Example of Consigned Inventory Accounting in a Simple Purchase Order
When an organization receives a shipment of goods under a consignment purchase order, the ownership of the goods remains with the supplier even after they are in the custody of the buyer. Ownership passes from the supplier to the buyer when the inventory is consumed.
When the inventory is consumed, two events occur: First there is a transfer of ownership to the buyer and the consigned goods become owned inventory for a brief period of time, then the owned inventory is depleted.
The following example illustrates:
-
The physical and financial flow of consigned inventory under a consigned purchase order (PO).
-
The transaction that flows from Oracle Inventory Management into Oracle Cost Accounting and Oracle Receipt Accounting.
-
Accounting entries that Cost Accounting and Receipt Accounting generate for the forward flow.
-
Accounting entries that Cost Accounting and Receipt Accounting generate for the return flow.
Scenario
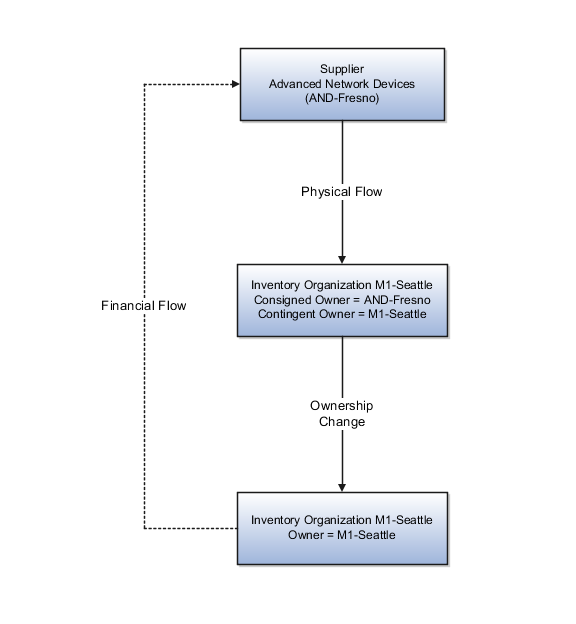
Supplier Advanced Network Devices (AND-Fresno) ships the goods under a consigned purchase order to inventory organization M1-Seattle.
The following diagram illustrates the flow of consigned inventory:
Transaction from Inventory Management
Cost Accounting and Receipt Accounting receive the following transaction from Inventory Management:
-
Supplier Advanced Network Devices (AND-Fresno).
-
Consignment Purchase Order #1000.
-
Purchase Order price USD 100.
-
Ship-to organization is M1-Seattle which is the contingent owner. Contingent owner assumes ownership from the supplier when inventory is consumed.
-
Receipt and put away transactions performed in M1-Seattle inventory organization in consigned status.
-
When the goods are consumed ownership changes from supplier AND-Fresno to inventory organization M1-Seattle.
Analysis
Receipt Accounting and Cost Accounting create accounting distributions for the forward and return shipment of goods.
Accounting Entries
The following diagram illustrates the accounting entries for the forward flow from supplier AND-Fresno to inventory organization M1-Seattle.
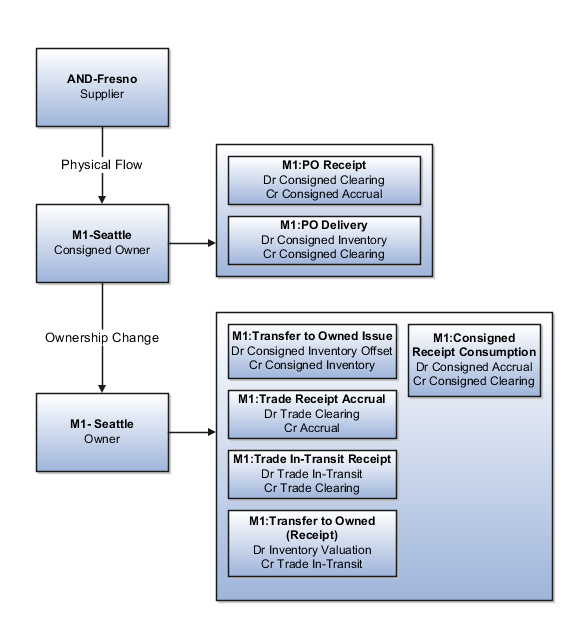
Receipt Accounting and Cost Accounting generate accounting entries under inventory organization M1-Seattle for the receipt of goods.
The following table describes those accounting entries:
|
Subledger |
Event Type |
Accounting Line Type |
Transaction Type |
Amount in Functional Currency |
Functional Currency |
Basis of Amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Receipt Accounting |
PO Receipt |
Consigned Clearing |
Debit |
100 |
USD |
PO Price |
|
Receipt Accounting |
PO Receipt |
Consigned Accrual |
Credit |
100 |
USD |
PO Price |
|
Cost Accounting |
PO Delivery |
Consigned Inventory |
Debit |
100 |
USD |
PO Price |
|
Cost Accounting |
PO Delivery |
Consigned Clearing |
Credit |
100 |
USD |
PO Price |
Receipt Accounting and Cost Accounting generate accounting entries under inventory organization M1-Seattle for the change of ownership from supplier AND-Fresno to M1-Seattle.
