Job and Position Structures
Job and position structures identify the descriptive flexfield structure that enables you to specify additional attributes that you want to capture when you define jobs and positions.
Job and position attributes provide further detail to make jobs and positions more specific. You also use attributes to define the structure of your jobs and positions. You can specify attributes at the enterprise level for jobs and positions, at the business unit level for positions, and at the reference data set level for jobs. Job and position structures are optional.
Enterprise-Level Job Attributes
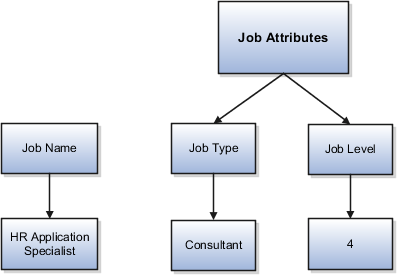
When you define a job, you enter a value for the name of the job. To make job names more specific, set up attributes to identify additional details about the job. This includes the nature of the work that is performed or the relative skill level required. If these attributes apply to all jobs within your enterprise, set up enterprise-level job attributes. Standard capabilities mean that you can use the different segments of the name to:
-
Identify common jobs or job holders for analysis or compensation.
-
Group records in reports, such as to find all jobs of a specific job type.
Don't use attributes with values that change regularly, for example, salary ranges or expense approval levels that change every year.
Enterprise-Level Position Attributes
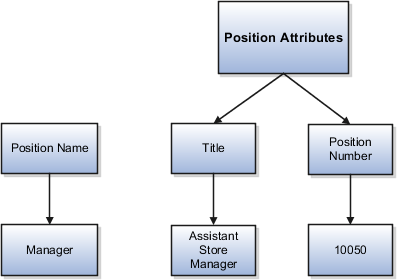
Position attributes at the enterprise level are similar to those for jobs. Each position that you define identifies a specific role in the enterprise, which you can manage independently of the person in the position. A position belongs to one specific department or organization. The name of each position must be unique. To simplify the process of managing unique names for positions, set up enterprise-level attributes to identify separate components of the position name. For example, you can set up an attribute for position title and one for position number. When defining the attributes that make up the structure of a position name, consider whether any of your attributes are part of the definition of a common job type. Using job types for a position can help you manage common information that applies to many different positions.
For example, you can:
-
Define a job type of Manager.Level 1.
-
Use it for comparison of positions across departments or lines of business or for setting common job requirements.
-
Define multiple manager-type positions in your HR department, each of which has responsibility for a different management function or group.
Business Unit-Level Attributes for Positions
If you have information that you want to capture for positions that are specific to each business unit, then you can define attributes at the business unit level for positions. When you create positions, these attributes appear in addition to any enterprise-level attributes. For example, you might want to identify the sales region for all positions in the sales business unit. You can set up a text attribute called Sales Region and use it to enter the necessary information when creating positions for the sales business unit.
Reference Data Set-Level Attributes for Jobs
If you have information for jobs that applies to specific reference data sets, set up attributes for jobs at the reference data set level. When you create jobs, these attributes appear in addition to any enterprise-level attributes. For example, you might want to identify all information technology (IT) jobs within a specific set. You can set up a text attribute called Function and use it to enter IT in jobs that you create that perform an IT function within a specific set.