Overview of Loading Payroll Costing
Using HCM Data Loader, you can create payroll costing setup information for the different payroll accounts. For example, cost, offset, suspense, default, payroll liability, cash clearing, and cash accounts.
You can define costing at various levels, such as Payroll, Element Eligibility, Department, Job, Position, Person, and Payment Source.
This figure shows the different levels of the costing hierarchy.
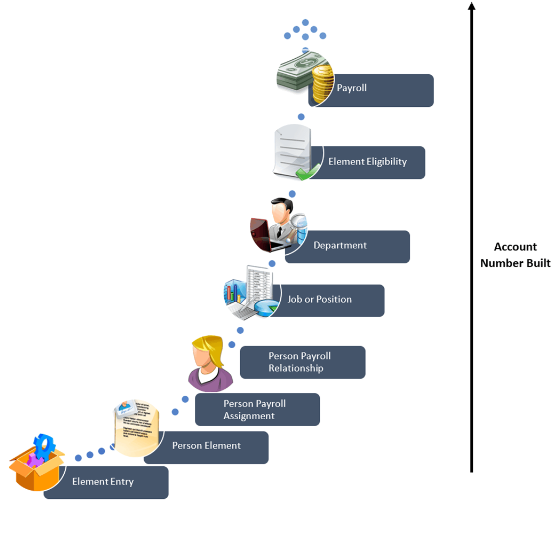
You enter the account information and any overrides for the different levels of the cost hierarchy. The application builds the account number, starting with the lowest level (element entry) of the cost hierarchy and ending with the highest level (payroll). It checks each level sequentially until it finds a value. If it finds an invalid cost combination, it places the costing result in a suspense account.
Before You Begin
To load payroll costing records, do these tasks:
-
Create Cost Allocation key flexfield. This flexfield creates a structure to capture the account codes used to create accounting entries and to track and report labor costs.
-
Enable cost hierarchy with levels to support each cost allocation key flexfield cost account segment.
-
Assign cost Allocation key flexfield to a legislative data group.
Payroll Costing Accounts
Load accounts to cost payroll run and payment results, and to store invalid and accounts that aren't allocated.
Using HCM Data Loader, you can do all of these tasks.
-
Load cost accounts that store expenses and employer liabilities and charges.
-
Create overrides by entering cost account numbers at lower levels of the cost hierarchy.
-
Use priority accounts to cost elements that require the same account combination. For example, you use a priority account for an hourly earning element for laboratory work that's charged to a grant fund.
-
Allocate a cost to more than one account by creating several accounts for an object. Specify the percentage to charge to each account. For example, allocate costs to split salary costs for a job shared between two cost centers.
-
Load Offset accounts that create balancing entries required for double-entry bookkeeping.
-
Set up suspense and default accounts at the payroll level and override them if required, with suspense and default accounts at the department level.