 Segment Value Security
Segment Value Security
Secure access to create or view financial data for each business function. Selectively enable enforcement using segment value security rules by business function, including by General Ledger, Payables, Receivables, Assets, Intercompany and Subledger Accounting. Security administrators can grant account values access to users based on certain business functions, data security context, and read-only or read/write access levels.
BUSINESS BENEFITS
1. Provide greater precision in securing account access for each user to each product module, including General Ledger, Payables, Receivables, Assets, Intercompany and Subledger Accounting. Limit security enforcement to the modules where this is required.
This feature addresses a wide range of financial data security requirements by providing a fine-grained chart of accounts-based data security control using highly precise grants of secured account values to users qualified by:
- Business function
- Data security context
- Read-Only vs. Read/Write access level
This ensures that all users only get the exact and appropriate access to the financial data they need to work with.
For example, with the General Ledger business function, you may have some select accountants in your organization who not only manage the financial accounting for their region but are also responsible for calculating the global bad debt reserve. They require full read/write access to all accounts when working with the financial data specific to their assigned region but should have read-only access to specific accounts of the worldwide financial data related to calculating the global bad debt reserve. It would be possible to achieve this type of access control with this feature by enabling security enforcement for the General Ledger business function. Such users would then be assigned rules that granted read-only access to those select bad debt reserve related accounts when working with the global ledgers outside of their region, while being given access to all accounts on a read/write basis when working with their regional ledger.
2. Reduce the time needed to set up and maintain rules. Users with unrestricted access to accounts are automatically granted all account values; users who require restricted access are assigned an explicit security configuration.
Streamlined configuration and administration of this chart of accounts security feature is achieved by selectively enabling security enforcement for distinct business functions. Simplified onboarding via management by exception is achieved through initially providing access to all secured account values by default to all users. Only those users who should work with just certain accounts for their given usage scenarios need to be actively managed and assigned distinct rules to limit their access.
Setup efficiency is optimized with rule assignments that can be flexibly configured with varying degrees of specificity to fit the unique data security requirements of a particular user, or with more generic rule assignments, these can be shared between groups of users with similar access requirements to secured accounts.
Steps to Enable
Segment value security by business function is a new method of chart of accounts security that is available if you are new to segment value security. With this release, an environment that does not have any value set enabled for security will automatically be identified with this new model, and this is set at the enterprise level. Any chart of accounts value set enabled for security in such environments will enforce segment value security by business function as it is described.
For an environment where there is at least one existing value set enabled for security, including one that is assigned to your chart of accounts segment or other application key flexfields, it will continue to behave in the same manner as it had all along in previous releases, enforcing segment value security without the business function distinction. Any future value set enabled for security in such an environment will also apply enforcement in this same manner. If this is your scenario and you wish to switch to segment value security with business function, Oracle can work with you to navigate through that switch.
Only a singular segment value security enforcement method is applicable at the enterprise level, and for a given environment, security will be enforced using that singular method for any secured chart of accounts segment's value set.
This is a summary of the key steps to configure segment value security enforcement by business function.
1. Select business functions that enforce segment value security.
2. Enable security for a value set.
3. Deploy the accounting flexfield and publish account hierarchies to the General Ledger balances cube.
4. Create rules and rule assignments in the Manage Segment Value Security Rules spreadsheet.
These are the details for each of the steps.
1. Select business functions that enforce segment value security.
The business functions that you select affect all secured value sets in all charts of accounts that the value sets are used in.
- In the Setup and Maintenance work area, go to the Manage Chart of Accounts Configurations page and click Manage Segment Value Security by Business Function.
NOTE: If the button doesn’t appear, your environment wasn’t identified for segment value security by business function.
- Select the business functions where segment value security must be enforced.
You can select from among the following business functions:
- General Ledger
- Payables
- Receivables
- Intercompany
- Assets
Selecting one or more of these business functions automatically enables security enforcement for Oracle Subledger Accounting because it’s an integration module between Oracle General Ledger and the other subledger business functions listed.
2. Enable security for a value set.
Enable security for a value set where segment value security enforcement is required.
- Search for the name of the chart of accounts that you want to secure in the Manage Chart of Accounts Configurations page. In the Segments section, select the segment row with the value set that you want to secure.
- On the Value Set tab in the Value Set section, select Enable security.
The application will automatically create the data security resource object for the secured value set. In addition, the application generates an All Values policy for this security object to the Authenticated User (ORA_FND_AUTHENTICATED_USER_ABSTRACT) role, which is automatically assigned to all users who successfully sign in to the application. This policy is the key mechanism enabling the segment value security by business function behavior where all users are first provided access to all account values of a secured value set by default. This default policy will be suppressed in usage scenarios where a user has a matching distinct policy assignment that restricts access to certain account values.
