Roles-Based Applications Security
In Oracle Applications Cloud, users have roles through which they gain access to functions and data. Users can have any number of roles. Roles are grouped hierarchically to reflect lines of authority and responsibility. User access to functions and data is determined by roles
Role-based security in Oracle Applications Cloud controls who can do what on which data. In role-based access:
|
Component |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Who |
Role assigned to a user |
|
What |
Function that users with the role can perform |
|
Which Data |
Set of data that users with the role can access when performing the function |
The following topics introduce different types of roles and how they work together through role inheritance to secure Oracle Applications Cloud.
-
Abstract roles
-
Job roles
-
Duty roles
-
Role inheritance
Abstract Roles
Abstract roles represent a worker's role in the enterprise independently of the job that you hire the worker to do. You can create your own abstract roles. All workers are likely to have at least one abstract role that allows them to access standard functions, such as managing their own information and searching the worker directory. You assign abstract roles directly to users. Employee is an example of an abstract role.
Job Roles
Job roles represent the job that you hire a worker to perform. You can create your own job roles. However, the IT Security Manager and Application Implementation Consultant predefined job roles are exceptions to this general rule because they're not considered Oracle Applications Cloud job roles. Warehouse Manager is an example of a job role.
Duty Roles
Duty roles represent the individual duties that users perform as part of their job. They grant access to work areas, dashboards, task flows, application pages, reports, batch programs, and so on. Job roles and abstract roles inherit duty roles. Duty roles can also inherit other duty roles. They're part of the security reference implementation, and are the building blocks of custom job and abstract roles. You can also create custom duty roles. You don't assign duty roles directly to users.
An example of a duty role is the Inventory Transaction Management Duty. Job and abstract roles inherit duty roles that determine the access to functions appropriate to the job. For example, the job role Warehouse Manager inherits the Inventory Transaction Management Duty.
Role Inheritance
Each role is a hierarchy of other roles:
-
Job and abstract roles inherit duty roles.
-
Duty roles can inherit other duty roles.
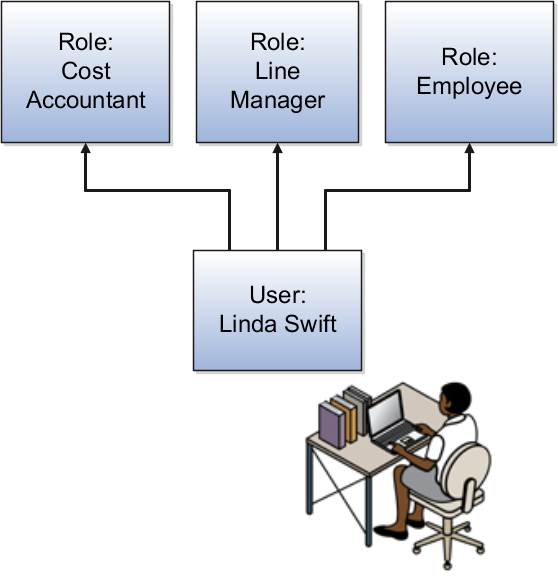
When Linda signs in to Oracle Applications Cloud, she doesn't have to select a role. All of these roles are active concurrently.
The functions and data that Linda can access are determined by this combination of roles.
-
As an employee, Linda can access employee functions and data.
-
As a line manager, Linda can access line-manager functions and data.
-
As a cost accountant, Linda can access cost accountant related functions and data for Vision Operations.