal entries.
-
-
-
Implementation Steps
Implementation Step Process Flow
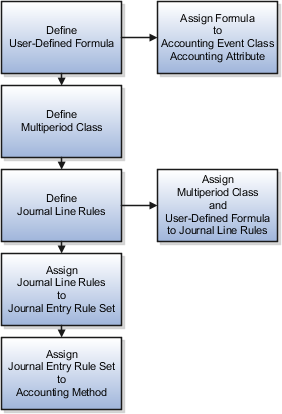
This figure illustrates the implementation steps.
-
Define a user-defined formula determining how to distribute the entered amount across accounting periods. If required, you can use the new multiperiod predefined sources. For example:
-
Multiperiod Original Entered Amount
-
Multiperiod Recognized Entered Amount
-
Last Multiperiod Accounting Date
-
Number of Days in Current Accounting Period
Assign the formula or source to the Entered Amount accounting attribute in the Manage Accounting Attributes task.
-
- Assign a source to each of the following accounting attributes to indicate the
multiperiod date range.
- Multiperiod Start Date
- Multiperiod End Date
-
Define Multiperiod Classes using the Manage Subledger Accounting Lookups task.
-
Lookup Type: ORA_XLA_MULTIPERIOD_CLASS
-
-
Define a non-multiperiod Journal Line Rule for the deferral entry specifying the Multiperiod Class. This rule is used to post the fee amount to the deferral account.
Define a non-multiperiod Journal Line Rule for the accrual entry:- Disable the Multiperiod option and specify a Multiperiod Class.
- Assign a source that has the accrual amount to the Entered Amount accounting attribute.
- Assign relevant sources to the Multiperiod Start Date and Multiperiod End Date accounting attributes.
-
Define a multiperiod Journal Line Rule for the recognition entry:
-
Enable the Multiperiod option and assign the same Multiperiod Class as in the non-multiperiod Journal Line Rule created in step 4 above.
-
Assign the user-defined formula to the Entered Amount accounting attribute.
-
Assign relevant sources to the Multiperiod Start Date and Multiperiod End Date accounting attributes.
-
-
Assign both journal line rules to the same journal entry rule set with:
-
A deferral account rule assigned to the non-multiperiod journal line rule.
-
A revenue or expense account rule assigned to the multiperiod journal line rule.
-
-
Assign the journal entry rule set to the accounting method.
-
Schedule the Create Multiperiod Accounting process to run after the Create Accounting process so that recognition journal entries are properly booked each period. If multiperiod accounting is also implemented in any of the subledger level secondary ledgers, you must schedule the Create Multiperiod Accounting process for the primary ledger as well as each of its subledger level secondary ledgers.