3. Deploy the accounting flexfield and publish account hierarchies to the General Ledger balances cube.
You must successfully deploy the accounting flexfield for enabling security for the value set to take effect. Click Deploy All Charts of Accounts in the Manage Chart of Accounts Configurations page and confirm its successful completion.
To update the General Ledger balances cube data security filters so that the current security enforcement settings are applied, you must publish the account hierarchies for the secured value sets. In the Setup and Maintenance work area, use the Publish Account Hierarchies page.
4. Create rules and rule assignments in the Manage Segment Value Security Rules spreadsheet.
After you’ve saved your changes to enable security for a value set, you can open the Manage Segment Value Security Rules spreadsheet to set up your security rules by clicking Manage Data Security. The spreadsheet will open within the context of the secured value set.
If there are users who should have access to only limited accounts of a secured value set at all times, or for their certain usage scenarios, then you must configure rules and user rule assignments for that secured value set.
This is necessary to suppress the All Values access that was granted by default to every user, which is a key feature of segment value security rules by business function.
- Create the rules
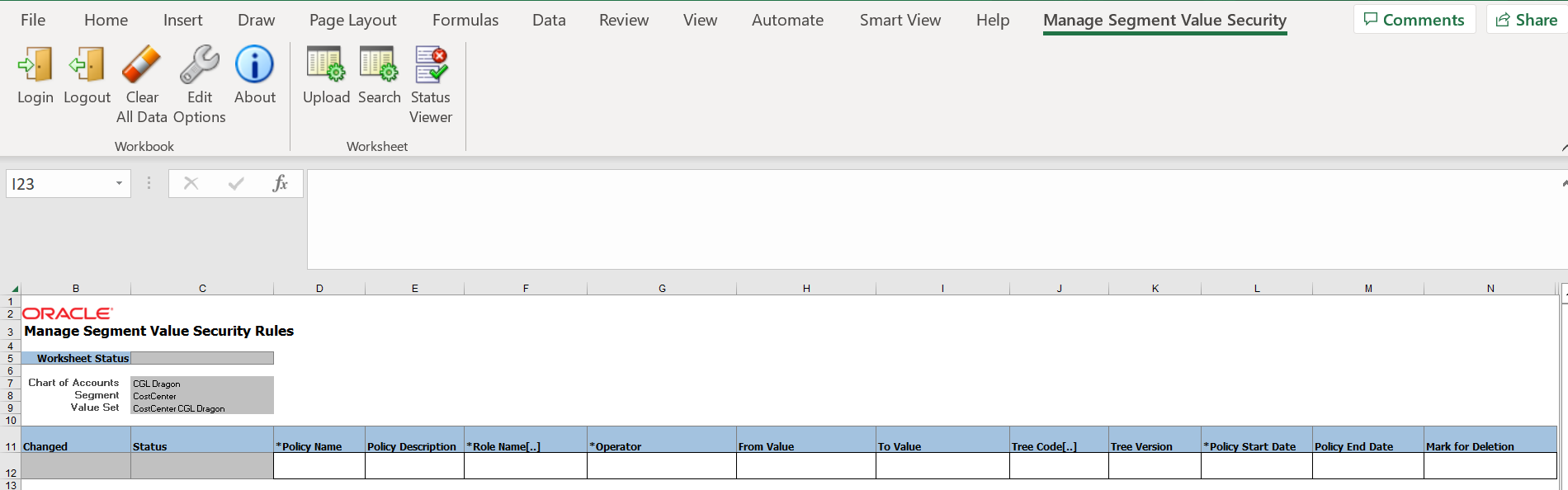
Manage Segment Value Security Spreadsheet Rules Sheet
The Rules worksheet of the Manage Segment Value Security Rules spreadsheet lets you define segment value security policies.
Policies can include one or more segment value security condition filters and are associated with a segment value security role. The segment value security role serves as the conduit to pass the security policy to users.
Here’s more information about key attributes on the Rules worksheet.
Policy Name
Identifies the specific condition to segment value security role association.
Segment Value Security Role Name
Identifies the predefined role to which you’re assigning the segment value security policy.
Operator
Indicates how to evaluate the succeeding values specified in the row for the purpose of determining what account values of the secured value set are being granted. This is a key attribute of a segment value security condition filter.
Available operators include the following: All Values, Equal to, Not equal to, Between, Contains, Ends with, Starts with, Is descendant of, Is last descendant of.
