Get the Corresponding Context
Extensible events and operations of UEF are supported on top of contexts like GlobalContext, TabContext, and RecordContext.
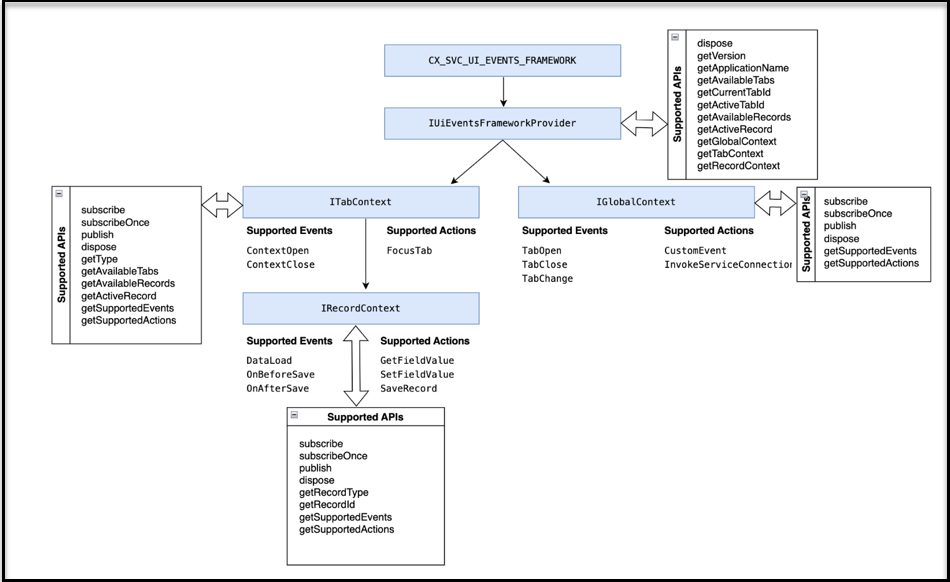
The following diagram details the hierarchy of these contexts that are maintained in UEF and the supported events, actions, and APIs supported in each context.
First, here's how you get the various contexts:
const globalContext: IGlobalContext = await frameworkProvider.getGlobalContext();
const tabContext: ITabContext = await frameworkProvider.getTabContext(browserTabId);
const availableRecords: IRecordContext[] = await frameworkProvider.getAvailableRecords();
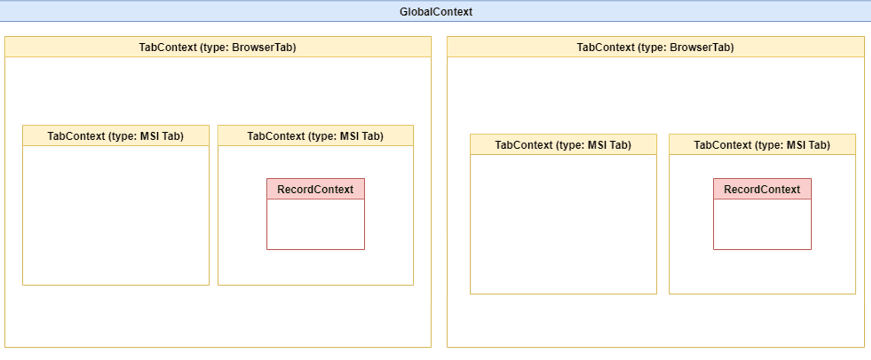
The following graphic illustrates the global context:
And this graphic shows the overall architecture:
<INSERT 2 GRAPHICS--UEF_Global_context AND UEF_diagram
Here's a table explaining the context types:
| Context Type | Support Events | Support Operations | Syntax |
|---|---|---|---|
| GlobalContext | TabOpen, TabClose, TabChange | PopOperation, InvokeServiceConnection | getGlobalContext(): Promise<IGlobalContext>; |
| TabContext | ContextOpen, ContextClose | FocusTab, CloseTab | getTabContext(browserTabId?:
string): Promise<ITabContext>; |
| RecordContext | FieldValueChange, OnBeforeSave(Controllable Event), OnAfterSave, OnDataLoad | GetFieldValue, SaveRecord, SetFieldValue | getAvailableRecords(tabId?: string):
Promise<IRecordContext[]>; |
Note: The OnBeforeSave (in Record Context) event is fired before firing the REST API
that commits the data into the server. End-users can do asynchronous operations in
this callback, or they can cancel this event. This event can wait for an
asynchronous operation to be completed.