187 DBMS_SQL
The DBMS_SQL package provides an interface to use dynamic SQL to parse any data manipulation language (DML) or data definition language (DDL) statement using PL/SQL.
For example, you can enter a DROP TABLE statement from within a stored procedure by using the PARSE Procedures supplied with the DBMS_SQL package.
This chapter contains the following topics:
See Also:
For more information on native dynamic SQL, see Oracle Database PL/SQL Language Reference.
187.1 DBMS_SQL Overview
Oracle lets you write stored procedures and anonymous PL/SQL blocks that use dynamic SQL. Dynamic SQL statements are not embedded in your source program; rather, they are stored in character strings that are input to, or built by, the program at runtime. This enables you to create more general-purpose procedures. For example, dynamic SQL lets you create a procedure that operates on a table whose name is not known until runtime.
Native Dynamic SQL is an alternative to DBMS_SQL that lets you place dynamic SQL statements directly into PL/SQL blocks. In most situations, Native Dynamic SQL is easier to use and performs better than DBMS_SQL. However, Native Dynamic SQL itself has certain limitations:
-
There is no support for so-called Method 4 (for dynamic SQL statements with an unknown number of inputs or outputs)
-
There are some tasks that can only be performed using
DBMS_SQL.For tasks that requireDBMS_SQL, see Oracle Database PL/SQL Language Reference.
The ability to use dynamic SQL from within stored procedures generally follows the model of the Oracle Call Interface (OCI).
See Also:
PL/SQL differs somewhat from other common programming languages, such as C. For example, addresses (also called pointers) are not user-visible in PL/SQL. As a result, there are some differences between the Oracle Call Interface and the DBMS_SQL package. These differences include the following:
-
The OCI binds by address and the
DBMS_SQLpackage binds by value. -
With
DBMS_SQLyou must callVARIABLE_VALUEto retrieve the value of anOUTparameter for an anonymous block, and you must callCOLUMN_VALUEafter fetching rows to retrieve the values of the columns in the rows into your program. -
The current release of the
DBMS_SQLpackage does not provideCANCELcursor procedures. -
Indicator variables are not required, because
NULLsare fully supported as values of a PL/SQL variable.
187.2 DBMS_SQL Security Model
DBMS_SQL is a SYS-owned package compiled with AUTHID CURRENT_USER. Any DBMS_SQL subprogram called from an anonymous PL/SQL block runs with the privileges of the current user.
See Also:
Oracle Database PL/SQL Language Reference for more information about using Invoker Rights or Definer Rights
Preventing Malicious or Accidental Access of Open Cursor Numbers
An error, ORA-29471, is raised when any DBMS_SQL subprogram is called with a cursor number that does not denote an open cursor. When the error is raised, an alert is issued to the alert log and DBMS_SQL becomes inoperable for the life of the session.
If the actual value for the cursor number in a call to the IS_OPEN Function denotes a cursor currently open in the session, the return value is TRUE. If the actual value is NULL, then the return value is FALSE. Otherwise, this raises an ORA-29471 error.
Preventing Inappropriate Use of a Cursor
Cursors are protected from security breaches that subvert known existing cursors.
Checks are made when binding and executing. Optionally, checks may be performed for every single DBMS_SQL subprogram call. The check is:
-
The
current_useris the same on calling the subprogram as it was on calling the most recent parse. -
The enabled roles on calling the subprogram must be identical to the enabled roles on calling the most recent parse.
-
The container is the same on calling the subprogram as it was on calling the most recent parse.
Consistent with the use of definer's rights subprograms, roles do not apply.
If either check fails, then an ORA-29470 error is raised.
The mechanism for defining when checks are performed is a new overload for the OPEN_CURSOR subprogram, which takes a formal parameter, security_level, with allowed values NULL, 1 and 2.
-
When
security_level=1(or isNULL), the checks are made only when binding and executing. -
When
security_level=2, the checks are always made.
Upgrade Considerations
This security regime is stricter than those in the previous releases. As a consequence, users of DBMS_SQL may encounter runtime errors on upgrade.
187.3 DBMS_SQL Constants
The DBMS_SQL Constants package provides constants that are used with the language_flag parameter of the PARSE Procedures.
These constants are described in the following table.
Table 187-1 DBMS_SQL Constants
| Name | Type | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Specifies Oracle database version 6 behavior |
|
|
|
|
Specifies normal behavior for the database to which the program is connected |
|
|
|
2 |
Specifies Oracle database version 7 behavior |
|
|
|
4294967295 |
Specifies a non-Oracle database syntax and behavior. The SQL statement to be parsed needs to be translated first using the SQL translation profile set in the database session. The SQL translation profile is a database schema object that directs how SQL statements are translated to Oracle. An error is raised if a profile is not set. |
Related Topics
187.4 DBMS_SQL Operational Notes
These operational notes describe processing queries, processing updates, inserts, and deletes, and locating errors.
Processing Queries
If you are using dynamic SQL to process a query, then you must perform the following steps:
-
Specify the variables that are to receive the values returned by the
SELECTstatement by calling the DEFINE_COLUMN Procedures, the DEFINE_COLUMN_LONG Procedure, or the DEFINE_ARRAY Procedure. -
Run your
SELECTstatement by calling the EXECUTE Function. -
Call the FETCH_ROWS Function (or
EXECUTE_AND_FETCH) to retrieve the rows that satisfied your query. -
Call COLUMN_VALUE Procedure or COLUMN_VALUE_LONG Procedure to determine the value of a column retrieved by the FETCH_ROWS Function for your query. If you used anonymous blocks containing calls to PL/SQL procedures, then you must call the VARIABLE_VALUE Procedures to retrieve the values assigned to the output variables of these procedures.
Processing Updates, Inserts, and Deletes
If you are using dynamic SQL to process an INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE, then you must perform the following steps:
-
Run your
INSERT,UPDATE, orDELETEstatement by calling the EXECUTE Function. -
If statements have the
returningclause, then you must call the VARIABLE_VALUE Procedures to retrieve the values assigned to the output variables.
Locating Errors
The DBMS_SQL package has additional functions for obtaining information about the last referenced cursor in the session. The values returned by these functions are meaningful only immediately after a SQL statement is run. In addition, some error-locating functions are meaningful only after certain DBMS_SQL calls. For example, you call the LAST_ERROR_POSITION Function immediately after calling one of the PARSE Procedures.
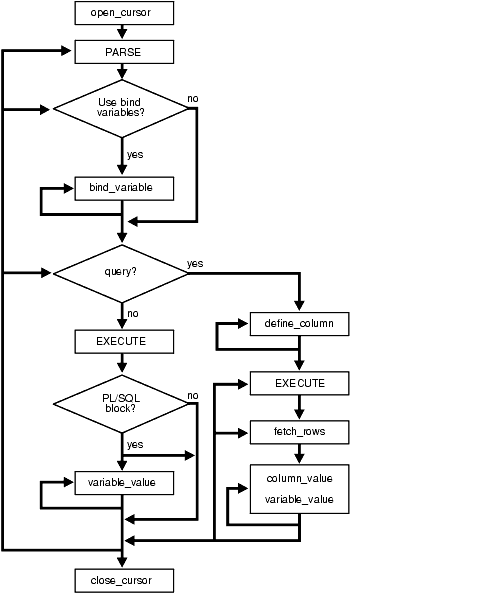
187.5 DBMS_SQL Execution Flow
These functions comprise the DBMS_SQL execution flow.
187.5.1 OPEN_CURSOR
To process a SQL statement, you must have an open cursor. When you call the OPEN_CURSOR Functions, you receive a cursor ID number for the data structure representing a valid cursor maintained by Oracle.
These cursors are distinct from cursors defined at the precompiler, OCI, or PL/SQL level, and are used only by the DBMS_SQL package.
Related Topics
187.5.2 PARSE
Every SQL statement must be parsed by calling the PARSE procedures. Parsing the statement checks the statement's syntax and associates it with the cursor in your program.
You can parse any DML or DDL statement. DDL statements are run on the parse, which performs the implied commit.
The execution flow of DBMS_SQL is shown in Figure 187-1.
Related Topics
187.5.3 BIND_VARIABLE, BIND_VARIABLE_PKG or BIND_ARRAY
Many DML statements require that data in your program be input to Oracle. When you define a SQL statement that contains input data to be supplied at runtime, you must use placeholders in the SQL statement to mark where data must be supplied.
For each placeholder in the SQL statement, you must call one of the BIND_ARRAY Procedures, or BIND_VARIABLE Procedures, or the BIND_VARIABLE_PKG Procedure to supply the value of a variable in your program (or the values of an array) to the placeholder. When the SQL statement is subsequently run, Oracle uses the data that your program has placed in the output and input, or bind variables.
DBMS_SQL can run a DML statement multiple times — each time with a different bind variable. The BIND_ARRAY procedure lets you bind a collection of scalars, each value of which is used as an input variable once for each EXECUTE. This is similar to the array interface supported by the OCI.
Note that the datatype of the values bound to placeholders cannot be PL/SQL-only datatypes.
187.5.4 DEFINE_COLUMN, DEFINE_COLUMN_LONG, or DEFINE_ARRAY
The DEFINE_COLUMN, DEFINE_COLUMN_LONG, and DEFINE_ARRAY procedures specify the variables that receive SELECT values on a query.
The columns of the row being selected in a SELECT statement are identified by their relative positions as they appear in the select list, from left to right. For a query, you must call one of the define procedures (DEFINE_COLUMN Procedures, DEFINE_COLUMN_LONG Procedure, or DEFINE_ARRAY Procedure) to specify the variables that are to receive the SELECT values, much the way an INTO clause does for a static query.
Use the DEFINE_COLUMN_LONG procedure to define LONG columns, in the same way that DEFINE_COLUMN is used to define non-LONG columns. You must call DEFINE_COLUMN_LONG before using the COLUMN_VALUE_LONG Procedure to fetch from the LONG column.
Use the DEFINE_ARRAY procedure to define a PL/SQL collection into which you want to fetch rows in a single SELECT statement. DEFINE_ARRAY provides an interface to fetch multiple rows at one fetch. You must call DEFINE_ARRAY before using the COLUMN_VALUE procedure to fetch the rows.
187.5.6 FETCH_ROWS or EXECUTE_AND_FETCH
The FETCH_ROWS Function retrieves the rows that satisfy the query. Each successive fetch retrieves another set of rows, until the fetch is unable to retrieve any more rows. Instead of calling EXECUTE Function and then FETCH_ROWS, you may find it more efficient to call EXECUTE_AND_FETCH Function if you are calling EXECUTE for a single execution.
Related Topics
187.5.7 VARIABLE_VALUE, VARIABLE_VALUE_PKG, COLUMN_VALUE, or COLUMN_VALUE_LONG
The type of call determines which procedure or function to use.
For queries, call the COLUMN_VALUE Procedure to determine the value of a column retrieved by the FETCH_ROWS Function.
For anonymous blocks containing calls to PL/SQL procedures or DML statements with returning clause, call the VARIABLE_VALUE Procedures or the VARIABLE_VALUE_PKG Procedure to retrieve the values assigned to the output variables when statements were run.
To fetch only part of a LONG database column (which can be up to two gigabytes in size), use the DEFINE_COLUMN_LONG Procedure. You can specify the offset (in bytes) into the column value, and the number of bytes to fetch.
187.5.8 CLOSE_CURSOR
When you no longer need a cursor for a session, close the cursor by calling the CLOSE_CURSOR Procedure. If you are using an Oracle Open Gateway, then you may need to close cursors at other times as well. Consult your Oracle Open Gateway documentation for additional information.
