Advanced Constraint Model Cubing
During the outbound process, one of the most common operations used is cubing, to calculate the outbound LPNs to be picked and packed. This is an area where, minimizing the number of Outbound LPNs to be shipped can improve pick/pack efficiency as well as reduce the amount of packaging used, this making this a good tool for sustainability. To support a more streamlined cubing process, we’re enhancing wave-based cubing modes 2 and 3 for cubed allocations, using a technology called Advanced Constraint Modeling which now results in fewer outbound containers in scenarios where there are larger shipping volumes.
Constraint modeling is an algorithmic AI technique that optimizes a solution given a set of constraints that must be followed. For example if the constraints are that each outbound LPN can have no more than two orders and no more than 3 SKU’s, constraint modeling is able to enforce these simultaneously while looking for solutions in the problem space. In a traditional approach, it is possible that some suboptimal LPNs may be generated.
Example
The current cubing feature of WMS employs an algorithm that relies on strict ordering and capacity checks. For example, a configuration which orders by item barcode, allowing for up to three distinct items per LPN and targeting an LPN type with a max volume of 10 would yield the following results:

Configuration by Item Barcode
Resulting LPN utilization:
- LPN1: 80%
- LPN2: 90%
- LPN3: 20%
You will notice that a third LPN is required due to the algorithm preserving a strict ordering. By removing the requirement of strict ordering, the new cubing modes will now employ a constraint model that enforces a constraint “no more than three distinct items per LPN.”
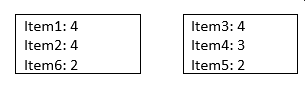
No More than Three Distinct Items
Resulting LPN utilization:
- LPN1: 100%
- LPN2: 90%
In general, the cubing results when using the constraint model will result in fewer LPNs than when using the strict ordering algorithm. The main difference with the Constraint Based vs the current Regular Cubing algorithm, has to do with how the break-by criteria are considered:
| Constraint Model Cubing | Regular Cubing |
|---|---|
| Uses an algorithm based on constraint modeling. | Uses an algorithm based on linear ordering. |
| Outbound Containers created by considering all conditions at the same time. | Outbound Containers created using criteria that is strictly ordered. |
We’ve added two new values to the Cubing Mode drop-down field in the Wave Template UI. The values are:
- Cube at wave with Constraint Model
- Cube at packing with Constraint Model
Cubing Mode
RECOMMENDATIONS
- Due to the requirements of solving complex combinatorial problems, the constraint model works best for company configurations that do not have too high precisions. The current default value for “max weight volume Dimension decimal precision” is 5. Although the constraint model will work with this level of precision, it is recommended to have this setting at 3 or below for better results.
- Note that SKUs that use integer UOMs are not affected by this.
- If it is not feasible to change the “max weight volume Dimension decimal precision.” There are two company parameters available which can be used to adjust the behavior of the constraint model: CONSTRAINT_BASED_CUBING_MAX_BATCH_SIZE (default value is 1024) and CONSTRAINT_BASED_CUBING_MIN_BATCH_SIZE (default value is 32).
- These parameters define the number of allocations being considered for cubing in batches.
- Note: In case of excessive constraint based errors, the recommendation is to reduce the max allocations in factors of 2.
- Generally, these parameters can be decreased to prevent the constraint-based solver from encountering errors. It is unlikely that these should be increased, but doing so may result in slightly improved results (i.e., fewer LPNs).
- In case of the solver failing for any reasons unknown, there will be a generic error "Constraint based service returned an error." It is very unlikely any of these settings needs to be changed, since these limitations only affect fewer common scenarios.
Steps to Enable
In the Wave Template UI, set the Cubing mode value to Cube at Wave or Cube at Packing with Constraint Model. This will enable constraint-based cubing, along with other regular cubing configurations (like the Cubing Rule/break by criteria and so on).