Tree Code and Tree Version
Identifies the tree and tree version to reference when you select a parent account value for the condition. This is a required attribute if you’re using the Is descendant of and Is last descendant of operators.
Mark for Deletion
Indicates whether to delete the selected condition filter row and remove it from the policy. This deletion indicator safeguards users from accidentally deleting condition filter rows for a policy from the application by requiring users to explicitly indicate this action for a given row.
- Create rule assignments
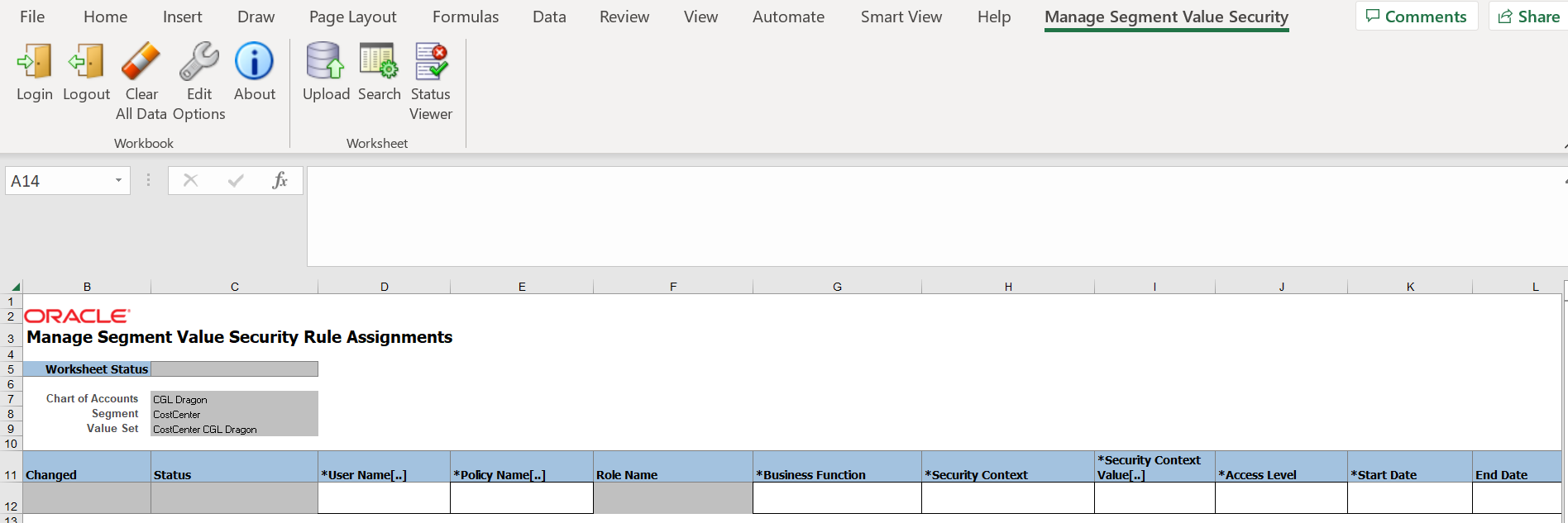
Manage Segment Value Security Spreadsheet Rule Assignments Sheet
The Rule Assignments worksheet of the Manage Segment Value Security Rules spreadsheet is for assigning policies to users, qualifying under which business function and security context the policy assignments are applicable for the user, and granting either a read only, or a read and write access level.
Here’s more information about key attributes on the Rule Assignments worksheet.
User Name
Identifies the user for the rule assignment. Select one of the following options:
- Select specific: Select to specify the sign in name of the user who is to be assigned the rule or policy for the given secured value set.
- Select all assigned to the policy role: Select to share the rule assignment with all users who are assigned the role for the specified policy.
Policy Name
Identifies the policy to assign to the user.
Role Name
Display only field that Identifies the role associated with the policy selected for the rule assignment.
Business Function
Identifies the business function that the rule assignment for the user applies to. The list corresponds to the product modules that support segment value security by business function. Choices include the following. Selecting any of these business functions automatically includes Oracle Subledger Accounting, a product module that integrates between General Ledger and the subledgers.
- Assets
- General Ledger
- Payables
- Provider intercompany
- Receivables
- Receiver intercompany
NOTE: The 2 Intercompany business functions allow you to further differentiate whether the rule assignment to the user for the specified intercompany organization is applicable when the intercompany organization is being used by the user to transact in the capacity of a provider or a receiver.
You can also select All business functions if the grant of the policy to the user isn’t limited for just a particular business function. It can also be used in the case of the Intercompany module when the rule assignment to an Intercompany user applies no matter when the specified intercompany organization is transacting in the capacity of a provider or receiver.
