RF Outbound Audit
- Audit Mode
- Audit - Default Reason Code
The Default Reason Code parameter allows you to add a reason code for your audit.
Audit Mode
The Audit Mode parameter has three choices:
- Simulated with Pending Audit
- Simulated without Pending Audit
RF Outbound Audit Screen
The RF_Outbound Audit screen prompts you to scan the container to be audited (in this case an OBLPN with unit allocations is scanned).
The following screen flow is applicable when the Simulated Audit mode screen parameter is set with the value None or Simulated Mode with Audit Pending or without Audit Pending.
Important: You can reduce quantity via RF Outbound Audit, but you cannot increase quantity in an OBLPN.
RF SKU Prompt Screen
After you scan the LPN, you are prompted to add the SKU:

When the allocation is done in terms of cases, the following is an example of the RF Outbound Audit Cases prompt screen:
The above RF screen flow is applicable when the Simulated Audit mode screen parameter is set as any of the following:
- None
- Simulated Mode with Audit Pending
- Simulated without Audit Pending.
Whether the Simulated Audit Mode is configured for Normal Mode or Simulated Mode, the following updates apply:
- When an extra unit or an item that does not belong to the OBLPN is scanned, the error “item does not belong to OBLPN Discrepancy will be recorded” displays. You can accept the message with Ctrl-A and physically take out the extra unit/sku that does not belong to the OBLPN at hand. If you press Ctrl-W, you are returned to the Sku Prompt screen without recording the discrepancy.
- Scanned items and quantity per item are recorded for each sku. The scanned items and quantity are stored and displayed in the Audit Detail History screen.
Based on the type of container you scan in the first screen, the RF Outbound Audit module behaves differently as follows:
The Audit OB LPN Transaction allows you to audit OB LPN or Pallets in Normal Mode when updates are performed as part of the audit transaction or in Simulated Mode.
The Audit Mode parameter choices are defined below:

Whether the Simulated Audit Mode Screen parameter is configured for Normal Mode or Simulated Mode, the following screen flow is applicable.
Once you scan all of the items in the OBLPN or finish the audit, you end the audit by pressing Ctrl-E.
The system asks you a verification question to end the audit and you accept message using Ctrl-A. Otherwise, you can press Ctrl-W to return to the previous screen and continue scanning more items.
After you end the audit, the system informs you of any discrepancies of scanned LPNs.
Serial Number Tracking
RF Audit supports scanning items which are serial number tracked. During audit, you are prompted to enter serial numbers if serial number tracking is enabled for an item
Scanned serial numbers are captured in inventory history records. No changes are made to audit history records. Also, serial number tracking is only applicable in non-simulated mode. If you encounter serial number tracked items during one of the simulated modes, an error is thrown and you will not be able to proceed with audit in these modes.
You can configure the system to trigger serial number verification only when the quantity is mismatched by using the screen parameter “verify-serialnbrs-on-qty-mismatch-only”.
This parameter ensures that serial number verification can be skipped to save time and streamline operations when the physical count matches the expected quantity.
The table summarizes the behavior of the screen parameter “verify-serialnbrs-on-qty-mismatch-only”:
| Parameter Value | Behavior |
| Yes |
The system prompts for serial numbers only when:
|
| No (default behavior) |
The system always prompts serial numbers, irrespective of any quantity mismatch. Note: If you end the audit without SKU scan, the
system bypasses the serial number prompt.
|
Rules to Determine if Item is Serial Number Tracked
In order to determine if the item is being tracked for serial numbers the following two parameters at the company and item level are checked:
- Company parameter for tracking serial needs to be set either to “Packing Only” or “End to End.”
- Item attributes that specify serial number tracking need to be set as “Track Serial Numbers”
Batch Numbers/Expiry Dates/Inventory Attributes Tracking
The RF Outbound Audit transaction prompts you to scan items or SKUs that track batch, expiry, or inventory attributes which is controlled by the the screen parameter “confirm_attributes_of _inventory”.
The table summarizes the behavior associated with the screen parameter “confirm_attributes_of _inventory”:
| Parameter Value | Behavior |
| Yes |
Irrespective of conflicts, the system prompts for batch numbers, expiry dates, or inventory attributes when the scanned SKU is set to track batch, expiry, or inventory attributes. Note: Auto-populating of attributes from
multi-field barcodes is currently unsupported.
|
| No (default behavior) | The system does not prompt for batch numbers, expiry dates, or inventory attributes. |
Screen Parameter column-ordering-rule Behavior
When performing an OBLPN Audit, if you encounter a situation where the audited inventory is less than anticipated, the system decreases the varied quantity from the assigned orders. You can control the deallocation sequence using the screen parameter “column-ordering-rule”.