Related Topics
187.6 DBMS_SQL Exceptions
This exception is raised by the COLUMN_VALUE Procedure or the VARIABLE_VALUE Procedures when the type of the given OUT parameter (for where to put the requested value) is different from the type of the value.
inconsistent_type EXCEPTION; pragma exception_init(inconsistent_type, -6562);
Related Topics
187.7 DBMS_SQL Examples
These example procedures use the DBMS_SQL package.
Example : Using DBMS_SQL Demo
This example does not need dynamic SQL because the text of the statement is known at compile time, but it illustrates the basic concept underlying the package.
The DEMO procedure deletes all of the employees from the EMP table whose salaries are greater than the salary that you specify when you run DEMO.
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE demo(salary IN NUMBER) AS
cursor_name INTEGER;
rows_processed INTEGER;
BEGIN
cursor_name := dbms_sql.open_cursor;
DBMS_SQL.PARSE(cursor_name, 'DELETE FROM emp WHERE sal > :x',
DBMS_SQL.NATIVE);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE(cursor_name, ':x', salary);
rows_processed := DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE(cursor_name);
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(cursor_name);
EXCEPTION
WHEN OTHERS THEN
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(cursor_name);
END;Example 2
The following sample procedure is passed a SQL statement, which it then parses and runs:
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE exec(STRING IN varchar2) AS
cursor_name INTEGER;
ret INTEGER;
BEGIN
cursor_name := DBMS_SQL.OPEN_CURSOR;
DDL statements are run by the parse call, which performs the implied commit.
DBMS_SQL.PARSE(cursor_name, string, DBMS_SQL.NATIVE); ret := DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE(cursor_name); DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(cursor_name); END;
Creating such a procedure enables you to perform the following operations:
-
The SQL statement can be dynamically generated at runtime by the calling program.
-
The SQL statement can be a DDL statement or a DML without binds.
For example, after creating this procedure, you could make the following call:
exec('create table acct(c1 integer)');
You could even call this procedure remotely, as shown in the following example. This lets you perform remote DDL.
exec@domain.com('CREATE TABLE acct(c1 INTEGER)');Example 3
The following sample procedure is passed the names of a source and a destination table, and copies the rows from the source table to the destination table. This sample procedure assumes that both the source and destination tables have the following columns:
id of type NUMBER name of type VARCHAR2(30) birthdate of type DATE
This procedure does not need the use of dynamic SQL; however, it illustrates the concepts of this package.
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE copy (
source IN VARCHAR2,
destination IN VARCHAR2) IS
id_var NUMBER;
name_var VARCHAR2(30);
birthdate_var DATE;
source_cursor INTEGER;
destination_cursor INTEGER;
ignore INTEGER;
BEGIN
-- Prepare a cursor to select from the source table:
source_cursor := dbms_sql.open_cursor;
DBMS_SQL.PARSE(source_cursor,
'SELECT id, name, birthdate FROM ' || source,
DBMS_SQL.NATIVE);
DBMS_SQL.DEFINE_COLUMN(source_cursor, 1, id_var);
DBMS_SQL.DEFINE_COLUMN(source_cursor, 2, name_var, 30);
DBMS_SQL.DEFINE_COLUMN(source_cursor, 3, birthdate_var);
ignore := DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE(source_cursor);
-- Prepare a cursor to insert into the destination table:
destination_cursor := DBMS_SQL.OPEN_CURSOR;
DBMS_SQL.PARSE(destination_cursor,
'INSERT INTO ' || destination ||
' VALUES (:id_bind, :name_bind, :birthdate_bind)',
DBMS_SQL.NATIVE);
-- Fetch a row from the source table and insert it into the destination table:
LOOP
IF DBMS_SQL.FETCH_ROWS(source_cursor)>0 THEN
-- get column values of the row
DBMS_SQL.COLUMN_VALUE(source_cursor, 1, id_var);
DBMS_SQL.COLUMN_VALUE(source_cursor, 2, name_var);
DBMS_SQL.COLUMN_VALUE(source_cursor, 3, birthdate_var);
-- Bind the row into the cursor that inserts into the destination table. You
-- could alter this example to require the use of dynamic SQL by inserting an
-- if condition before the bind.
DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE(destination_cursor, ':id_bind', id_var);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE(destination_cursor, ':name_bind', name_var);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE(destination_cursor, ':birthdate_bind',
birthdate_var);
ignore := DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE(destination_cursor);
ELSE
-- No more rows to copy:
EXIT;
END IF;
END LOOP;
-- Commit and close all cursors:
COMMIT;
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(source_cursor);
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(destination_cursor);
EXCEPTION
WHEN OTHERS THEN
IF DBMS_SQL.IS_OPEN(source_cursor) THEN
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(source_cursor);
END IF;
IF DBMS_SQL.IS_OPEN(destination_cursor) THEN
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(destination_cursor);
END IF;
RAISE;
END;
/ Example 4: RETURNING clause
With this clause, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements can return values of expressions in bind variables.
If a single row is inserted, updated, or deleted, then use DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE to bind these outbinds. To get the values in these bind variables, call DBMS_SQL.VARIABLE_VALUE
Note:
This process is similar to DBMS_SQL.VARIABLE_VALUE, which must be called after running a PL/SQL block with an outbind inside DBMS_SQL.
i) Single-row insert
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE single_Row_insert
(c1 NUMBER, c2 NUMBER, r OUT NUMBER) is
c NUMBER;
n NUMBER;
begin
c := DBMS_SQL.OPEN_CURSOR;
DBMS_SQL.PARSE(c, 'INSERT INTO tab VALUES (:bnd1, :bnd2) ' ||
'RETURNING c1*c2 INTO :bnd3', DBMS_SQL.NATIVE);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE(c, 'bnd1', c1);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE(c, 'bnd2', c2);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE(c, 'bnd3', r);
n := DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE(c);
DBMS_SQL.VARIABLE_VALUE(c, 'bnd3', r); -- get value of outbind variable
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(c);
END;
/
ii) Single-row update
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE single_Row_update
(c1 NUMBER, c2 NUMBER, r out NUMBER) IS
c NUMBER;
n NUMBER;
BEGIN
c := DBMS_SQL.OPEN_CURSOR;
DBMS_SQL.PARSE(c, 'UPDATE tab SET c1 = :bnd1, c2 = :bnd2 ' ||
'WHERE rownum < 2 ' ||
'RETURNING c1*c2 INTO :bnd3', DBMS_SQL.NATIVE);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE(c, 'bnd1', c1);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE(c, 'bnd2', c2);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE(c, 'bnd3', r);
n := DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE(c);
DBMS_SQL.VARIABLE_VALUE(c, 'bnd3', r);-- get value of outbind variable
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(c);
END;
/
iii) Single-row delete
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE single_Row_Delete
(c1 NUMBER, r OUT NUMBER) is
c NUMBER;
n number;
BEGIN
c := DBMS_SQL.OPEN_CURSOR;
DBMS_SQL.PARSE(c, 'DELETE FROM tab WHERE ROWNUM = :bnd1 ' ||
'RETURNING c1*c2 INTO :bnd2', DBMS_SQL.NATIVE);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE(c, 'bnd1', c1);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE(c, 'bnd2', r);
n := DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE(c);
DBMS_SQL.VARIABLE_VALUE(c, 'bnd2', r);-- get value of outbind variable
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(c);
END;
/
iv) Multiple-row insert
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE multi_Row_insert
(c1 DBMS_SQL.NUMBER_TABLE, c2 DBMS_SQL.NUMBER_TABLE,
r OUT DBMS_SQL.NUMBER_TABLE) is
c NUMBER;
n NUMBER;
BEGIN
c := DBMS_SQL.OPEN_CURSOR;
DBMS_SQL.PARSE(c, 'insert into tab VALUES (:bnd1, :bnd2) ' ||
'RETURNING c1*c2 INTO :bnd3', DBMS_SQL.NATIVE);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_ARRAY(c, 'bnd1', c1);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_ARRAY(c, 'bnd2', c2);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_ARRAY(c, 'bnd3', r);
n := DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE(c);
DBMS_SQL.VARIABLE_VALUE(c, 'bnd3', r);-- get value of outbind variable
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(c);
END;
/
v) Multiple-row update.
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE multi_Row_update
(c1 NUMBER, c2 NUMBER, r OUT DBMS_SQL.NUMBER_TABLE) IS
c NUMBER;
n NUMBER;
BEGIN
c := DBMS_SQL.OPEN_CURSOR;
DBMS_SQL.PARSE(c, 'UPDATE tab SET c1 = :bnd1 WHERE c2 = :bnd2 ' ||
'RETURNING c1*c2 INTO :bnd3', DBMS_SQL.NATIVE);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE(c, 'bnd1', c1);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE(c, 'bnd2', c2);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_ARRAY(c, 'bnd3', r);
n := DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE(c);
DBMS_SQL.VARIABLE_VALUE(c, 'bnd3', r);-- get value of outbind variable
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(c);
END;
/Note:
bnd1 and bnd2 can be arrays too. The value of the expression for all the rows updated will be in bnd3. There is no way to determine which rows were updated for each value of bnd1 and bnd2.
vi) Multiple-row delete
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE multi_row_delete
(c1 DBMS_SQL.NUMBER_TABLE,
r OUT DBMS_SQL.NUMBER_TABLE) is
c NUMBER;
n NUMBER;
BEGIN
c := DBMS_SQL.OPEN_CURSOR;
DBMS_SQL.PARSE(c, 'DELETE FROM tab WHERE c1 = :bnd1' ||
'RETURNING c1*c2 INTO :bnd2', DBMS_SQL.NATIVE);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_ARRAY(c, 'bnd1', c1);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_ARRAY(c, 'bnd2', r);
n := DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE(c);
DBMS_SQL.VARIABLE_VALUE(c, 'bnd2', r);-- get value of outbind variable
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(c);
END;
/
vii) outbind in bulk PL/SQL
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE foo (n NUMBER, square OUT NUMBER) IS
BEGIN square := n * n; END;/
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE bulk_plsql
(n DBMS_SQL.NUMBER_TABLE, square OUT DBMS_SQL.NUMBER_TABLE) IS
c NUMBER;
r NUMBER;
BEGIN
c := DBMS_SQL.OPEN_CURSOR;
DBMS_SQL.PARSE(c, 'BEGIN foo(:bnd1, :bnd2); END;', DBMS_SQL.NATIVE);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_ARRAY(c, 'bnd1', n);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_ARRAY(c, 'bnd2', square);
r := DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE(c);
DBMS_SQL.VARIABLE_VALUE(c, 'bnd2', square);
END;
/Note:
DBMS_SQL.BIND_ARRAY of number_Table internally binds a number. The number of times statement is run depends on the number of elements in an inbind array.
