1 Aims and Objectives of This Book
Java is a popular language among developers that is used to build various enterprise solutions.
This guide will help you understand all Java products used to build a Java application. You will learn how to model a Java Web application using MVC design pattern, Oracle JDBC Thin driver, Universal Connection Pool (UCP), and Java in the Database ( using embedded OJVM).
In the next few chapters, you will create a Java web application — ‘HR Web application’. This application helps the HR team of AnyCo Corporation to lookup or modify details of a specific employee, or all employees, delete an employee, or apply a salary raise to all employees.
The HR application has two users:
- hrstaff
- hradmin
Each user has a different set of roles and privileges.
This Chapter contains the following topics:
- Architecture of the Web Application
- Components of the Application
- Objectives and Tasks
1.1 Architecture of the HR Web Application
The HR Web application uses the MVC (Model, View, Controller) architecture and the latest tools and technologies. A Model View Controllder (MVC) is a design pattern that is easy-to-use. It separates the web application into three simple parts (Model-View-Controller).
The Model stores the data or the information that the web application is meant to operate on. It does not include any information about the user-interface.
The View contains all elements of the user interface (UI). This includes buttons, display box, links, input box etc.
The Controller connects Model and View.
As a user, you will see the interface (View) that could be a JSP page to an HTML page after you log into the application. The Controller (a Java Servlet) renders the correct View to the user during logging in, or any other flow. When you request for data or an update to the data, the Controller invokes the Model that represents the data in terms of tables or views, and renders the data. The Model represents the user data usually stored in an Oracle Database or any other database.
The Controller then passes on this data to the View to show it to the user in a presentable format.
Figure 1-1 Pictorial Depiction of the Web Application
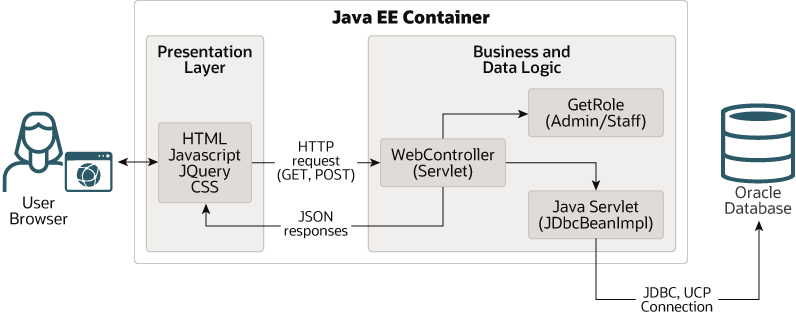
Description of "Figure 1-1 Pictorial Depiction of the Web Application"
The following table describes the various components of the application:
Table 1-1 Architecture of the Web Application
| Name | Technologies Used | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Model | Oracle Database, Java Beans | Represents the information or the data on which the application operates. |
| View | HTML, JavaScript, JQuery, CSS | User interface that renders the model to the end user. It includes all elements visible to the user such as buttons, links, input, etc. |
| Controller | Java Servlet | The controller processes and responds to user actions. It orchestrates the flow based on user input. It also connects Model and View and renders an output to the user. |
You will use HR schema and the Employees to understand the flows in the Web application.
1.2 Components and Repositories
The following table lists and describes all the components required for the application.
Table 1-2 Components Required for the Application
| Package Name | Description |
|---|---|
| src | Contains source files |
| target | Contains class files |
| src/main/java/com/oracle/jdbc/samples | - |
| /bean/JdbcBean.java | Defines the employee details as attributes |
| /bean/JdbcBeanImpl.java | Implementation class of the EmployeeBean |
| src/main/java/com/oracle/jdbc/samples | - |
| entity/Employee.java | Consists of all employee attributes and their defined datatypes |
| /web/WebController.java | Servlet that controls the application flow |
| /web/GetRole.java | Creates HRStaff and HRAdmin roles for the application |
| src/main/resources | - |
| SalaryHikeSP.java | Java class to be invoked from Java in the database to process an increment in salary |
| SalaryHikeSP.sql | SQL file with a procedure to increase the salary of the employees based on their salary range |
| src/main/webapp | - |
| about.html | Contains the details about the HR Web application |
| login.html | Contains the login page for the HR Web application |
| login-failed.html | Page to show when the login is unsuccessful |
| index.html | Landing page of the HR Web application |
| listAll.html | HTML page to display all employee records |
| listByName.html | HTML page to display the result when employees are searched by name |
| listById.html | HTML page to display the result when employees are searched by employee id |
| incrementSalary.html | HTML page to display the result after an increment is made to the salary |
| src/main/webapp | - |
| css/app.cs | Contains all style and font details used in the HR Web application |
| src/main/webapp | - |
| WEB-INF/web.xml | Controller for the HR Web application |
1.3 Objectives and Tasks
By the end of this book, you will be able to:
a. Understand the JDBC, UCP, Java in the database and run a simple Java program to get familiar with these products.
c. You will learn how to use Universal Connection Pool (UCP) and Java in the Database (OJVM).
b. Implement the functionality to list all employees, search and retrieve an employee and update an employee record.
An overview of each chapter is described as follows:
- Introduction to JDBC, UCP and Java in the Database: This chapter familiarizes you with the products, associated binaries and packages through a sample code.
- Overview of the HR Web Application: This chapter discusses the HR Web application in depth and familiarize you with the flows of the Web application, packages and files that you create as a part of the web application.
- Getting Started with the Application: In this
chapter, you understand the prerequisites for
building the application and how to get the
environment ready. It starts with signing up for the
Oracle Cloud Free Tier or installing the Oracle
Database on premise. Later, you install IntelliJ, an
IDE to build the application. You use Tomcat Java EE
container to deploy and run the application.
The chapter also helps you download any other tools, such as Maven, that helps you to build the application.
- List All Employees: This chapter helps you to put all the components together and build an initial functionality to connect to the Oracle Database, and retrieve employee details from the database.
- Search By Employee ID: This chapter provides details on how to implement the ‘Search by Employee ID’ functionality.
- Update an Employee Record: In this chapter, you learn how to update employee records. This is a two step process. Firstly, you search the employee’s records, based on first name. Once you retrieve the required results, you can update the salary, job ID, firstname, lastname and other details.
- Delete an Employee Record: In this chapter, you learn how to delete an employee record, in a two-step process.
- Increase Salary to All Employees: In this chapter, you understand how to provide an increment to the salary of the employees listed in the table, using ‘Java in the database’.
- Creating Application Users: This chapter shows how to create ‘hradmin’ and ‘hrstaff’ users in Tomcat and IntelliJ.
- Summary: This chapter summarizes all that you have learnt so far. It also provides appropriate references and links for enhancing your use of the web application.