Auditing
LGFAPI - URI Format
The lgfapi URI structure is broken down into several components. In general, lgfapi URIs is using the following schema:
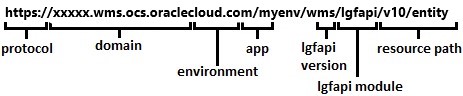
The first portion of the URI (protocol, domain, environment, and app) is consistent with the URL of the environment’s UI accessed via a web browser. The remaining pieces after “lgfapi” are specific to the lgfapi and designate the version and path to any child modules and/or resources.
Versioning
Lgfapi requires a version number in all URIs. The format is “v#’, starting with “v9” as the first release. New versions are created only for major releases of the Oracle WMS Cloud application, not for minor versions. For example, the release of WMS 9.0.0 included the lgfapi v9 release, but there will not be a new lgfapi version number with the release of WMS 9.0.1. However, the APIs will continue to be updated with new features and improvements along with the minor releases of WMS.
The purpose of version control is to give customers some ability to remain on their current integrations until they can complete any changes required to handle the newest lgfapi version. It is strongly encouraged that all customers use the latest version of lgfapi. Version control is a tool to assist with upgrades and testing, it is not meant to be used in production for extended periods of time. The previous versions of lgfapi will unavoidably become out of sync with newer versions of WMS, and eventually will no longer be compatible.
Oracle will not make changes to previous versions of lgfapi to maintain expired functionality or compatibility. Therefore, it is always in the best interest to use the latest version. New API versions are planned approximately once a year. Older API versions will be supported approximately one year after a newer one is released.
lgfapi Modules
Lgfapi contains modules that can be utilized by customers. These are groupings of functionality that may have their own formats and requirements.
For example, lgfapi’s “entity” module is designed to allow customers to examine and interact with OCWMS business resources from outside the application.
Resource Path : The final component to the URI is the resource path. This may take many different forms depending on the HTTP method and any module-specific requirements.
Optional Trailing Slashes: A trailing slash at the end of and lgfapi URIs is optional and does not affect functionality.
LGFAPI - Resource Result Set Filtering
Lgfapi offers the ability to apply filters to GET and HEAD requests to narrow down the final result set. This is done by adding query string filter parameters to the URI. Furthermore, lgfapi supports several built-in lookup functions to assist in common filtering tasks.
It is important to note that all entity data is automatically filtered by the user’s eligible facilities and companies. This prevents users from being able to access and/or change data outside of their assigned scope that same way that data is isolated in the UI or RF features. The difference with lgfapi is that users may access data from multiple eligible facilities and companies in a single request. In the UI and RF, this typically requires manually changing the user’s context.
-
The most basic format for a filter simply uses the exact operator (“=”): .../?field=value
-
This can be chained to apply multiple filters: .../?field1=value1&field2=value2
Lgfapi uses double underscore (“ ”) notation to join multiple fields or functions in the query string filters. The double underscore is used to distinguish the field names when filtering on a related resource’s attributes or when applying a lookup function.
-
Applying a lookup function: .../?field lookup=value
-
Filtering on a related resource: .../?relation_id related_field=value
-
Applying a lookup function on a related resource: .../?relation_id related_field lookup=value
Please refer to the Rest API Guide for more information.