Example 5: Binds and Defines of User-defined Types in DBMS_SQL
CREATE TYPE dnames_var IS VARRAY(7) OF VARCHAR2(30)
/
CREATE TABLE depts (region VARCHAR2(25), dept_names dnames_var)
/
INSERT INTO depts VALUES('Europe', dnames_var('Shipping','Sales','Finance'))
/
INSERT INTO depts VALUES('Americas', dnames_var('Sales','Finance','Shipping'))
/
INSERT INTO depts VALUES('Asia', dnames_var('Finance','Payroll','Shipping','Sales'))
/
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE update_depts(new_dnames dnames_var, region VARCHAR2) IS
some_dnames dnames_var;
c NUMBER;
r NUMBER;
sql_stmt VARCHAR2(32767) :=
'UPDATE depts SET dept_names = :b1 WHERE region = :b2 RETURNING dept_names INTO :b3';
BEGIN
c := DBMS_SQL.OPEN_CURSOR;
DBMS_SQL.PARSE(c, sql_stmt, dbms_sql.native);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE(c, 'b1', new_dnames);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE(c, 'b2', region);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE(c, 'b3', some_dnames);
r := DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE(c);
-- Get value of outbind variable
DBMS_SQL.VARIABLE_VALUE(c, 'b3', some_dnames);
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(c);
-- select dept_names
sql_stmt := 'SELECT dept_names FROM depts WHERE region = :b1';
c := DBMS_SQL.OPEN_CURSOR;
DBMS_SQL.PARSE(c, sql_stmt, dbms_sql.native);
DBMS_SQL.DEFINE_COLUMN(c, 1, some_dnames);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE(c, 'b1', region);
r := DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE_AND_FETCH(c);
DBMS_SQL.COLUMN_VALUE(c, 1, some_dnames);
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(c);
-- loop through some_dnames collections
FOR i IN some_dnames.FIRST .. some_dnames.LAST LOOP
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('Dept. Name = ' || some_dnames(i) || ' Updated!');
END LOOP;
END;
/
DECLARE
new_dnames dnames_var;
BEGIN
new_dnames := dnames_var('Benefits', 'Advertising', 'Contracting',
'Executive', 'Marketing');
update_depts(new_dnames, 'Asia');
END;
/187.8 DBMS_SQL Data Structures
The DBMS_SQL package defines RECORD type and TABLE type data structures.
RECORD Types
TABLE Types for DESCRIBE_COLUMNS Procedures
TABLE Types For Scalar and LOB Collections
DBMS_SQL bulk operations are only supported with these predefined DBMS_SQL TABLE types.
187.8.1 DBMS_SQL DESC_REC Record Type
This record type holds the describe information for a single column in a dynamic query.
Note:
This type has been deprecated in favor of the DESC_REC2 Record Type.
It is the element type of the DESC_TAB table type and the DESCRIBE_COLUMNS Procedure.
Syntax
TYPE desc_rec IS RECORD (
col_type BINARY_INTEGER := 0,
col_max_len BINARY_INTEGER := 0,
col_name VARCHAR2(32) := '',
col_name_len BINARY_INTEGER := 0,
col_schema_name VARCHAR2(32) := '',
col_schema_name_len BINARY_INTEGER := 0,
col_precision BINARY_INTEGER := 0,
col_scale BINARY_INTEGER := 0,
col_charsetid BINARY_INTEGER := 0,
col_charsetform BINARY_INTEGER := 0,
col_null_ok BOOLEAN := TRUE);
TYPE desc_tab IS TABLE OF desc_rec INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER;Fields
Table 187-2 DESC_REC Fields
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Type of column |
|
|
Maximum column length |
|
|
Name of column |
|
|
Length of column name |
|
|
Column schema name |
|
|
Length of column schema name |
|
|
Precision of column |
|
|
Scale of column |
|
|
Column character set id |
|
|
Column character set form |
|
|
|
187.8.2 DBMS_SQL DESC_REC2 Record Type
DESC_REC2 is the element type of the DESC_TAB2 table type and the DESCRIBE_COLUMNS2 Procedure.
This record type is identical to DESC_REC except for the col_name field, which has been expanded to the maximum possible size for VARCHAR2. It is therefore preferred to DESC_REC because column name values can be greater than 32 characters. DESC_REC is deprecated as a result.
Syntax
TYPE desc_rec2 IS RECORD ( col_type binary_integer := 0, col_max_len binary_integer := 0, col_name varchar2(32767) := '', col_name_len binary_integer := 0, col_schema_name varchar2(32) := '', col_schema_name_len binary_integer := 0, col_precision binary_integer := 0, col_scale binary_integer := 0, col_charsetid binary_integer := 0, col_charsetform binary_integer := 0, col_null_ok boolean := TRUE);
Fields
Table 187-3 DESC_REC2 Fields
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Type of column |
|
|
Maximum column length |
|
|
Name of column |
|
|
Length of column name |
|
|
Column schema name |
|
|
Length of column schema name |
|
|
Precision of column |
|
|
Scale of column |
|
|
Column character set id |
|
|
Column character set form |
|
|
|
Related Topics
187.8.3 DBMS_SQL DESC_REC3 Record Type
DESC_REC3 is the element type of the DESC_TAB3 table type and the DESCRIBE_COLUMNS3 Procedure.
DESC_REC3 is identical to DESC_REC2 except for two additional fields to hold the type name (type_name) and type name len (type_name_len) of a column in a dynamic query. These two fields hold the type name and type name length when the column is a user-defined type (a collection or object type). The col_type_name and col_type_name_len fields are only populated when the col_type field's value is 109, the Oracle type number for user-defined types.
Syntax
TYPE desc_rec3 IS RECORD ( col_type binary_integer := 0, col_max_len binary_integer := 0, col_name varchar2(32767) := '', col_name_len binary_integer := 0, col_schema_name varchar2(32) := '', col_schema_name_len binary_integer := 0, col_precision binary_integer := 0, col_scale binary_integer := 0, col_charsetid binary_integer := 0, col_charsetform binary_integer := 0, col_null_ok boolean := TRUE, col_type_name varchar2(32767) := '', col_type_name_len binary_integer := 0);
Fields
Table 187-4 DESC_REC3 Fields
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Type of column |
|
|
Maximum column length |
|
|
Name of column |
|
|
Length of column name |
|
|
Column schema name |
|
|
Length of column schema name |
|
|
Precision of column |
|
|
Scale of column |
|
|
Column character set ID |
|
|
Column character set form |
|
|
|
|
|
User-define type column type name, this field is valid when |
|
|
Length of user-define type column type name, this field is valid when |
Related Topics
187.8.4 DBMS_SQL DESC_REC4 Record Type
DESC_REC4 is the element type of the DESC_TAB4 table type and the DESCRIBE_COLUMNS3 Procedure.
DESC_REC4 is identical to DESC_REC3 except that it supports longer identifiers in the fields that hold the schema name (col_schema_name) and type name (col_type_name) of a column in a dynamic query.
Syntax
TYPE desc_rec4 IS RECORD ( col_type binary_integer := 0, col_max_len binary_integer := 0, col_name varchar2(32767) := '', col_name_len binary_integer := 0, col_schema_name DBMS_ID := '', col_schema_name_len binary_integer := 0, col_precision binary_integer := 0, col_scale binary_integer := 0, col_charsetid binary_integer := 0, col_charsetform binary_integer := 0, col_null_ok boolean := TRUE, col_type_name DBMS_ID := '', col_type_name_len binary_integer := 0);
See Also:
Oracle Database PL/SQL Language Reference for more information about the predefined subtype DBMS_ID.Fields
Table 187-5 DESC_REC4 Fields
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Type of column |
|
|
Maximum column length |
|
|
Name of column |
|
|
Length of column name |
|
|
Column schema name |
|
|
Length of column schema name |
|
|
Precision of column |
|
|
Scale of column |
|
|
Column character set ID |
|
|
Column character set form |
|
|
|
|
|
User-define type column type name, this field is valid when |
|
|
Length of user-define type column type name, this field is valid when |
Related Topics
187.8.5 DBMS_SQL BFILE_TABLE Table Type
This is a table of BFILE.
Syntax
TYPE bfile_table IS TABLE OF BFILE INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER;
187.8.6 DBMS_SQL BINARY_DOUBLE_TABLE Table Type
This is a table of BINARY_DOUBLE.
Syntax
TYPE binary_double_table IS TABLE OF BINARY_DOUBLE INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER;
187.8.7 DBMS_SQL BINARY_FLOAT_TABLE Table Type
This is a table of BINARY_FLOAT.
Syntax
TYPE binary_float_table IS TABLE OF BINARY_FLOAT INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER;
187.8.8 DBMS_SQL BLOB_TABLE Table Type
This is a table of BLOB.
Syntax
TYPE blob_table IS TABLE OF BLOB INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER;
187.8.9 DBMS_SQL BOOLEAN_TABLE Table Type
This is a table of BOOLEAN.
Syntax
TYPE boolean_table IS TABLE OF BOOLEAN INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER;
187.8.10 DBMS_SQL CLOB_TABLE Table Type
This is a table of CLOB.
Syntax
TYPE clob_table IS TABLE OF CLOB INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER;
187.8.11 DBMS_SQL DATE_TABLE Table Type
This is a table of DATE.
Syntax
type date_table IS TABLE OF DATE INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER;
187.8.12 DBMS_SQL DESC_TAB Table Type
This is a table of DESC_REC Record Type.
Syntax
TYPE desc_tab IS TABLE OF desc_rec INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER;
Related Topics
187.8.13 DBMS_SQL DESC_TAB2 Table Type
This is a table of DESC_REC2 Record Type.
Syntax
TYPE desc_tab2 IS TABLE OF desc_rec2 INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER;
Related Topics
187.8.14 DBMS_SQL DESC_TAB3 Table Type
This is a table of DESC_REC3 Record Type.
Syntax
TYPE desc_tab3 IS TABLE OF desc_rec3 INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER;
Related Topics
187.8.15 DBMS_SQL DESC_TAB4 Table Type
This is a table of DBMS_SQL DESC_REC4 Record Type.
Syntax
TYPE DESC_TAB4 IS TABLE OF DESC_REC4 INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER;
Related Topics
187.8.16 DBMS_SQL INTERVAL_DAY_TO_SECOND_TABLE Table Type
This is a table of DSINTERVAL_UNCONSTRAINED.
Syntax
TYPE interval_day_to_second_Table IS TABLE OF
DSINTERVAL_UNCONSTRAINED INDEX BY binary_integer;187.8.17 DBMS_SQL INTERVAL_YEAR_TO_MONTH_TABLE Table Type
This is a table of YMINTERVAL_UNCONSTRAINED.
Syntax
TYPE interval_year_to_month_table IS TABLE OF YMINTERVAL_UNCONSTRAINED INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER;
187.8.18 DBMS_SQL JSON_TABLE Table Type
This is a table of JSON.
Syntax
TYPE JSON_TABLE IS TABLE OF JSON INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER;
187.8.19 DBMS_SQL NUMBER_TABLE Table Type
This is a table of NUMBER.
Syntax
TYPE number_table IS TABLE OF NUMBER INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER;
187.8.20 DBMS_SQL TIME_TABLE Table Type
This is a table of TIME_UNCONSTRAINED.
Syntax
TYPE time_table IS TABLE OF TIME_UNCONSTRAINED INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER;
187.8.21 DBMS_SQL TIME_WITH_TIME_ZONE_TABLE Table Type
This is a table of TIME_TZ_UNCONSTRAINED.
Syntax
TYPE time_with_time_zone_table IS TABLE OF TIME_TZ_UNCONSTRAINED INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER;;
187.8.22 DBMS_SQL TIMESTAMP_TABLE Table Type
This is a table of TIMESTAMP_UNCONSTRAINED.
Syntax
TYPE timestamp_table IS TABLE OF TIMESTAMP_UNCONSTRAINED INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER;
187.8.23 DBMS_SQL TIMESTAMP_WITH_LTZ_TABLE Table Type
This is a table of TIMESTAMP_LTZ_UNCONSTRAINED
Syntax
TYPE timestamp_with_ltz_table IS TABLE OF
TIMESTAMP_LTZ_UNCONSTRAINED INDEX BY binary_integer;187.8.24 DBMS_SQL TIMESTAMP_WITH_TIME_ZONE_TABLE Table Type
This is a table of TIMESTAMP_TZ_UNCONSTRAINED.
