 Before You Begin
Before You Begin
This 15-minute tutorial shows you how to create a SQL Performance Analyzer report, which compares SQL performance on two Oracle databases.
Background
You can use SQL Performance Analyzer to analyze and compare the performance of a SQL workload on two different Oracle databases. This procedure assumes that a SQL tuning set was created on one Oracle database and then transferred to another Oracle database. The SQL tuning set contains a SQL workload. Create a SQL Performance Analyzer task, and then populate it with two trials: a pre-change trial, which describes the performance of the workload on the original database, and a post-change trial, which describes the performance of the same workload on the current database.
What Do You Need?
- An Oracle database
- The
SYSDBAadministrative privilege - A SQL tuning set, which was created on another Oracle database and then transferred to the Oracle database used in this tutorial. This tutorial assumes that the SQL tuning set is named
MY_WORKLOAD_STS.
 Create a SQL Performance Analyzer Task
Create a SQL Performance Analyzer Task
- Use SQL*Plus to log in to the database as a user who has the
SYSDBAadministrative privilege.$ sqlplus / as sysdba
- Create SQL Performance Analyzer task
MY_WORKLOAD_TASK. The task uses the SQL tuning setMY_WORKLOAD_STS, which was created on another database, and then transferred to the current database.
SQL> VARIABLE task_name VARCHAR2(100);
SQL> EXEC :task_name := DBMS_SQLPA.CREATE_ANALYSIS_TASK( -
> sqlset_name => 'MY_WORKLOAD_STS', -
> task_name => 'MY_WORKLOAD_TASK', -
> description => 'Peak Usage Workload');
 Create a Pre-Change Trial and a Post-Change Trial
Create a Pre-Change Trial and a Post-Change Trial
- Create a pre-change trial, which represents workload performance on the original database, by converting the SQL tuning set
MY_WORKLOAD_STS. - Create a post-change trial, which represents workload performance on the current database, by executing the SQL statements from SQL tuning set
MY_WORKLOAD_STS.SQL> BEGIN
2 DBMS_SQLPA.EXECUTE_ANALYSIS_TASK(
3 task_name => 'MY_WORKLOAD_TASK',
4 execution_type => 'TEST EXECUTE',
5 execution_name => 'POST_CHANGE_TRIAL');
6 END;
7 /
SQL> BEGIN
2 DBMS_SQLPA.EXECUTE_ANALYSIS_TASK(
3 task_name => 'MY_WORKLOAD_TASK',
4 execution_type => 'CONVERT SQLSET',
5 execution_name => 'PRE_CHANGE_TRIAL');
6 END;
7 /
 Create a SQL Performance Analyzer Report
Create a SQL Performance Analyzer Report
- Use SQL Performance Analyzer to analyze and compare the performance of the pre-change trial and the post-change trial. For a comparison metric, this report uses
buffer_gets, which represents the number of times the database accessed a block.SQL> BEGIN
2 DBMS_SQLPA.EXECUTE_ANALYSIS_TASK(
3 task_name => 'MY_WORKLOAD_TASK',
4 execution_type => 'COMPARE PERFORMANCE',
5 execution_params => DBMS_ADVISOR.ARGLIST(
6 'execution_name1', 'PRE_CHANGE_TRIAL', 'execution_name2',
7 'POST_CHANGE_TRIAL', 'comparison_metric', 'buffer_gets'),
8 execution_desc => 'Compare buffer_gets');
9 END;
10 / - Produce a SQL Performance Analyzer Report in HTML.
SQL> SET LONG 100000 LONGCHUNKSIZE 100000 LINESIZE 130 PAGESIZE 0 ECHO OFF
SQL> spool my_workload_spa_report.html
SQL> SELECT DBMS_SQLPA.REPORT_ANALYSIS_TASK('MY_WORKLOAD_TASK', 'html') FROM DUAL;
SQL> spool off - Exit SQL*Plus.
SQL> exit
- Open in an editor the file
my_workload_spa_report.html. If the following is the first line in the file, remove it:SQL> SELECT DBMS_SQLPA.REPORT_ANALYSIS_TASK('MY_WORKLOAD_TASK', 'html') FROM DUAL;The first line of the file should be:<html>
- Save the file
my_workload_spa_report.html. - Open
my_workload_spa_report.htmlin a web browser.
If you cannot open this file in a browser on the database host, transfer the file to a system on which you are able to open it in a browser.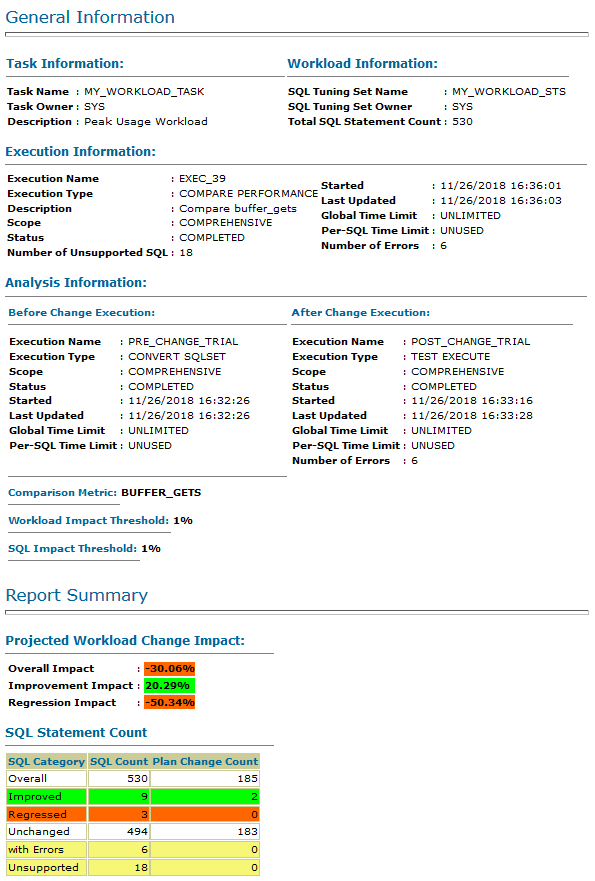
Description of the illustration spa_report.png - Review the report to identify any regressions.
- Tune any regressed SQL statements.
 Create a SQL Performance Analyzer Report
Create a SQL Performance Analyzer Report