The selection for this attribute also determines which choice is valid for the following Security Context attribute because the security context corresponds to the selected business function.
Security Context
Identifies the type of security context under which the policy or rule assignment should be valid for the user. You must select a security context that correlates to the selected business function. For example, for the General Ledger business function, the applicable security context is data access set.
Here are the possible choices.
- Business unit: Applies to the Payables and Receivables business functions.
- Asset books: Applies to the Assets business function.
- Data access set: Applies to the General Ledger business function.
- Intercompany organization: Applies to the Intercompany business functions.
- All security contexts: Applies to any business function.
The selection for this attribute also determines which choice is applicable for the following Security Context Value attribute because the context value corresponds to the selected security context.
Security Context Value
Specifies the security context value for the selected security context type and business functions under which the policy or rule assignment will be effective for the user. The possible choices include the valid asset books, business units, data access sets, or intercompany organizations in the system, depending on the security context that was selected for the rule assignment. There is also a choice of All security context values if you do not wish to indicate a specific value. This is also the only valid choice if All security contexts were selected for the preceding Security Context column. This would make this policy always applicable to the user, no matter what data access context that user is working with.
Access Level
Indicates whether the user rule or policy assignment for the given business function, security context, and context value should be granted on a read only or read and write basis.
For rule assignments that are set to Read only, the account values allowed will only be applicable in read-only features, such as an inquiry page or a report. Where the product feature involves update capabilities for accounting data, these account values with read-only access will not be available to the user.
For rule assignments that are set to Read and write, the account values allowed will be applicable in read-only features as well as those features that involve update capabilities for accounting data.
Tips And Considerations
http://docs.oracle.com/pls/topic/lookup?ctx=fa-latest&id=u30251546The following are some key considerations when implementing segment value security by business functions:
Identification of Environment Qualified for Segment Value Security by Business Function
- The evaluation and designation for a Cloud Applications environment of the enforcement method of segment value security by business function or without business function is applied distinctly on each pod, based on their distinct pod name + pod type. Two pods with the same letter name but of different types (e.g., Pod WXYZ Prod vs. Pod WXYZ Test) are considered individually, and the segment value security enforcement method will be set for each pod based on the presence or absence of value sets enabled for security, independent of the other like-named pod. If you have a case where your related pods are each set to different methods of segment value security enforcement based on this evaluation methodology, and you wish to make a change, please contact Oracle for assistance.
Enabling Segment Value Security by Business Function for Product Modules and Chart of Accounts
-
Enforcement of chart of accounts segment value security by business function can only be applied for General Ledger, Payables, Receivables, Assets, Intercompany and Subledger Accounting. For all other product modules, there is no enforcement when security is enabled for the chart of accounts segment value set, and users working with these other modules will have access to all accounts.
- You must use the Manage Chart of Accounts Configurations page to enable security for a value set. Don’t use the Manage Value Set, Edit Value Set, or Edit Value Set Data Security pages because the initialization for the value set required for segment value security by business function won’t be successful and the security configuration for the value set won’t be correct.
- You don’t have to make all your business function selections for security enforcement at once. You can select additional business functions later. You can also deselect business functions after they have previously been selected.
-
Value set security applies at the value set level, not to the individual segment of a chart of accounts that references that value set. If a value set is used in multiple charts of accounts, then all chart of accounts segments that are assigned that value set will be enabled for security. Also, access to secured segment values is evaluated individually for each secured segment or value set according to its defined security rules, and independent of another segment that is enabled for security.
-
For a secured Accounting Flexfield (GL#) value set that's shared with other key flexfields, such as the Budgeting Flexfield (XCC), the Cost Allocation Flexfield (COST), the Asset Key Flexfield (KEY#), the Location Flexfield (LOC#), and others, security will not be enforced for that secured value set with these other types of key flexfields.
-
If value sets in other types of key flexfields that are not shared with the Accounting Flexfield (GL#) are enabled for security, such value sets in the non-GL# key flexfields will still enforce segment value security in the mode without the business function distinction. As such, there can be differences in segment value security enforcement across the segments of such key flexfields.
-
It's possible to deselect the Enable Security checkbox and stop enforcement of segment value security for a value set. If you deselect the checkbox, just like when you originally selected to enable security, you must successfully redeploy the GL# Accounting Key Flexfield to process such a metadata change to the chart of accounts for this to take effect.
-
Don’t delete or end date the All Values policy created automatically by the system for your secured value set. This policy is integral to the overall functioning of the segment value security by business function solution.