Syntax
TYPE timestamp_with_time_zone_Table IS TABLE OF
TIMESTAMP_TZ_UNCONSTRAINED INDEX BY binary_integer;187.8.25 DBMS_SQL UROWID_TABLE Table Type
This is a table of UROWID.
Syntax
TYPE urowid_table IS TABLE OF UROWID INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER;
187.8.26 DBMS_SQL VARCHAR2_TABLE Table Type
This is table of VARCHAR2(4000).
Syntax
TYPE varchar2_table IS TABLE OF VARCHAR2(4000) INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER;
187.8.27 DBMS_SQL VARCHAR2A Table Type
This is table of VARCHAR2(32767).
Syntax
TYPE varchar2a IS TABLE OF VARCHAR2(32767) INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER;
187.8.28 DBMS_SQL VARCHAR2S Table Type
This is table of VARCHAR2(256).
Note:
This type has been superseded by the VARCHAR2A Table Type. Although it is currently retained for backward compatibility of legacy code, it is in the process of deprecation and will be de-supported in a future release.
Syntax
TYPE varchar2s IS TABLE OF VARCHAR2(256) INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER;
187.9 Summary of DBMS_SQL Subprograms
This table lists the DBMS_SQL subprograms and briefly describes them.
Table 187-6 DBMS_SQL Package Subprograms
| Subprogram | Description |
|---|---|
|
Binds a given value to a given collection. |
|
|
Binds a given value to a given variable. |
|
|
Binds a given value to a given package variable. |
|
|
Closes given cursor and frees memory. |
|
|
Returns value of the cursor element for a given position in a cursor. |
|
|
Returns a selected part of a |
|
|
Defines a collection to be selected from the given cursor, used only with |
|
|
Defines a column to be selected from the given cursor, used only with |
|
|
Defines a column of type |
|
|
Defines a |
|
|
Defines a column of type |
|
|
Defines a column of type |
|
|
Describes the columns for a cursor opened and parsed through |
|
|
Describes the specified column, an alternative to DESCRIBE_COLUMNS Procedure. |
|
|
Describes the specified column, an alternative to DESCRIBE_COLUMNS Procedure. |
|
|
Executes a given cursor. |
|
|
Executes a given cursor and fetch rows. |
|
|
Fetches a row from a given cursor. |
|
|
Gets the statement of the next result returned to the caller of the recursive statement or, if this caller sets itself as the client for the recursive statement, the next result returned to this caller as client. |
|
|
Returns |
|
|
Returns byte offset in the SQL statement text where the error occurred. |
|
|
Returns cumulative count of the number of rows fetched |
|
|
Returns |
|
|
Returns SQL function code for statement. |
|
|
Returns cursor ID number of new cursor. |
|
|
Parses given statement. |
|
|
Returns the result of an executed statement to the client application. |
|
|
Takes an |
|
|
Takes an |
|
|
Returns value of named variable for given cursor. |
|
|
Returns value of named variable for given cursor. It is used to return the values of bind variables inside PL/SQL blocks or DML statements with returning clause for a declared package. The type of the variable must be declared in the package specification. |
187.9.1 BIND_ARRAY Procedures
This procedure binds a given value or set of values to a given variable in a cursor, based on the name of the variable in the statement.
Syntax
DBMS_SQL.BIND_ARRAY ( c IN INTEGER, name IN VARCHAR2, <variable> IN <table_type> [,index1 IN INTEGER, index2 IN INTEGER)] );
Where the <variable> and its corresponding
<table_type> can be any one of the following matching pairs, with
BIND_ARRAY being overloaded to accept different data types.
bdbl_tab Binary_Double_Table
bf_tab Bfile_Table
bflt_tab Binary_Float_Table
bl_tab Blob_Table
bool_tab Boolean_Table
c_tab Varchar2_Table
c_tab Varchar2A
cl_tab Clob_Table
d_tab Date_Table
ids_tab Interval_Day_To_Second_Table
iym_tab Interval_Year_To_Month_Table
j_tab Json_Table
n_tab Number_Table
tm_tab Time_Table
tms_tab Timestamp_Table
tstz_tab Timestamp_With_ltz_Table
tstz_tab Timestamp_With_Time_Zone_Table
ttz_tab Time_With_Time_Zone_Table
ur_tab Urowid_Table
v_tab Vector_Table
Parameters
Table 187-7 BIND_ARRAY Procedure Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
ID number of the cursor to which you want to bind a value. |
|
|
Name of the collection in the statement. |
|
|
Local variable that has been declared as
< |
|
|
Index for the table element that marks the lower bound of the range. |
|
|
Index for the table element that marks the upper bound of the range. |
Usage Notes
For binding a range, the table must contain the elements that specify the range — tab(index1) and tab(index2) — but the range does not have to be dense. Index1 must be less than or equal to index2. All elements between tab(index1) and tab(index2) are used in the bind.
If you do not specify indexes in the bind call, and two different binds in a statement specify tables that contain a different number of elements, then the number of elements actually used is the minimum number between all tables. This is also the case if you specify indexes — the minimum range is selected between the two indexes for all tables.
Not all bind variables in a query have to be array binds. Some can be regular binds and the same value are used for each element of the collections in expression evaluations (and so forth).
Bulk Array Binds
Bulk selects, inserts, updates, and deletes can enhance
the performance of applications by bundling many calls into one. The
DBMS_SQL package lets you work on collections of data using the PL/SQL
table type.
Table items are unbounded homogeneous collections. In persistent storage, they are like other relational tables and have no intrinsic ordering. But when a table item is brought into the workspace (either by querying or by navigational access of persistent data), or when it is created as the value of a PL/SQL variable or parameter, its elements are given subscripts that can be used with array-style syntax to get and set the values of elements.
The subscripts of these elements need not be dense, and can be any number including negative numbers. For example, a table item can contain elements at locations -10, 2, and 7 only.
When a table item is moved from transient workspace to persistent storage, the subscripts are not stored; the table item is unordered in persistent storage.
At bind time the table is copied out from the PL/SQL buffers into local
DBMS_SQL buffers (the same as for all scalar types) and then the table is
manipulated from the local DBMS_SQL buffers. Therefore, if you change the
table after the bind call, then that change does not affect the way the execute acts.
Example 187-1 Use DBMS_SQL.BIND_ARRAY with VECTOR
CREATE TABLE vec_seq_table(
col_vector VECTOR(1, float32),
col_seq NUMBER
);
SET SERVEROUTPUT ON;
DECLARE
cur NUMBER;
stmt_1 VARCHAR2(255) :=
'INSERT INTO vec_seq_table(col_vector, col_seq) VALUES (:1, :2)';
number_array DBMS_SQL.NUMBER_TABLE;
v_array DBMS_SQL.VECTOR_TABLE;
rowsProcessed NUMBER;
BEGIN
FOR cnt IN 1 .. 5 LOOP
v_array(cnt) := TO_VECTOR('[' || cnt || ']', 1, float32);
number_array(cnt) := cnt;
END LOOP;
cur := DBMS_SQL.OPEN_CURSOR();
DBMS_SQL.PARSE(cur, stmt_1, DBMS_SQL.NATIVE);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_ARRAY(cur, ':1', v_array);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_ARRAY(cur, ':2', number_array);
rowsProcessed := DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE(cur);
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(cur);
COMMIT;
END;
/
SELECT * FROM vec_seq_table ORDER BY col_seq;Result:
COL_VECTOR COL_SEQ
----------- -------
[1.0E+000] 1
[2.0E+000] 2
[3.0E+000] 3
[4.0E+000] 4
[5.0E+000] 5
Example 187-2 Examples Using Bulk DML
This series of examples shows how to use bulk array binds (table items) in the SQL DML statements INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE.
Here is an example of a bulk INSERT statement that demonstrates adding seven new employees to the emp table:
DECLARE
stmt VARCHAR2(200);
empno_array DBMS_SQL.NUMBER_TABLE;
empname_array DBMS_SQL.VARCHAR2_TABLE;
jobs_array DBMS_SQL.VARCHAR2_TABLE;
mgr_array DBMS_SQL.NUMBER_TABLE;
hiredate_array DBMS_SQL.VARCHAR2_TABLE;
sal_array DBMS_SQL.NUMBER_TABLE;
comm_array DBMS_SQL.NUMBER_TABLE;
deptno_array DBMS_SQL.NUMBER_TABLE;
c NUMBER;
dummy NUMBER;
BEGIN
empno_array(1):= 9001;
empno_array(2):= 9002;
empno_array(3):= 9003;
empno_array(4):= 9004;
empno_array(5):= 9005;
empno_array(6):= 9006;
empno_array(7):= 9007;
empname_array(1) := 'Dopey';
empname_array(2) := 'Grumpy';
empname_array(3) := 'Doc';
empname_array(4) := 'Happy';
empname_array(5) := 'Bashful';
empname_array(6) := 'Sneezy';
empname_array(7) := 'Sleepy';
jobs_array(1) := 'Miner';
jobs_array(2) := 'Miner';
jobs_array(3) := 'Miner';
jobs_array(4) := 'Miner';
jobs_array(5) := 'Miner';
jobs_array(6) := 'Miner';
jobs_array(7) := 'Miner';
mgr_array(1) := 9003;
mgr_array(2) := 9003;
mgr_array(3) := 9003;
mgr_array(4) := 9003;
mgr_array(5) := 9003;
mgr_array(6) := 9003;
mgr_array(7) := 9003;
hiredate_array(1) := '06-DEC-2006';
hiredate_array(2) := '06-DEC-2006';
hiredate_array(3) := '06-DEC-2006';
hiredate_array(4) := '06-DEC-2006';
hiredate_array(5) := '06-DEC-2006';
hiredate_array(6) := '06-DEC-2006';
hiredate_array(7) := '06-DEC-2006';
sal_array(1):= 1000;
sal_array(2):= 1000;
sal_array(3):= 1000;
sal_array(4):= 1000;
sal_array(5):= 1000;
sal_array(6):= 1000;
sal_array(7):= 1000;
comm_array(1):= 0;
comm_array(2):= 0;
comm_array(3):= 0;
comm_array(4):= 0;
comm_array(5):= 0;
comm_array(6):= 0;
comm_array(7):= 0;
deptno_array(1):= 11;
deptno_array(2):= 11;
deptno_array(3):= 11;
deptno_array(4):= 11;
deptno_array(5):= 11;
deptno_array(6):= 11;
deptno_array(7):= 11;
stmt := 'INSERT INTO emp VALUES(
:num_array, :name_array, :jobs_array, :mgr_array, :hiredate_array,
:sal_array, :comm_array, :deptno_array)';
c := DBMS_SQL.OPEN_CURSOR;
DBMS_SQL.PARSE(c, stmt, DBMS_SQL.NATIVE);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_ARRAY(c, ':num_array', empno_array);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_ARRAY(c, ':name_array', empname_array);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_ARRAY(c, ':jobs_array', jobs_array);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_ARRAY(c, ':mgr_array', mgr_array);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_ARRAY(c, ':hiredate_array', hiredate_array);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_ARRAY(c, ':sal_array', sal_array);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_ARRAY(c, ':comm_array', comm_array);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_ARRAY(c, ':deptno_array', deptno_array);
dummy := DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE(c);
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(c);
EXCEPTION WHEN OTHERS THEN
IF DBMS_SQL.IS_OPEN(c) THEN
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(c);
END IF;
RAISE;
END;
/
SHOW ERRORS;
Here is an example of a bulk UPDATE statement that demonstrates updating salaries for four existing employees in the emp table:
DECLARE
stmt VARCHAR2(200);
empno_array DBMS_SQL.NUMBER_TABLE;
salary_array DBMS_SQL.NUMBER_TABLE;
c NUMBER;
dummy NUMBER;
BEGIN
empno_array(1):= 7369;
empno_array(2):= 7876;
empno_array(3):= 7900;
empno_array(4):= 7934;
salary_array(1) := 10000;
salary_array(2) := 10000;
salary_array(3) := 10000;
salary_array(4) := 10000;
stmt := 'update emp set sal = :salary_array
WHERE empno = :num_array';
c := DBMS_SQL.OPEN_CURSOR;
DBMS_SQL.PARSE(c, stmt, DBMS_SQL.NATIVE);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_ARRAY(c, ':num_array', empno_array);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_ARRAY(c, ':salary_array', salary_array);
dummy := DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE(c);
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(c);
EXCEPTION WHEN OTHERS THEN
IF DBMS_SQL.IS_OPEN(c) THEN
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(c);
END IF;
RAISE;
END;
/In a DELETE statement, for example, you could bind an array in the WHERE clause and have the statement be run for each element in the array:
DECLARE
stmt VARCHAR2(200);
dept_no_array DBMS_SQL.NUMBER_TABLE;
c NUMBER;
dummy NUMBER;
begin
dept_no_array(1) := 10; dept_no_array(2) := 20;
dept_no_array(3) := 30; dept_no_array(4) := 40;
dept_no_array(5) := 30; dept_no_array(6) := 40;
stmt := 'delete from emp where deptno = :dept_array';
c := DBMS_SQL.OPEN_CURSOR;
DBMS_SQL.PARSE(c, stmt, DBMS_SQL.NATIVE);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_ARRAY(c, ':dept_array', dept_no_array, 1, 4);
dummy := DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE(c);
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(c);
EXCEPTION WHEN OTHERS THEN
IF DBMS_SQL.IS_OPEN(c) THEN
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(c);
END IF;
RAISE;
END;
/
In the preceding example, only elements 1 through 4 are used as specified by the BIND_ARRAY call. Each element of the array potentially deletes a large number of employees from the database.