The following table describes those accounting entries:
|
Subledger |
Event Type |
Accounting Line Type |
Transaction Type |
Amount in Functional Currency |
Functional Currency |
Cost Element |
Basis of Amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Cost Accounting |
Transfer to Owned Issue |
Consigned Inventory Offset |
Debit |
100 |
USD |
Material |
PO Price |
|
Cost Accounting |
Transfer to Owned Issue |
Consigned Inventory |
Credit |
100 |
USD |
Material |
PO Price |
|
Receipt Accounting |
Consigned Receipt Consumption |
Consigned Accrual |
Debit |
100 |
USD |
Not applicable |
PO Price |
|
Receipt Accounting |
Consigned Receipt Consumption |
Consigned Clearing |
Credit |
100 |
USD |
Not applicable |
PO Price |
|
Receipt Accounting |
Trade Receipt Accrual |
Trade Clearing |
Debit |
100 |
USD |
Not applicable |
PO Price |
|
Receipt Accounting |
Trade Receipt Accrual |
Accrual |
Credit |
100 |
USD |
Not applicable |
PO Price |
|
Cost Accounting |
Trade In-Transit Receipt |
Trade In-Transit |
Debit |
100 |
USD |
Material |
PO Price |
|
Cost Accounting |
Trade In-Transit Receipt |
Trade Clearing |
Credit |
100 |
USD |
Material |
PO Price |
|
Cost Accounting |
Transfer to Owned (Receipt) |
Inventory Valuation |
Debit |
100 |
USD |
Material |
PO Price |
|
Cost Accounting |
Transfer to Owned (Receipt) |
Trade In-Transit |
Credit |
100 |
USD |
Material |
PO Price |
Organization M1-Seattle returns goods to supplier AND-Fresno.
This figure illustrates the accounting entries for the return flow from M1-Seattle to AND-Fresno.
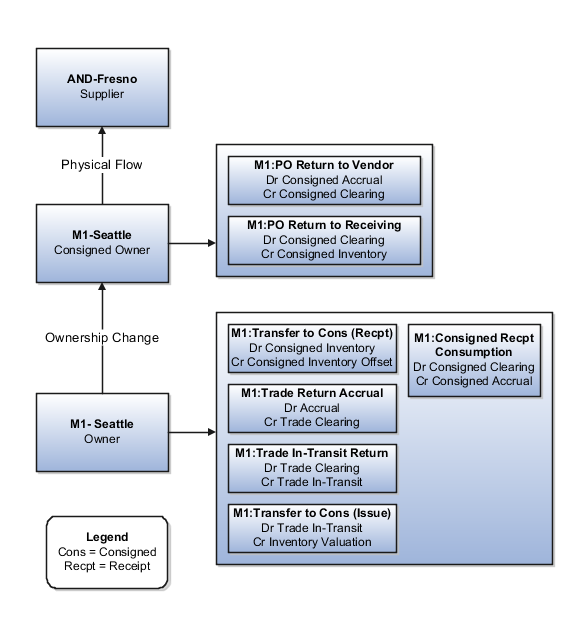
Receipt Accounting and Cost Accounting generate accounting entries under inventory organization M1-Seattle for the change of ownership from M1-Seattle to supplier AND-Fresno.
The following table describes the accounting entries for the change in ownership.
|
Subledger |
Event Type |
Accounting Line Type |
Transaction Type |
Amount in Functional Currency |
Functional Currency |
Cost Element |
Basis of Amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Cost Accounting |
Transfer to Consigned (Receipt) |
Consigned Inventory |
Debit |
100 |
USD |
Material |
PO Price |
|
Cost Accounting |
Transfer to Consigned (Receipt) |
Consigned Inventory Offset |
Credit |
100 |
USD |
Material |
PO Price |
|
Receipt Accounting |
Consigned Receipt Consumption |
Consigned Clearing |
Debit |
100 |
USD |
Not applicable |
PO Price |
|
Receipt Accounting |
Consigned Receipt Consumption |
Consigned Accrual |
Credit |
100 |
USD |
Not applicable |
PO Price |
|
Receipt Accounting |
Trade Return Accrual |
Accrual |
Debit |
100 |
USD |
Not applicable |
PO Price |
|
Receipt Accounting |
Trade Return Accrual |
Trade Clearing |
Credit |
100 |
USD |
Not applicable |
PO Price |
|
Receipt Accounting |
Trade In-Transit Return |
Trade Clearing |
Debit |
100 |
USD |
Not applicable |
PO Price |
|
Receipt Accounting |
Trade In-Transit Return |
Trade In-Transit |
Credit |
100 |
USD |
Not applicable |
PO Price |
|
Cost Accounting |
Transfer to Consigned Issue |
Trade In-Transit |
Debit |
100 |
USD |
Material |
PO Price |
|
Cost Accounting |
Transfer to Consigned Issue |
Cost Variance* |
Debit |
5 |
USD |
Not applicable |
Inventory is received at the current cost, and the difference between transfer price and cost is booked as cost variance. |
|
Cost Accounting |
Transfer to Consigned Issue |
Inventory Valuation |
Credit |
105 |
USD |
Material |
Current Cost |
* Inventory is received at the current cost, and the difference between transfer price and cost is booked as cost variance.
Receipt Accounting generates accounting entries under inventory organization M1-Seattle for the return of consigned goods from M1-Seattle to AND-Fresno.
The following table describes those accounting entries:
|
Subledger |
Event Type |
Accounting Line Type |
Amount in Functional Currency +Dr/-Cr |
Functional Currency |
Basis of Amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Receipt Accounting |
PO Return to Supplier |
Consigned Accrual |
100 |
USD |
PO Price |
|
Receipt Accounting |
PO Return to Supplier |
Consigned Clearing |
-100 |
USD |
PO Price |
|
Receipt Accounting |
PO Return to Receiving |
Consigned Clearing |
100 |
USD |
PO Price |
|
Receipt Accounting |
PO Return to Receiving |
Consigned Inventory |
-100 |
USD |
PO Price |