To set the deallocation sequence, do the following configurations:
- Enter a column ordering rule in the screen parameter “column-ordering-rule” value.
- On the Column Ordering screen, you must configure the same column
ordering rule.Note:
- If you enable the flag “Order by Descending Flag”, the system sequences the orders in the descending order based on the configured criteria.
- If you disable the flag “Order by Descending Flag”, the system sequences the orders in the ascending order based on the configured criteria.
Example:
Consider an OBLPN “OBLPN01” has the following allocations.
| OBLPN | SKU | Quantity | Order Number | Order Priority | Order Create TS |
| OBLPN01 | ABC | 10 | ORDER001 | 1 | 6th January |
| OBLPN01 | ABC | 10 | ORDER002 | 2 | 6th January |
In this case, the screen parameter “column-ordering-rule” is set to “RKRULE01” that has the following configuration:
| Column Ordering Rule Name | Order By Field | Sequence Number | Order by Descending Flag |
| RKRULE01 | Order priority | 1 | Yes |
| RKRULE01 | Order Create Ts | 2 | Yes |
Now, let's assume you have performed the OBLPN Audit of “OBLPN01” for a single inventory “ABC”, which is associated with two different orders (ORDER001 and ORDER002). If you enter a lesser quantity (15), the system needs to deallocate 5 units. Based on the Column Ordering Rule configuration, the system selects ORDER002 for deallocation due to its order priority “2”.
Apply Lock Code For Inventory Discrepancy
As an Auditor, applying lock codes to Outbound LPNs during an OBLPN Audit is essential, especially when discrepancies arise, such as quantity mismatches, unexpected SKUs, or damaged LPNs. By utilizing lock codes, you can prevent these issues from slipping through the cracks and ensure that OBLPNs with discrepancies are not accidentally loaded or shipped.
The screen parameter “prompt-lockcode-for-invn-discrepancy”controls whether the system prompts for a lock code during the OBLPN Audit when discrepancies are identified.
The table outlines the behavior of the screen parameter “prompt-lockcode-for-invn-discrepancy”:
| Parameter Value | Behavior |
| Yes | The system prompts a lock code if any discrepancy is encountered during the physical audit. |
| No (default behavior) | The system does not prompt a lock code. |
During the RF Outbound Audit transaction, you can invoke the hotkey “Ctrl-L: Apply Lock” to associate a lock code to the scanned OBLPN. This enables you to apply lock code like Damaged if LPN being audited is Damaged.
Additionally, after completing the audit with “Ctrl-E: End Audit”, the system prompts for a lock code if there are any inventory discrepancies.
If you want to prevent shipping or manifesting on the OBLPN due to discrepancies, apply a lock code that is disabled with the following flags:
- Allow Loading
- Allow Manifesting
Inventory and Audit History Update
When conducting physical audit, let’s assume you found the OBLPN has a quantity discrepancy. In such cases, the system records this discrepancy and associates it with the relevant OBLPN in the Audit History UI.
The table outlines the system behavior with respect to inventory and audit history under different audit scenarios:
| Audit Scenario | Inventory Update | Audit History Record |
| Anticipated SKU audited with lesser inventory than expected | Yes | Yes |
| Anticipated SKU audited with more inventory than expected | No | Yes |
| Anticipated SKU audited with unanticipated Batch/Expiry/Inventory Attribute | No | Yes |
Audit History
The Audit History screen shows most of the detailed information for the audit so that you often do not need to go to the details screen to view details and discrepancies. The following screen shows what the Audit History screen looks like. Refer to the Audit Detail History Columns section below for more details.