187.9.2 BIND_VARIABLE Procedures
These procedures bind a given value or set of values to a given variable in a cursor, based on the name of the variable in the statement.
Syntax
DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE ( c IN INTEGER, name IN VARCHAR2, value IN <datatype>);
Where <datatype> can be any one of the following types:
ADT (user-defined object types) BINARY_DOUBLE BINARY_FLOAT BFILE BLOB BOOLEAN CLOB CHARACTER SET ANY_CS DATE DSINTERVAL_UNCONSTRAINED JSON NESTED table NUMBER OPAQUE types REF TIME_UNCONSTRAINED TIME_TZ_UNCONSTRAINED TIMESTAMP_LTZ_UNCONSTRAINED TIMESTAMP_TZ_UNCONSTRAINED TIMESTAMP_UNCONSTRAINED UROWID VARCHAR2 CHARACTER SET ANY_CS VARRAY VECTOR YMINTERVAL_UNCONSTRAINED
Notice that BIND_VARIABLE is overloaded to accept different data
types.
The following syntax is also supported for BIND_VARIABLE. The square brackets [] indicate an optional parameter for the BIND_VARIABLE procedure.
DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE ( c IN INTEGER, name IN VARCHAR2, value IN VARCHAR2 CHARACTER SET ANY_CS [,out_value_size IN INTEGER]);
To bind CHAR, RAW, and ROWID data, you can use the following variations on the syntax:
DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE_CHAR ( c IN INTEGER, name IN VARCHAR2, value IN CHAR CHARACTER SET ANY_CS [,out_value_size IN INTEGER]); DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE_RAW ( c IN INTEGER, name IN VARCHAR2, value IN RAW [,out_value_size IN INTEGER]); DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE_ROWID ( c IN INTEGER, name IN VARCHAR2, value IN ROWID);
Pragmas
pragma restrict_references(bind_variable,WNDS);
Parameters
Table 187-8 BIND_VARIABLE Procedures Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
ID number of the cursor to which you want to bind a value. |
|
|
Name of the variable in the statement. The length of the bind variable name must be <=30 bytes. |
|
|
Value that you want to bind to the variable in the cursor. For |
|
|
Maximum expected If no size is given, then the length of the current value is used. This parameter must be specified if the |
Usage Notes
If the variable is an IN or IN/OUT variable or an IN collection, then the given bind value must be valid for the variable or array type. Bind values for OUT variables are ignored.
The bind variables or collections of a SQL statement are identified by their names. When binding a value to a bind variable or bind array, the string identifying it in the statement must contain a leading colon, as shown in the following example:
SELECT emp_name FROM emp WHERE SAL > :X;
For this example, the corresponding bind call would look similar to
BIND_VARIABLE(cursor_name, ':X', 3500); or BIND_VARIABLE (cursor_name, 'X', 3500);
187.9.3 BIND_VARIABLE_PKG Procedure
This procedures binds a variable given value or set of values to a given variable in a cursor, based on the name of the variable in the statement. The type of the variable must be declared in the package specification. Bulk operations are not supported for these types.
Syntax
DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE_PKG ( c IN INTEGER, name IN VARCHAR2, value IN <datatype>);
Where <datatype> can be any one of the following data types:
-
RECORD
-
VARRAY
-
NESTED TABLE
-
INDEX BY PLS_INTEGER TABLE
-
INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER TABLE
Table 187-9 BIND_VARIABLE_PKG Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
ID number of the cursor from which to get the values. |
|
|
Name of the variable in the statement for which you are retrieving the value. |
|
|
|
Example 187-3 Dynamic SQL using DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE_PKG to Bind a Package Variable
The variables types are declared in the package specification. The BIND_VARIABLE_PKG is used to bind the variable v1 in the cursor SQL statement.
CREATE OR REPLACE PACKAGE ty_pkg AS
TYPE rec IS RECORD ( n1 NUMBER, n2 NUMBER);
TYPE trec IS TABLE OF REC INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER;
TYPE trect IS TABLE OF NUMBER;
TYPE trecv IS VARRAY(100) OF NUMBER;
END ty_pkg;
/
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE dyn_sql_ibbi AS
dummy NUMBER;
cur NUMBER;
v1 ty_pkg.trec;
str VARCHAR2(3000);
n1 NUMBER;
n2 NUMBER;
BEGIN
FOR i in 1..3 LOOP
v1(i).n1 := i*10;
v1(i).n2 := i*20;
END LOOP;
str := 'SELECT * FROM TABLE(:v1)' ;
cur := DBMS_SQL.OPEN_CURSOR();
DBMS_SQL.PARSE(cur, str, DBMS_SQL.NATIVE);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE_PKG(cur, ':v1', v1);
dummy := DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE(cur);
DBMS_SQL.DEFINE_COLUMN(cur, 1, n1);
DBMS_SQL.DEFINE_COLUMN(cur, 2, n2);
LOOP
IF DBMS_SQL.FETCH_ROWS(cur) > 0 THEN
-- get column values of the row
DBMS_SQL.COLUMN_VALUE(cur, 1, n1);
DBMS_SQL.COLUMN_VALUE(cur, 2, n2);
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('n1 = '||n1||' n2 = '||n2);
ELSE
-- No more rows
EXIT;
END IF;
END LOOP;
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(cur);
END dyn_sql_ibbi;
/
EXEC dyn_sql_ibbi;
n1 = 10 n2 = 20
n1 = 20 n2 = 40
n1 = 30 n2 = 60
187.9.4 CLOSE_CURSOR Procedure
This procedure closes a given cursor.
Syntax
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR ( c IN OUT INTEGER);
Pragmas
pragma restrict_references(close_cursor,RNDS,WNDS);
Parameters
Table 187-10 CLOSE_CURSOR Procedure Parameters
| Parameter | Mode | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
ID number of the cursor that you want to close. |
|
|
|
Cursor is set to null. After you call |
187.9.5 COLUMN_VALUE Procedure
This procedure returns the value of the cursor element for a given position in a given cursor. This procedure is used to access the data fetched by calling FETCH_ROWS.
Syntax
DBMS_SQL.COLUMN_VALUE ( c IN INTEGER, position IN INTEGER, value OUT <datatype> [,column_error OUT NUMBER] [,actual_length OUT INTEGER]);
Where square brackets [ ] indicate optional parameters and <datatype> can be any one of the following types:
BINARY_DOUBLE BINARY_FLOAT BFILE BLOB BOOLEAN CLOB CHARACTER SET ANY_CS DATE DSINTERVAL_UNCONSTRAINED JSON NUMBER TIME_TZ_UNCONSTRAINED TIME_UNCONSTRAINED TIMESTAMP_LTZ_UNCONSTRAINED TIMESTAMP_TZ_UNCONSTRAINED TIMESTAMP_UNCONSTRAINED UROWID VARCHAR2 CHARACTER SET ANY_CS VECTOR YMINTERVAL_UNCONSTRAINED user-defined object types collections (VARRAYs and nested tables) REFs Opaque types
For variables containing CHAR, RAW, and ROWID data, you can use the following variations on the syntax:
DBMS_SQL.COLUMN_VALUE_CHAR ( c IN INTEGER, position IN INTEGER, value OUT CHAR CHARACTER SET ANY_CS [,column_error OUT NUMBER] [,actual_length OUT INTEGER]); DBMS_SQL.COLUMN_VALUE_RAW ( c IN INTEGER, position IN INTEGER, value OUT RAW [,column_error OUT NUMBER] [,actual_length OUT INTEGER]); DBMS_SQL.COLUMN_VALUE_ROWID ( c IN INTEGER, position IN INTEGER, value OUT ROWID [,column_error OUT NUMBER] [,actual_length OUT INTEGER]);
The following syntax enables the COLUMN_VALUE procedure to accommodate bulk operations:
DBMS_SQL.COLUMN_VALUE( c IN INTEGER, position IN INTEGER, <param_name> IN OUT NOCOPY <table_type>);
Where the <param_name> and its corresponding <table_type> can be any one of these matching pairs:
bdbl_tab Binary_Double_Table bf_tab Bfile_Table bflt_tab Binary_Float_Table bl_tab Blob_Table bool_tab Boolean_Table c_tab Varchar2_Table c_tab Varchar2A cl_tab Clob_Table d_tab Date_Table ids_tab Interval_Day_To_Second_Table iym_tab Interval_Year_To_Month_Table j_tab Json_table n_tab Number_Table tm_tab Time_Table tms_tab Timestamp_Table tstz_tab Timestamp_With_ltz_Table tstz_tab Timestamp_With_Time_Zone_Table ttz_tab Time_With_Time_Zone_Table ur_tab Urowid_Table v_tab Vector_Table
Pragmas
pragma restrict_references(column_value,RNDS,WNDS);
Parameters
Table 187-11 COLUMN_VALUE Procedure Parameters (Single Row)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
ID number of the cursor from which you are fetching the values. |
|
|
Relative position of the column in the cursor. The first column in a statement has position 1. |
|
|
Returns the value at the specified column. Oracle raises exception |
|
|
Returns any error code for the specified column value. |
|
|
The actual length, before any truncation, of the value in the specified column. |
Table 187-12 COLUMN_VALUE Procedure Parameters (Bulk)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
ID number of the cursor from which you are fetching the values. |
|
|
Relative position of the column in the cursor. The first column in a statement has position 1. |
|
|
Local variable that has been declared < For bulk operations, the subprogram appends the new elements at the appropriate (implicitly maintained) index. For instance if on utilizing the DEFINE_ARRAY Procedure a batch size (the |
Exceptions
INCONSISTENT_TYPE (ORA-06562) is raised if the type of the given OUT parameter value is different from the actual type of the value. This type was the given type when the column was defined by calling procedure DEFINE_COLUMN.
