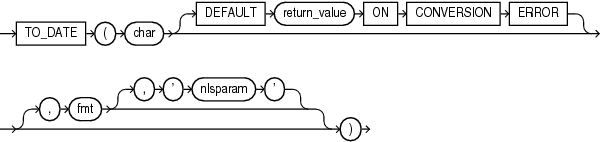
TO_DATE
Syntax
Purpose
TO_DATE converts char to a value of DATE data type.
For char, you can specify any expression that evaluates to a character string of CHAR, VARCHAR2, NCHAR, or NVARCHAR2 data type.
Note:
This function does not convert data to any of the other datetime data types. For information on other datetime conversions, refer to TO_TIMESTAMP, TO_TIMESTAMP_TZ, TO_DSINTERVAL, and TO_YMINTERVAL.
The optional DEFAULT return_value ON CONVERSION ERROR clause allows you to specify the value this function returns if an error occurs while converting char to DATE. This clause has no effect if an error occurs while evaluating char. The return_value can be an expression or a bind variable, and it must evaluate to a character string of CHAR, VARCHAR2, NCHAR, or NVARCHAR2 data type, or null. The function converts return_value to DATE using the same method it uses to convert char to DATE. If return_value cannot be converted to DATE, then the function returns an error.
The fmt is a datetime model format specifying the format of char. If you omit fmt, then char must be in the default date format. The default date format is determined implicitly by the NLS_TERRITORY initialization parameter or can be set explicitly by the NLS_DATE_FORMAT parameter. If fmt is J, for Julian, then char must be an integer.
Caution:
It is good practice always to specify a format mask (fmt) with TO_DATE, as shown in the examples in the section that follows. When it is used without a format mask, the function is valid only if char uses the same format as is determined by the NLS_TERRITORY or NLS_DATE_FORMAT parameters. Furthermore, the function may not be stable across databases unless the explicit format mask is specified to avoid dependencies.
The 'nlsparam' argument specifies the language of the text string that is being converted to a date. This argument can have this form:
'NLS_DATE_LANGUAGE = language'
Do not use the TO_DATE function with a DATE value for the char argument. The first two digits of the returned DATE value can differ from the original char, depending on fmt or the default date format.
This function does not support CLOB data directly. However, CLOBs can be passed in as arguments through implicit data conversion.
See Also:
"Datetime Format Models" and "Data Type Comparison Rules" for more information
Examples
The following example converts a character string into a date:
SELECT TO_DATE(
'January 15, 1989, 11:00 A.M.',
'Month dd, YYYY, HH:MI A.M.',
'NLS_DATE_LANGUAGE = American')
FROM DUAL;
TO_DATE('
---------
15-JAN-89
The value returned reflects the default date format if the NLS_TERRITORY parameter is set to 'AMERICA'. Different NLS_TERRITORY values result in different default date formats:
ALTER SESSION SET NLS_TERRITORY = 'KOREAN';
SELECT TO_DATE(
'January 15, 1989, 11:00 A.M.',
'Month dd, YYYY, HH:MI A.M.',
'NLS_DATE_LANGUAGE = American')
FROM DUAL;
TO_DATE(
--------
89/01/15The following example returns the default value because the specified expression cannot be converted to a DATE value, due to a misspelling of the month:
SELECT TO_DATE('Febuary 15, 2016, 11:00 A.M.'
DEFAULT 'January 01, 2016 12:00 A.M.' ON CONVERSION ERROR,
'Month dd, YYYY, HH:MI A.M.') "Value"
FROM DUAL;
Value
---------
01-JAN-16