Examples of Positions
Positions are typically used by industries that use detailed approval rules, which perform detailed budgeting and maintain headcounts, or have high turnover rates.
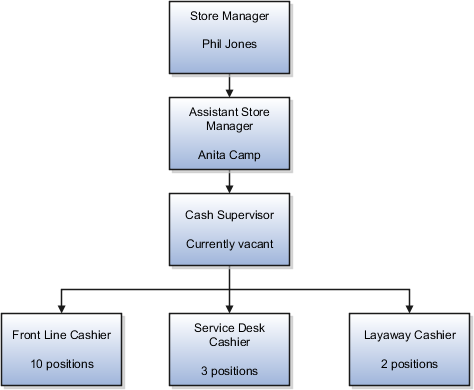
Retail Industry
ABC Corporation has high turnovers. It loses approximately 5% of its cashiers monthly. The job of the cashier includes three positions: front line cashier, service desk cashier, and layaway cashier. Each job is cross-trained to take over another cashier's position. When one cashier leaves from any of the positions, another existing cashier from the front line, service desk or layaway can assist where needed. But to ensure short lines and customer satisfaction, ABC Corporation must replace each cashier lost to turnover. Since turnover is high in retail it's better for this industry to use positions.
Note the following:
-
You have to create a vacancy manually when position synchronization is used and an employee terminates employment (when an incumbent moves out of the position).
-
The position exists even when there are no holders. Having the position continue to exist is important if the person who leaves the company is a manager or supervisor with direct reports.
-
All direct reports continue reporting to the position even if the position is empty.
-
You don't have to reassign these employees to another manager or supervisor. The replacement manager is assigned to the existing position.
Also, an added advantage to using Positions is when you hire somebody new, many of the attributes are inherited from the position. This speeds up the hiring process.
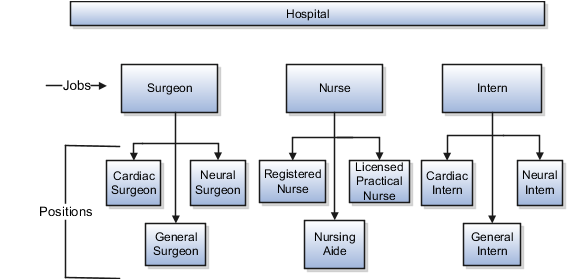
Health Care Industry
Health care is an industry that must regulate employment, roles, and compensation according to strict policies and procedures. Fixed roles tend to endure over time, surviving multiple incumbents. Industries that manage roles rather than individuals, where roles continue to exist after individuals leave, typically model the workforce using positions.
The hospital has a structured headcount and detailed budgeting. For example, a specific number of surgeons, nurses, and interns of various types are needed. These positions must be filled in order for the hospital to run smoothly. Use jobs and positions when you apply detailed headcount rules.