Example 187-4 Use COLUMN_VALUE Procedure with the VECTOR Data Type
This example demonstrates using the COLUMN_VALUE procedure
along with the procedures DEFINE_ARRAY, the table type
VECTOR_Table, and the function FROM_VECTOR to interact
with a table with a VECTOR column.
DROP TABLE dbmsSqlTable;
CREATE TABLE dbmsSqlTable (embedding VECTOR(3, float32), id NUMBER);
INSERT INTO dbmsSqlTable VALUES ('[1.11, 2.22, 3.33]', 1);
INSERT INTO dbmsSqlTable VALUES ('[4.44, 5.55, 6.66]', 2);
INSERT INTO dbmsSqlTable VALUES ('[7.77, 8.88, 9.99]', 3);
SET SERVEROUTPUT ON;
DECLARE
cur NUMBER;
stmt_1 VARCHAR2(255) := 'SELECT embedding FROM dbmsSqlTable ORDER BY id';
vecArray DBMS_SQL.VECTOR_TABLE;
rowsProcessed NUMBER;
BEGIN
cur := DBMS_SQL.OPEN_CURSOR();
DBMS_SQL.PARSE(cur, stmt_1, DBMS_SQL.NATIVE);
DBMS_SQL.DEFINE_ARRAY(cur, 1, vecArray, 3, 1);
rowsProcessed := DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE_AND_FETCH(cur);
FOR i IN 1..rowsProcessed LOOP
DBMS_SQL.COLUMN_VALUE(cur, 1, vecArray);
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('fetched ID ' || i || ': ' || FROM_VECTOR(vecArray(i)));
END LOOP;
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(cur);
END;
/Result:
fetched ID 1: [1.11000001E+000,2.22000003E+000,3.32999992E+000]
fetched ID 2: [4.44000006E+000,5.55000019E+000,6.65999985E+000]
fetched ID 3: [7.76999998E+000,8.88000011E+000,9.98999977E+000]187.9.6 COLUMN_VALUE_LONG Procedure
This procedure gets part of the value of a long column.
Syntax
DBMS_SQL.COLUMN_VALUE_LONG ( c IN INTEGER, position IN INTEGER, length IN INTEGER, offset IN INTEGER, value OUT VARCHAR2, value_length OUT INTEGER);
Pragmas
pragma restrict_references(column_value_long,RNDS,WNDS);
Parameters
Table 187-13 COLUMN_VALUE_LONG Procedure Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Cursor ID number of the cursor from which to get the value. |
|
|
Position of the column of which to get the value. |
|
|
Number of bytes of the long value to fetch. |
|
|
Offset into the long field for start of fetch. |
|
|
Value of the column as a |
|
|
Number of bytes actually returned in value. |
187.9.7 DEFINE_ARRAY Procedure
This procedure defines the collection for column into which you want to
fetch rows (with a FETCH_ROWS call). This procedure lets you do batch fetching
of rows from a single SELECT statement. A single fetch call brings over a
number of rows into the PL/SQL aggregate object.
When you fetch the rows, they are copied into DBMS_SQL buffers until
you run a COLUMN_VALUE call, at which time the rows are copied into the
table that was passed as an argument to the COLUMN_VALUE call.
Syntax
DBMS_SQL.DEFINE_ARRAY ( c IN INTEGER, position IN INTEGER, <variable> IN <table_type> cnt IN INTEGER, lower_bound IN INTEGER);
Where <variable> and its corresponding
<table_type> can be any one of the following matching pairs, with
DEFINE_ARRAY being overloaded to accept different data types:
bdbl_tab Binary_Double_Table
bf_tab Bfile_Table
bflt_tab Binary_Float_Table
bl_tab Blob_Table
bool_tab Boolean_Table
c_tab Varchar2_Table
c_tab Varchar2A
cl_tab Clob_Table
d_tab Date_Table
ids_tab Interval_Day_To_Second_Table
iym_tab Interval_Year_To_Month_Table
j_tab Json_Table
n_tab Number_Table
tm_tab Time_Table
tms_tab Timestamp_Table
tstz_tab Timestamp_With_ltz_Table
tstz_tab Timestamp_With_Time_Zone_Table
ttz_tab Time_With_Time_Zone_Table
ur_tab Urowid_Table
v_tab Vector_TablePragmas
pragma restrict_references(define_array,RNDS,WNDS);
The subsequent FETCH_ROWS call fetch "count" rows. When the
COLUMN_VALUE call is made, these rows are placed in positions
lower_bound, lower_bound+1,
lower_bound+2, and so on. While there are still rows coming, the user keeps
issuing FETCH_ROWS/COLUMN_VALUE calls. The rows keep
accumulating in the table specified as an argument in the COLUMN_VALUE
call.
Parameters
Table 187-14 DEFINE_ARRAY Procedure Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
ID number of the cursor to which you want to bind an array. |
|
|
Relative position of the column in the array being defined. The first column in a statement has position 1. |
|
|
Local variable that has been declared as
< |
|
|
Number of rows that must be fetched. |
|
|
Results are copied into the collection, starting at this lower bound index. |
Usage Notes
The count (cnt) must be an integer greater than zero; otherwise an
exception is raised. The lower_bound can be positive, negative, or zero. A
query on which a DEFINE_ARRAY call was issued cannot contain array
binds.
Examples
PROCEDURE BULK_PLSQL(deptid NUMBER)
TYPE namelist IS TABLE OF employees.last_name%TYPE;
TYPE sallist IS TABLE OF employees.salary%TYPE;
names namelist;
sals sallist;
c NUMBER;
r NUMBER;
sql_stmt VARCHAR2(32767) :=
'SELECT last_name, salary FROM employees WHERE department_id = :b1';
BEGIN
c := DBMS_SQL.OPEN_CURSOR;
DBMS_SQL.PARSE(c, sql_stmt, dbms_sql.native);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE(c, 'b1', deptid);
DBMS_SQL.DEFINE_ARRAY(c, 1, names, 5);
DBMS_SQL.DEFINE_ARRAY(c, 2, sals, 5);
r := DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE(c);
LOOP
r := DBMS_SQL.FETCH_ROWS(c);
DBMS_SQL.COLUMN_VALUE(c, 1, names);
DBMS_SQL.COLUMN_VALUE(c, 2, sals);
EXIT WHEN r != 5;
END LOOP;
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(c);
-- loop through the names and sals collections
FOR i IN names.FIRST .. names.LAST LOOP
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('Name = ' || names(i) || ', salary = ' || sals(i));
END LOOP;
END;
/Example 187-5 Example: Defining an Array
The following examples show how to use the DEFINE_ARRAY procedure:
declare
c NUMBER;
d NUMBER;
n_tab DBMS_SQL.NUMBER_TABLE;
indx NUMBER := -10;
BEGIN
c := DBMS_SQL.OPEN_CURSOR;
dBMS_SQL.PARSE(c, 'select n from t order by 1', DBMS_SQL.NATIVE);
DBMS_SQL.DEFINE_ARRAY(c, 1, n_tab, 10, indx);
d := DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE(c);
loop
d := DBMS_SQL.FETCH_ROWS(c);
DBMS_SQL.COLUMN_VALUE(c, 1, n_tab);
EXIT WHEN d != 10;
END LOOP;
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(c);
EXCEPTION WHEN OTHERS THEN
IF DBMS_SQL.IS_OPEN(c) THEN
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(c);
END IF;
RAISE;
END;
/
Each time the preceding example calls FETCH_ROWS Function, it fetches 10 rows that are kept in DBMS_SQL buffers. When the COLUMN_VALUE Procedure is called, those rows move into the PL/SQL table specified (in this case n_tab), at positions -10 to -1, as specified in the DEFINE statements. When the second batch is fetched in the loop, the rows go to positions 0 to 9; and so on.
A current index into each array is maintained automatically. This index is initialized to "indx" at EXECUTE time and is updated every time COLUMN_VALUE is called. If you reexecute at any point, then the current index for each DEFINE is reinitialized to "indx".
In this way the entire result of the query is fetched into the table. When FETCH_ROWS cannot fetch 10 rows, it returns the number of rows actually fetched (if no rows could be fetched, then it returns zero) and exits the loop.
Here is another example of using the DEFINE_ARRAY procedure:
Consider a table MULTI_TAB defined as:
CREATE TABLE multi_tab (num NUMBER,
dat1 DATE,
var VARCHAR2(24),
dat2 DATE)
To select everything from this table and move it into four PL/SQL tables, you could use the following simple program:
DECLARE
c NUMBER;
d NUMBER;
n_tab DBMS_SQL.NUMBER_TABLE;
d_tab1 DBMS_SQL.DATE_TABLE;
v_tab DBMS_SQL.VARCHAR2_TABLE;
d_tab2 DBMS_SQL.DATE_TABLE;
indx NUMBER := 10;
BEGIN
c := DBMS_SQL.OPEN_CURSOR;
DBMS_SQL.PARSE(c, 'select * from multi_tab order by 1', DBMS_SQL.NATIVE);
DBMS_SQL.DEFINE_ARRAY(c, 1, n_tab, 5, indx);
DBMS_SQL.DEFINE_ARRAY(c, 2, d_tab1, 5, indx);
DBMS_SQL.DEFINE_ARRAY(c, 3, v_tab, 5, indx);
DBMS_SQL.DEFINE_ARRAY(c, 4, d_tab2, 5, indx);
d := DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE(c);
LOOP
d := DBMS_SQL.FETCH_ROWS(c);
DBMS_SQL.COLUMN_VALUE(c, 1, n_tab);
DBMS_SQL.COLUMN_VALUE(c, 2, d_tab1);
DBMS_SQL.COLUMN_VALUE(c, 3, v_tab);
DBMS_SQL.COLUMN_VALUE(c, 4, d_tab2);
EXIT WHEN d != 5;
END LOOP;
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(c);
/*
The four tables can be used for anything. One usage might be to use BIND_ARRAY to move the rows to another table by using a statement such as 'INSERT into SOME_T values (:a, :b, :c, :d);
*/
EXCEPTION WHEN OTHERS THEN
IF DBMS_SQL.IS_OPEN(c) THEN
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(c);
END IF;
RAISE;
END;
/187.9.8 DEFINE_COLUMN Procedures
This procedure defines a column to be selected from the given cursor. This
procedure is only used with SELECT cursors.
The column being defined is identified by its relative position in the SELECT list of the statement in the given cursor. The type of the COLUMN value determines the type of the column being defined.
See also the DEFINE_COLUMN_CHAR Procedure, DEFINE_COLUMN_LONG Procedure, DEFINE_COLUMN_RAW Procedure and DEFINE_COLUMN_ROWID Procedure.
Syntax
DBMS_SQL.DEFINE_COLUMN ( c IN INTEGER, position IN INTEGER, column IN <datatype>);
Where <datatype> can be any one of the following types:
BINARY_DOUBLE BINARY_FLOAT BFILE BLOB BOOLEAN CLOB CHARACTER SET ANY_CS DATE DSINTERVAL_UNCONSTRAINED JSON NUMBER TIME_UNCONSTRAINED TIME_TZ_UNCONSTRAINED TIMESTAMP_LTZ_UNCONSTRAINED TIMESTAMP_TZ_UNCONSTRAINED TIMESTAMP_UNCONSTRAINED UROWID VECTOR YMINTERVAL_UNCONSTRAINED user-defined object types collections (VARRAYs and nested tables) REFs Opaque types
Note that DEFINE_COLUMN is overloaded to accept different datatypes.
