How Business Units Work with Reference Data Sets
Reference data sharing enables you to group set-enabled reference data such as jobs or grades to share the data across different parts of the organization.
Sets also enable you to filter reference data at the transaction level so that only data assigned to certain sets is available to be selected. To filter reference data, Oracle Fusion Human Capital Management (HCM), applications use the business unit on the transaction. To set up reference data sharing in Oracle Fusion HCM, you create business units and sets, and then assign the sets to the business units.
Common Set Versus Specific Sets
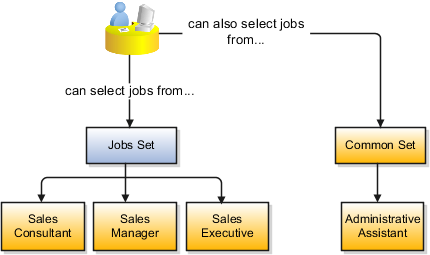
Some reference data in your organization may be considered global, and should therefore be made available for use within the entire enterprise. You can assign this type of data to the Common Set, which is a predefined set. Regardless of the business unit on a transaction, reference data assigned to the Common Set is always available, in addition to the reference data assigned to the set that corresponds to the business unit on the transaction.
Other types of reference data can be specific to certain business units, so you can restrict the use of the data to those business units. In this case, you can create sets specifically for this type of data, and assign the sets to the business units.
Business Unit Set Assignment
When you assign reference data sets to business units, you assign a default reference data set to use for all reference data types for that business unit. You can override the set assignment for one or more data types.
Example: Assigning Sets to Business Units
InFusion Corporation has two divisions: Lighting and Security, and the divisions each have two locations. Each location has one or more business functions.
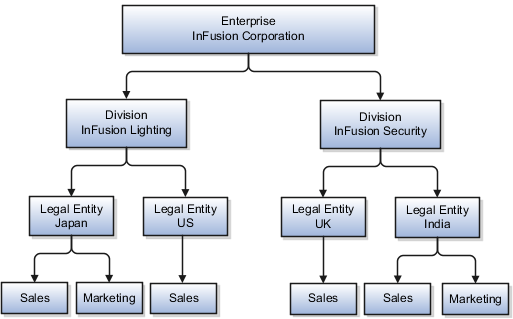
When deciding how to create business units, InFusion decides to create them using the country and business function level. Therefore, they created the following business units:
-
Sales_Japan
-
Marketing_Japan
-
Sales_US
-
Sales_UK
-
Marketing_India
-
Sales_India
Because locations, departments, and grades are specific to each business unit, InFusion does not want to share these types of reference data across business units. They create a reference data set for each business unit so that data of those types can be set up separately. Because the jobs in the Sales business function are the same across many locations, InFusion decides to create one additional set called Jobs. They override the set assignment for the Jobs reference data group and assign it to the Jobs set. Based on these requirements, they create the following sets:
-
Sales_Japan_Set
-
Mktg_Japan_Set
-
Sales_US_Set
-
Sales_UK_Set
-
Mktg_India_Set
-
Sales_India_Set
-
Grades_Set
The following table describes the default set assignment and the set assignment overrides for each business unit in InFusion:
|
Business Unit |
Default Set Assignment |
Set Assignment Overrides |
|---|---|---|
|
Sales_Japan |
Sales_Japan_Set for grades, departments, and locations |
Jobs set for jobs |
|
Marketing_Japan |
Mktg_Japan_Set for grades, departments, and locations |
None |
|
Sales_US |
Sales_US_Set for grades, departments, and locations |
Jobs set for jobs |
|
Sales_UK |
Sales_UK_Set for grades, departments, and locations |
Jobs set for jobs |
|
Marketing_India |
Mktg_India_Set for grades, departments, and locations |
None |
|
Sales_India |
Sales_India_Set for grades, departments, and locations |
Jobs set for jobs |
When setting up grades, departments, and locations for the business units, InFusion assigns the data to the default set for each business unit. When setting up jobs, they assign the Jobs set and assign the Common Set to any jobs that may be used throughout the entire organization.
When using grades, departments, and locations at the transaction level, users can select data from the set that corresponds to the business unit they enter on the transaction, and any data assigned to the Common Set. For example, for transactions for the Marketing_Japan business unit, grades, locations, and departments from the Mktg_Japan_Set is available to select, as well as from the Common Set.
When using jobs at the transaction level, users can select jobs from the Jobs set and from the Common Set when they enter a sales business unit on the transaction. For example, when a manager hires an employee for the Sales_India business unit, the list of jobs is filtered to show jobs from the Jobs and Common sets.