HCM Data Roles
HCM data roles combine a job role with the data that users with the role must access. You identify the data in security profiles. As data roles are specific to the enterprise, no predefined HCM data roles exist.
To create an HCM data role, you perform the Assign Security Profiles to Role task in the Setup and Maintenance work area. After implementation, you can also perform this task in the Workforce Structures work area. The Assign Security Profiles to Role task opens the Manage Data Roles and Security Profiles page. You must have the IT Security Manager job role to perform this task.
Job Role Selection
When you create an HCM data role, you include a job role. The secured HCM object types that the job role accesses are identified automatically, and sections for the appropriate security profiles appear.
For example, if you select the job role Human Resource Analyst, then sections for managed person, public person, organization, position, LDG, document type, and payroll flow appear. You select or create security profiles for those object types in the HCM data role.
If you select a job role that doesn't access objects secured by security profiles, then you can't create an HCM data role.
Security Profiles
For each object type, you can include only one security profile in an HCM data role.
Components of the HCM Data Role
The following figure summarizes the components of an HCM data role. The job role that you select in the HCM data role is granted many function security privileges and data security policies directly. It also inherits many aggregate privileges, and might inherit some duty roles. Each aggregate privilege or duty role has its own function security privileges and related data security policies. Relevant HCM object types are identified automatically from the data security policies that the job role is granted either directly or indirectly. The specific instances of the objects required by this HCM data role are identified in security profiles and stored in a data instance set. This figure shows these components of the HCM data role.
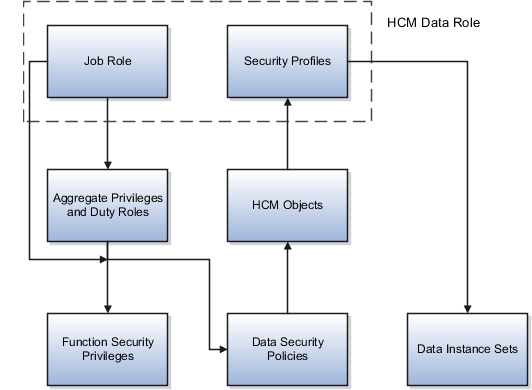
For example, the human resource specialist job role inherits the Manage Work Relationship and Promote Worker aggregate privileges, among many others. The aggregate privileges provide both function security privileges, such as Manage Work Relationship and Promote Worker, and access to objects, such as Assignment. Security profiles identify specific instances of those objects for the HCM data role, such as persons with assignments in a specified legal employer.