The following syntax is also supported for the DEFINE_COLUMN procedure:
DBMS_SQL.DEFINE_COLUMN ( c IN INTEGER, position IN INTEGER, column IN VARCHAR2 CHARACTER SET ANY_CS, column_size IN INTEGER);
Pragmas
pragma restrict_references(define_column,RNDS,WNDS);
Parameters
Table 187-15 DEFINE_COLUMN Procedure Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
ID number of the cursor for the row being defined to be selected. |
|
|
Relative position of the column in the row being defined. The first column in a statement has position 1. |
|
|
Value of the column being defined. The type of this value determines the type for the column being defined. |
|
|
Maximum expected size of the column value in bytes for columns of type |
Usage Notes
When using character length semantics the maximum number of bytes that can be returned for a column value of type VARCHAR2 is calculated as: column_size * maximum character byte size for the current character set. For example, specifying the column_size as 10 means that a maximum of 30 (10*3) bytes can be returned when using character length semantics with a UTF8 character set regardless of the number of characters this represents.
187.9.9 DEFINE_COLUMN_CHAR Procedure
This procedure defines a column with CHAR data to be selected from the given cursor. This procedure is only used with SELECT cursors.
The column being defined is identified by its relative position in the SELECT list of the statement in the given cursor. The type of the COLUMN value determines the type of the column being defined.
See also the DEFINE_COLUMN Procedures, DEFINE_COLUMN_LONG Procedure, DEFINE_COLUMN_RAW Procedure and DEFINE_COLUMN_ROWID Procedure.
Syntax
DBMS_SQL.DEFINE_COLUMN_CHAR ( c IN INTEGER, position IN INTEGER, column IN CHAR CHARACTER SET ANY_CS, column_size IN INTEGER);
Pragmas
pragma restrict_references(define_column,RNDS,WNDS);
Parameters
Table 187-16 DEFINE_COLUMN_CHAR Procedure Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
ID number of the cursor for the row being defined to be selected |
|
|
Relative position of the column in the row being defined.The first column in a statement has position 1. |
|
|
Value of the column being defined. The type of this value determines the type for the column being defined. |
|
|
Maximum expected size of the column value in characters for columns of type |
187.9.10 DEFINE_COLUMN_LONG Procedure
This procedure defines a LONG column for a SELECT cursor. The column being defined is identified by its relative position in the SELECT list of the statement for the given cursor. The type of the COLUMN value determines the type of the column being defined.
See also the DEFINE_COLUMN Procedures, DEFINE_COLUMN_CHAR Procedure, DEFINE_COLUMN_RAW Procedure and DEFINE_COLUMN_ROWID Procedure.
Syntax
DBMS_SQL.DEFINE_COLUMN_LONG ( c IN INTEGER, position IN INTEGER);
Parameters
Table 187-17 DEFINE_COLUMN_LONG Procedure Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
ID number of the cursor for the row being defined to be selected. |
|
|
Relative position of the column in the row being defined. The first column in a statement has position 1. |
187.9.11 DEFINE_COLUMN_RAW Procedure
This procedure defines a column of type RAW to be selected from the given cursor.
This procedure is only used with SELECT cursors.
The column being defined is identified by its relative position in the SELECT list of the statement in the given cursor. The type of the COLUMN value determines the type of the column being defined.
See also the DEFINE_COLUMN Procedures, DEFINE_COLUMN_CHAR Procedure, DEFINE_COLUMN_LONG Procedure and DEFINE_COLUMN_ROWID Procedure.
Syntax
DBMS_SQL.DEFINE_COLUMN_RAW ( c IN INTEGER, position IN INTEGER, column IN RAW, column_size IN INTEGER);
Pragmas
pragma restrict_references(define_column,RNDS,WNDS);
Parameters
Table 187-18 DEFINE_COLUMN_RAW Procedure Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
ID number of the cursor for the row being defined to be selected. |
|
|
Relative position of the column in the row being defined.The first column in a statement has position 1. |
|
|
Value of the column being defined. The type of this value determines the type for the column being defined. |
|
|
Maximum expected size of the column value in bytes for columns of |
187.9.12 DEFINE_COLUMN_ROWID Procedure
This procedure defines a column of type ROWID to be selected from the given cursor. This procedure is only used with SELECT cursors.
The column being defined is identified by its relative position in the SELECT list of the statement in the given cursor. The type of the COLUMN value determines the type of the column being defined.
See also the DEFINE_COLUMN Procedures, DEFINE_COLUMN_CHAR Procedure, DEFINE_COLUMN_LONG Procedure and DEFINE_COLUMN_RAW Procedure.
Syntax
DBMS_SQL.DEFINE_COLUMN_ROWID ( c IN INTEGER, position IN INTEGER, column IN ROWID);
Pragmas
pragma restrict_references(define_column,RNDS,WNDS);
Parameters
Table 187-19 DEFINE_COLUMN_ROWID Procedure Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
ID number of the cursor for the row being defined to be selected |
|
|
Relative position of the column in the row being defined.The first column in a statement has position 1. |
|
|
Value of the column being defined. The type of this value determines the type for the column being defined. |
187.9.13 DESCRIBE_COLUMNS Procedure
This procedure describes the columns for a cursor opened and parsed through DBMS_SQL.
Syntax
DBMS_SQL.DESCRIBE_COLUMNS ( c IN INTEGER, col_cnt OUT INTEGER, desc_t OUT DESC_TAB);
Parameters
Table 187-20 DESCRIBE_COLUMNS Procedure Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
ID number of the cursor for the columns being described |
|
|
Number of columns in the select list of the query |
|
|
Describe table to fill in with the description of each of the columns of the query |
Example 187-6 Describe Columns
This code can be used as a substitute to the SQL*Plus DESCRIBE call by using a SELECT * query on the table that you want to describe.
DECLARE
c NUMBER;
d NUMBER;
col_cnt INTEGER;
f BOOLEAN;
rec_tab DBMS_SQL.DESC_TAB;
col_num NUMBER;
PROCEDURE print_rec(rec in DBMS_SQL.DESC_REC) IS
BEGIN
DBMS_OUTPUT.NEW_LINE;
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('col_type = ' || rec.col_type);
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('col_maxlen = ' || rec.col_max_len);
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('col_name = ' || rec.col_name);
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('col_name_len = ' || rec.col_name_len);
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('col_schema_name = ' || rec.col_schema_name);
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('col_schema_name_len = ' || rec.col_schema_name_len);
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('col_precision = ' || rec.col_precision);
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('col_scale = ' || rec.col_scale);
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT('col_null_ok = ');
IF (rec.col_null_ok) THEN
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('true');
ELSE
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('false');
END IF;
END;
BEGIN
c := DBMS_SQL.OPEN_CURSOR;
DBMS_SQL.PARSE(c, 'SELECT * FROM scott.bonus', DBMS_SQL.NATIVE);
d := DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE(c);
DBMS_SQL.DESCRIBE_COLUMNS(c, col_cnt, rec_tab);
/*
* Following loop could simply be for j in 1..col_cnt loop.
* Here we are simply illustrating some of the PL/SQL table
* features.
*/
col_num := rec_tab.first;
IF (col_num IS NOT NULL) THEN
LOOP
print_rec(rec_tab(col_num));
col_num := rec_tab.next(col_num);
EXIT WHEN (col_num IS NULL);
END LOOP;
END IF;
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(c);
END;
/187.9.14 DESCRIBE_COLUMNS2 Procedure
This procedure describes the specified column. This is an alternative to DESCRIBE_COLUMNS Procedure.
Syntax
DBMS_SQL.DESCRIBE_COLUMNS2 ( c IN INTEGER, col_cnt OUT INTEGER, desc_t OUT DESC_TAB2);
Pragmas
PRAGMA RESTRICT_REFERENCES(describe_columns2,WNDS);
Parameters
Table 187-21 DESCRIBE_COLUMNS2 Procedure Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
ID number of the cursor for the columns being described. |
|
|
Number of columns in the select list of the query. |
|
|
Describe table to fill in with the description of each of the columns of the query. This table is indexed from one to the number of elements in the select list of the query. |
Related Topics
187.9.15 DESCRIBE_COLUMNS3 Procedure
This procedure describes the specified column. This is an alternative to DESCRIBE_COLUMNS Procedure.
Syntax
DBMS_SQL.DESCRIBE_COLUMNS3 ( c IN INTEGER, col_cnt OUT INTEGER, desc_t OUT DESC_TAB3); BMS_SQL.DESCRIBE_COLUMNS3 ( c IN INTEGER, col_cnt OUT INTEGER, desc_t OUT DESC_TAB4);
Pragmas
PRAGMA RESTRICT_REFERENCES(describe_columns3,WNDS);
Parameters
Table 187-22 DESCRIBE_COLUMNS3 Procedure Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
ID number of the cursor for the columns being described. |
|
|
Number of columns in the select list of the query. |
|
|
Describe table to fill in with the description of each of the columns of the query. This table is indexed from one to the number of elements in the select list of the query. |
Usage Notes
The cursor passed in by the cursor ID has to be OPENed and PARSEd, otherwise an "invalid cursor id" error is raised.
Examples
CREATE TYPE PROJECT_T AS OBJECT
( projname VARCHAR2(20),
mgr VARCHAR2(20))
/
CREATE TABLE projecttab(deptno NUMBER, project HR.PROJECT_T)
/
DECLARE
curid NUMBER;
desctab DBMS_SQL.DESC_TAB3;
colcnt NUMBER;
sql_stmt VARCHAR2(200) := 'select * from projecttab';
BEGIN
curid := DBMS_SQL.OPEN_CURSOR;
DBMS_SQL.PARSE(curid, sql_stmt, DBMS_SQL.NATIVE);
DBMS_SQL.DESCRIBE_COLUMNS3(curid, colcnt, desctab);
FOR i IN 1 .. colcnt LOOP
IF desctab(i).col_type = 109 THEN
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT(desctab(i).col_name || ' is user-defined type: ');
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(desctab(i).col_schema_name || '.' ||
desctab(i).col_type_name);
END IF;
END LOOP;
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(curid);
END;
/
Output:
PROJECT is user-defined type: HR.PROJECT_TRelated Topics
187.9.16 EXECUTE Function
This function executes a given cursor. This function accepts the ID number of the cursor and returns the number of rows processed.
The return value is only valid for INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements; for other types of statements, including DDL, the return value is undefined and must be ignored.
Syntax
DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE ( c IN INTEGER) RETURN INTEGER;
Parameters
Table 187-23 EXECUTE Function Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Cursor ID number of the cursor to execute. |
Return Values
Returns number of rows processed
Usage Notes
The DBMS_SQL cursor that is returned by the TO_CURSOR_NUMBER Function performs in the same way as a DBMS_SQL cursor that has already been executed. Consequently, calling EXECUTE for this cursor will cause an error.
187.9.17 EXECUTE_AND_FETCH Function
This function executes the given cursor and fetches rows.
This function provides the same functionality as calling EXECUTE and then calling FETCH_ROWS. Calling EXECUTE_AND_FETCH instead, however, may reduce the number of network round-trips when used against a remote database.
The EXECUTE_AND_FETCH function returns the number of rows actually fetched.
Syntax
DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE_AND_FETCH ( c IN INTEGER, exact IN BOOLEAN DEFAULT FALSE) RETURN INTEGER;
Pragmas
pragma restrict_references(execute_and_fetch,WNDS);
Parameters
Table 187-24 EXECUTE_AND_FETCH Function Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
ID number of the cursor to execute and fetch. |
|
|
Set to Note: Oracle does not support the exact fetch TRUE option with LONG columns. Even if an exception is raised, the rows are still fetched and available. |
Return Values
Returns designated rows
187.9.18 FETCH_ROWS Function
This function fetches a row from a given cursor.
