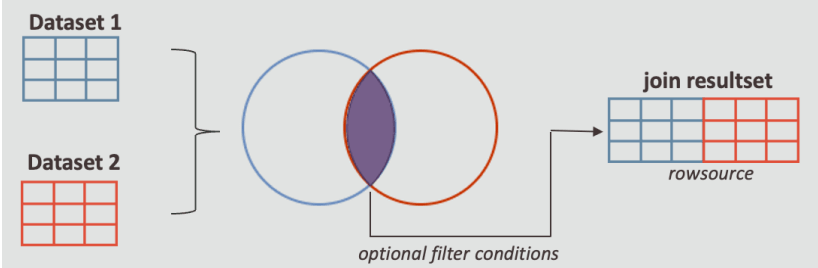
Rowsource
ROWSOURCE defines the initial data before any transformations are performed.
You can consider ROWSOURCE as an input from a single table, multiple table joins or unions, and filter conditions, that you can further refine to produce the final dataset.
ROWSOURCE with a single dataset
In its most basic form,
ROWSOURCE points directly to a single table:
IMPORT SOURCE CUSTOMERS
DEFINE DATASET CUSTOMERS_D
ROWSOURCE CUSTOMERS;
THIS = CUSTOMERS;
END
In this example, the ROWSOURCE stores all the records from the CUSTOMERS table.
You can rewrite this code example in the most compact form as shown:
IMPORT SOURCE CUSTOMERS
DEFINE DATASET CUSTOMERS_D FROM CUSTOMERS END
ROWSOURCE with multiple datasets
ROWSOURCE becomes more powerful when complex operations, such as joins, are performed.
IMPORT SOURCE [CUSTOMERS,COUNTRIES]
DEFINE DATASET CUSTOMERS_D
ROWSOURCE CUSTOMERS;
THIS = CUSTOMERS;
END
DEFINE DATASET GAMING_CUSTOMER_C
ROWSOURCE CUSTOMERS_D INNER JOIN COUNTRIES ON (CUSTOMERS_D.COUNTRY_ID =
COUNTRIES.COUNTRY_ID) WHERE CUSTOMERS_D.CUST_YEAR_OF_BIRTH > 1983;
THIS = CUSTOMERS_D;
THIS = COUNTRIES[COUNTRY_NAME,COUNTRY_REGION,COUNTRY_SUBREGION];
PRIMARYKEY[CUST_ID];
END
In this example, the ROWSOURCE for creating the target dataset GAMING_CUSTOMER_C is created using the COUNTRIES source, CUSTOMERS_D dataset, and CUST_YEAR_OF_BIRTH filter.