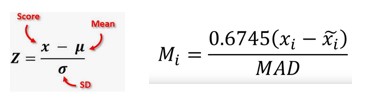Modified Z-Score
The Z-score method relies on the mean and standard deviation of a group of data to measure central tendency and dispersion. This is troublesome, because the mean and standard deviation are highly affected by outliers – they are not robust. In fact, the skewing that outliers bring is one of the biggest reasons for finding and removing outliers from a dataset! Another drawback of the Z-score method is that it behaves strangely in small datasets – in fact, the Z-score method will never detect an outlier if the dataset has fewer than 12 items in it.
This motivated the development of a modified Z-score method, which does not suffer from the same limitation. This method works well for skewed data or data that is not normally distributed & where the number of observations is less. MAD is Median Absolute Deviation. A further benefit of the modified Z-score method is that it uses the median and MAD rather than the mean and standard deviation. The median and MAD are robust measures of central tendency and dispersion, respectively.