Configuring Rules and Rule Assignments
- Use the Segment Value Security Rules Spreadsheet exclusively to set up rules and rule assignments to properly capture all the required configuration attributes for segment value security by business function. Commingling the usage of the Manage Segment Value Security Rules spreadsheet with the Edit Data Security page or the Rapid Implementation spreadsheet to maintain your segment value security setups will result in serious data inconsistencies that will cause the incorrect enforcement of segment value security.
- A rule or policy can have a one-to-many relationship with condition filters. You can do this in the spreadsheet by using the same policy name across multiple rows. The different condition filters defined in these multiple rows will be treated as a group that's associated with that one policy. This helps you adhere to the best practice of keeping in check the number of security policies defined for a secured value set and keeping setups manageable.
-
Related condition rows for the same rule or policy created using the spreadsheet will always be set to the Match Any option or to using the Or conjunction when stringing together the various condition filter rows to determine what account values are involved. This means that the account values being granted by the policy just need to match one of the condition rows stipulated in the group, rather than simultaneously match every one of the condition rows in that group, which would more than likely result in a non-match, or no account value, since an account value is unlikely to satisfy every one of those conditions.
-
For audit purposes, segment value security policies are never deleted. The Policy End Date attribute is used instead to indicate that the policy is no longer applicable.
- Improve rule efficiency by using tree operators where possible. Using tree operators in rules would also reduce change management complexities because changes to detailed values are encapsulated in the rule definitions.
-
With segment value security rules based on conditions with hierarchical operators, ensure that the referenced tree and its versions are successfully flattened for such a security rule to work correctly.
-
While a distinct tree code is associated with each segment in a chart of accounts, as specified by the Default Hierarchy value in the chart of accounts structure setup, you can refer to any tree that’s defined for the secured value set when using hierarchical operators with rule filters.
- Use smart numbering of segment values to allow the use of operators such as Between, Starts with, Ends with and Contains. By using these operators rather than enumerated values, self-maintaining segment value security conditions can potentially be defined to automatically include new accounts within the condition that are subsequently created.
- Separate discretionary access from non-discretionary access. Use role-specific policy assignments for non-discretionary access and user-specific policy assignments only for discretionary access. This would reduce the number of assignments required, thus reducing change management complexities.
-
Use the Not equal operator carefully and sparingly. Don't use it in multiple condition rows for the same policy or in different policies for the same secured value set. The different conditions could end up canceling each other out, resulting in unintended access being granted to account values you want to secure.
-
To form a complete user rule assignment, you must assign the segment value security role of the policy to the users you want to assign the policy.
-
For the policy or rule assignment to be a relevant and effective one for the users to which they are assigned, ensure that the selected asset book, business unit, data access set, or intercompany organization for that rule assignment is one that is assigned to the user in the Manage Data Access for Users page and to which the user has been granted data access.
Using Export and Import Services with Segment Value Security by Business Functions Configurations
- You need to ensure that the source and target environments involved with such an export/import process are compatible for segment value security. They must be based on the same segment value security method of either segment value security by business function or segment value security without the business function distinction. Mixing and matching of source and target environments identified with different segment value security methods for such export and import processes will cause data corruptions with the setup configurations in the target environment.
- You need to ensure when using export and import services for segment value security rules and rules assignments from a source to a target environment that the method by which such setup records are created are the same in both environments. Commingling the usage of the Manage Segment Value Security Rules spreadsheet with the Edit Data Security page or the Rapid Implementation spreadsheet to maintain your segment value security setups will result in serious data inconsistencies that will cause the incorrect enforcement of segment value security.
Key Resources
- Overview of Segment Value Security
- This feature originated from the Idea Labs on Cloud Customer Connect: Idea 938513
Access Requirements
You will need to have a role that is based on either the Application Implementation Consultant (ORA_ASM_APPLICATION_IMPLEMENTATION_CONSULTANT_JOB) or the Financial Application Administrator (ORA_FUN_FINANCIAL_APPLICATION_ADMINISTRATOR_JOB), and the IT Security Administrator (ORA_FND_IT_SECURITY_MANAGER_JOB) job roles to have access to the full range of functions required to set up all the elements involved with configuring segment value security by business function for users in the system.
The new Manage Advanced Chart of Accounts Segment Value Security/ FUN_MANAGE_ADVANCED_CHART_OF_ACCOUNTS_SEGMENT_VALUE_SECURITY_PRIV privilege controls access to the Manage Segment Value Security Rules and Rule Assignments spreadsheet. You will also need a custom role that is assigned this privilege to access the spreadsheet.