Double Moving Average (DMA)
Applies the moving average technique twice, once to the original data and then to the resulting single moving average data. This method then uses both sets of smoothed data to project forward.
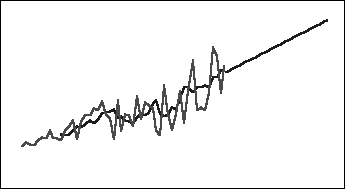
This method is best for historical data with a trend but no seasonality. It results in a straight, sloped-line forecast.
Figure A-2 Typical Double Moving Average Data, Fit, and Forecast Line