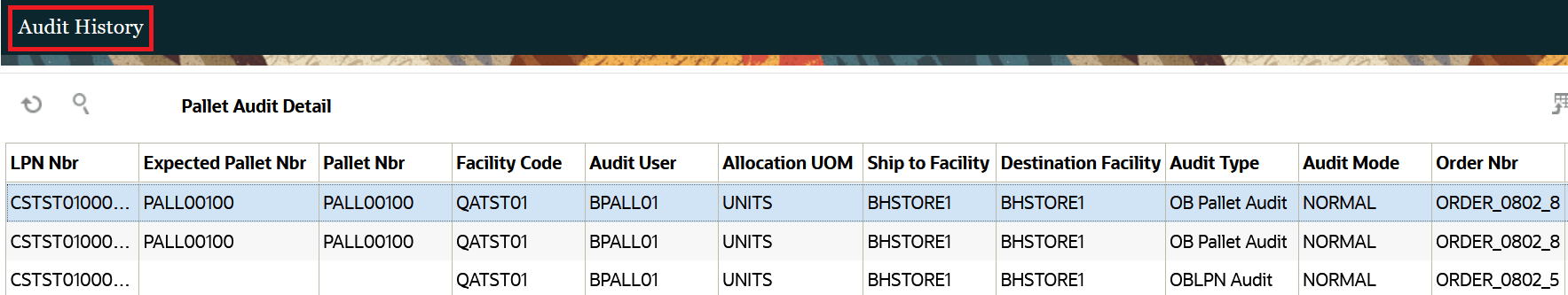
From the Audit History screen, you can click Pallet Audit Detail to view details such as expected and scanned number of LPNs, difference, number of expected LPNs scanned, and OBLPNs not anticipated.
Audit History Columns
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Pallet Number | Pallet Number which has been scanned in Audit, If Pallet not Scanned display null |
| Audit OB LPN Number | Outbound LPN which has undergone Audit |
| Load Number | Load Number associated to the Pallet/OB LPN. If OB LPN is associated with Parcel carrier then display Load Number field blank |
| Expected Pallet Number | When OB Pallet is scanned, this column depicts the pallet number associated with the OB LPN Scanned |
| Audit Mode | Normal or Simulated |
| Audit Type | OB LPN Audit or OB Pallet Audit |
| Item Code | Item Scanned, If Outbound LPN scanned has multiple sku’s write different rows for each sku |
| Packed Qty | Packed Qty associated to the inventory record for OB LPN. Qty Present on the OB LPN when the Outbound LPN was Packed. |
| Current Qty | Qty present in OB LPN during Audit (Can be 0 if Sku scanned is not anticipated in the OB LPN Scanned |
| Audit Qty | Quantity audited by User (Can be Zero or less or equal or greater than current qty) |
| Unit Variance | Current Qty-Audit Qty (If Audit Qty is greater than Current Qty, display the value in brackets). |
| Total Pack Cost | Unit_Cost for the item times the quantity expected for the sku in the OB LPN |
| Total Audit Cost | Unit_Cost for the item times the quantity Audited for the sku |
| Cost Variance | Total Pack Cost-Total Audit Cost. (If Total Audit Cost is greater than total pack cost, display the value in brackets). |
| Alternate Item Code | An alternate representation of the SKU, which concentrates SKU parts A through F into a single record. |
| Audit User | User who performed the audit transaction |
| Item Description | Description of the item. |
| Destination Facility Code | Destination facility for the OB LPN Scanned in Audit |
| Ship to Facility Code | Ship to facility for the OB LPN Scanned in Audit |
| Allocation UOM | Units/Packs/Cases |
| Pack Qty | Item’s Standard Pack Qty |
| Standard Case Qty | Standard Case qty from item |
| Pick User | Pick user associated to the Outbound LPN |
| Pack User | Person who Packed the Outbound LPN. |
| Audit _ts | Create time stamp of when Audit Performed |
| Packed_ts | Time Stamp of when the Outbound LPN was packed |
| Manifest Number | If Outbound LPN is not associated to load, display manifest number, if associated to Manifest |
| Order Number | Order Number associated to the OB LPN |
| Order Type | Order Types differentiate orders based on certain characteristics. |
| OB LPN Type | Container Type associated with the Outbound LPN Audited |
| Allocation Type | Allocation Type from the Corresponding Allocation Record associated with the Outbound LPN |
| Batch Number | Batch Number for the Item Associated with the Outbound LPN Audited. |
| Item Hierarchy Code | Describes the item hierarchy. |
| priority_date | Priority Date of the item associated with the Outbound LPN Audited. |
| invn_attr_a to invn_attr_o | Inventory attributes of the item associated with the Outbound LPN Audited. |
| exp_date | Expiry Date of the item associated with the Outbound LPN Audited. |
| facility_code | Facility Code of the item associated with the Outbound LPN Audited. |
| wave_nbr | Refers to a grouping or batch of orders that are processed together as part of a single wave. |
| mod_user | User ID of the user who executed the Outbound LPN Audit. |
| alloc_mod_user | User ID of the user who executed the Outbound LPN Allocation. |
| discrepancy | Yes/No. Denotes if there is a difference in the current quantity and audited quantity. |
| reason_code | Records the reason code mentioned during the audit. |