You can call FETCH_ROWS repeatedly as long as there are rows remaining to be fetched. These rows are retrieved into a buffer, and must be read by calling COLUMN_VALUE, for each column, after each call to FETCH_ROWS.
The FETCH_ROWS function accepts the ID number of the cursor to fetch, and returns the number of rows actually fetched.
Syntax
DBMS_SQL.FETCH_ROWS ( c IN INTEGER) RETURN INTEGER;
Pragmas
pragma restrict_references(fetch_rows,WNDS);
Parameters
Table 187-25 FETCH_ROWS Function Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
ID number. |
Return Values
Returns a row from a given cursor
187.9.19 GET_NEXT_RESULT Procedures
This procedure gets the statement of the next result returned to the caller of the recursive statement or, if this caller sets itself as the client for the recursive statement, the next result returned to this caller as client.
The statements are returned in same order as they are returned by the RETURN_RESULT Procedures.
Syntax
DBMS_SQL.GET_NEXT_RESULT( c IN INTEGER, rc OUT SYS_REFCURSOR); DBMS_SQL.GET_NEXT_RESULT( c IN INTEGER, rc OUT INTEGER);
Parameters
Table 187-26 GET_NEXT_RESULT Procedure Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Recursive statement cursor |
|
|
Cursor or ref cursor of the statement of the next returned result |
Exceptions
ORA-01403 no_data_found: This is raised when there is no further returned statement result.
Usage Notes
-
After the cursor of a statement result is retrieved, the caller must close the cursor properly when it is no longer needed.
-
The cursors for all unretrieved returned statements will be closed after the cursor of the recursive statement is closed.
Examples
DECLARE
c INTEGER;
rc SYS_REFCURSOR;
BEGIN
c := DBMS_SQL.OPEN_CURSOR(treat_as_client_for_results => TRUE);
DBMS_SQL.PARSE(c => c,
statement => 'begin proc; end;');
DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE(c);
LOOP
BEGIN
DBMS_SQL.GET_NEXT_RESULT(c, rc);
EXCEPTIONS
WHEN no_data_found THEN
EXIT;
END;
LOOP
FETCH rc INTO ...
...
END LOOP;
END LOOP;
END;187.9.20 IS_OPEN Function
This function checks to see if the given cursor is currently open.
Syntax
DBMS_SQL.IS_OPEN ( c IN INTEGER) RETURN BOOLEAN;
Pragmas
pragma restrict_references(is_open,RNDS,WNDS);
Parameters
Table 187-27 IS_OPEN Function Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Cursor ID number of the cursor to check. |
Return Values
Returns TRUE for any cursor number that has been opened but not closed, and FALSE for a NULL cursor number. Note that the CLOSE_CURSOR Procedure Procedure NULLs out the cursor variable passed to it.
Exceptions
ORA-29471 DBMS_SQL access denied: This is raised if an invalid cursor ID number is detected. Once a session has encountered and reported this error, every subsequent DBMS_SQL call in the same session will raise this error, meaning that DBMS_SQL is non-operational for this session.
187.9.21 LAST_ERROR_POSITION Function
This function returns the byte offset in the SQL statement text where the error occurred. The first character in the SQL statement is at position 0.
Syntax
DBMS_SQL.LAST_ERROR_POSITION RETURN INTEGER;
Pragmas
pragma restrict_references(last_error_position,RNDS,WNDS);
Return Values
Returns the byte offset in the SQL statement text where the error occurred
Usage Notes
Call this function after a PARSE call, before any other DBMS_SQL procedures or functions are called.
187.9.22 LAST_ROW_COUNT Function
This function returns the cumulative count of the number of rows fetched.
Syntax
DBMS_SQL.LAST_ROW_COUNT RETURN INTEGER;
Pragmas
pragma restrict_references(last_row_count,RNDS,WNDS);
Return Values
Returns the cumulative count of the number of rows fetched
Usage Notes
Call this function after a FETCH_ROWS or an EXECUTE_AND_FETCH call. If called after an EXECUTE call, then the value returned is zero.
187.9.23 LAST_ROW_ID Function
This function returns the ROWID of the last row processed.
Syntax
DBMS_SQL.LAST_ROW_ID RETURN ROWID;
Pragmas
pragma restrict_references(last_row_id,RNDS,WNDS);
Return Values
Returns the ROWID of the last row processed
Usage Notes
Call this function after a FETCH_ROWS or an EXECUTE_AND_FETCH call.
187.9.24 LAST_SQL_FUNCTION_CODE Function
This function returns the SQL function code for the statement.
These codes are listed in the Oracle Call Interface Programmer's Guide.
Syntax
DBMS_SQL.LAST_SQL_FUNCTION_CODE RETURN INTEGER;
Pragmas
pragma restrict_references(last_sql_function_code,RNDS,WNDS);
Return Values
Returns the SQL function code for the statement
Usage Notes
You must call this function immediately after the SQL statement is run; otherwise, the return value is undefined.
187.9.25 OPEN_CURSOR Functions
This function opens a new cursor.
The security_level parameter allows for application of fine-grained control to the security of the opened cursor.
Syntax
DBMS_SQL.OPEN_CURSOR ( treat_as_client_for_results IN BOOLEAN DEFAULT FALSE) RETURN INTEGER; DBMS_SQL.OPEN_CURSOR ( security_level IN INTEGER, treat_as_client_for_results IN BOOLEAN DEFAULT FALSE) RETURN INTEGER;
Parameters
Table 187-28 OPEN_CURSOR Function Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Specifies the level of security protection to enforce on the opened cursor. Valid security level values are
|
|
|
Allows the caller of the recursive statement to set itself as the client to receive the statement results returned from the recursive statement to client. The statement results returned may be retrieved by the GET_NEXT_RESULT Procedures. |
Pragmas
pragma restrict_references(open_cursor,RNDS,WNDS);
Return Values
Returns the cursor ID number of the new cursor
Usage Notes
-
When you no longer need this cursor, you must close it explicitly by calling the CLOSE_CURSOR Procedure.
-
You can use cursors to run the same SQL statement repeatedly or to run a new SQL statement. When a cursor is reused, the contents of the corresponding cursor data area are reset when the new SQL statement is parsed. It is never necessary to close and reopen a cursor before reusing it.
187.9.26 PARSE Procedures
This procedure parses the given statement in the given cursor. All statements are parsed immediately. In addition, DDL statements are run immediately when parsed.
There are multiple versions of the PARSE procedure:
-
Taking a
VARCHAR2statement as an argument
-
Taking a segmented string, one taking
VARCHAR2A, aTABLE OF VARCHAR2(32767), and another, takingVARCHAR2S, aTABLE OF VARCHAR2(256), as argument. These overloads concatenate elements of a PL/SQL table statement and parse the resulting string. You can use these procedures to parse a statement that is longer than the limit for a singleVARCHAR2variable by splitting up the statement.
-
Taking a
CLOBstatement as an argument. You can use theCLOBoverload version of the parse procedure to parse a SQL statement larger than 32K bytes.
Syntax
Each version has multiple overloads.
DBMS_SQL.PARSE ( c IN INTEGER, statement IN VARCHAR2, language_flag IN INTEGER[ [,edition IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL], apply_crossedition_trigger IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL, fire_apply_trigger IN BOOLEAN DEFAULT TRUE] [,schema IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL] [,container IN VARCHAR2)];
DBMS_SQL.PARSE ( c IN INTEGER, statement IN CLOB, language_flag IN INTEGER[ [,edition IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL], apply_crossedition_trigger IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL, fire_apply_trigger IN BOOLEAN DEFAULT TRUE] [,schema IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL] [,container IN VARCHAR2)];
DBMS_SQL.PARSE ( c IN INTEGER, statement IN VARCHAR2A, lb IN INTEGER, ub IN INTEGER, lfflg IN BOOLEAN, language_flag IN INTEGER[ [,edition IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL], apply_crossedition_trigger IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL, fire_apply_trigger IN BOOLEAN DEFAULT TRUE] [,schema IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL] [,container IN VARCHAR2)]; DBMS_SQL.PARSE ( c IN INTEGER, statement IN VARCHAR2s, lb IN INTEGER, ub IN INTEGER, lfflg IN BOOLEAN, language_flag IN INTEGER[ [,edition IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL], apply_crossedition_trigger IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL, fire_apply_trigger IN BOOLEAN DEFAULT TRUE] [,schema IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL] [,container IN VARCHAR2)];
Parameters
Table 187-29 PARSE Procedure Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
ID number of the cursor in which to parse the statement. |
|
|
SQL statement to be parsed. SQL statements larger than 32K that may be stored in Unlike a PL/SQL statement, your SQL statement must not include a final semicolon. For example:
|
|
|
Lower bound for elements in the statement |
|
|
Upper bound for elements in the statement |
|
|
If |
|
|
Specifies the behavior for the SQL statement. For more information about the possible values and its corresponding behaviors, see DBMS_SQL Constants |
|
|
Specifies the edition in which to run the statement under the following conditions:
The following general conditions apply. The contents of the string are processed as a SQL identifier; double quotation marks must surround the remainder of the string if special characters or lowercase characters are present in the edition's actual name, and if double quotation marks are not used the contents will be uppercased. |
|
|
Specifies the unqualified name of a forward crossedition trigger that is to be applied to the specified SQL. The name is resolved using the edition and |
|
|
Indicates whether the specified |
|
|
Specifies the schema in which to resolve unqualified object names. If |
|
|
Name of the target container in which the cursor is to run. If |
Usage Notes
-
Using
DBMS_SQLto dynamically run DDL statements can cause the program to stop responding. For example, a call to a procedure in a package results in the package being locked until the execution returns to the user side. Any operation that results in a conflicting lock, such as dynamically trying to drop the package before the first lock is released, stops the program from running. -
Because client-side code cannot reference remote package variables or constants, you must explicitly use the values of the constants.
For example, the following code does not compile on the client:
DBMS_SQL.PARSE(cur_hdl,stmt_str,DBMS_SQL.NATIVE); -- uses constantDBMS_SQL.NATIVEThe following code works on the client, because the argument is explicitly provided:
DBMS_SQL.PARSE(cur_hdl,stmt_str,1); -- compiles on the client -
The
VARCHAR2Stype is currently supported for backward compatibility of legacy code. However, you are advised to useVARCHAR2Aboth for its superior capability and becauseVARCHAR2Swill be deprecated in a future release. -
To parse SQL statements larger than 32 KB, the new
CLOBoverload version of the PARSE procedure can be used instead of theVARCHAR2Aoverload. -
If the
containerparameter value is the same as the calling container, a container switch will not occur. However, the default roles of the current user will be in effect.
Exceptions
If you create a type, procedure, function, or package using DBMS_SQL that has compilation warnings, an ORA-24344 exception is raised, and the PL/SQL unit is still created.
187.9.27 RETURN_RESULT Procedures
This procedure returns the result of an executed statement to the client application.
The result can be retrieved later by the client. Alternatively, it can return the statement result to and be retrieved later by the immediate caller that executes a recursive statement in which this statement result will be returned.
The caller can be:
-
A PL/SQL stored procedure executing the recursive statement using
DBMS_SQL -
A Java stored procedure using JDBC
-
A
.NETstored procedure usingADO.NET -
An external procedure using the Oracle Call Interface (OCI)
Syntax
DBMS_SQL.RETURN_RESULT( rc IN OUT SYS_REFCURSOR, to_client IN BOOLEAN DEFAULT TRUE); DBMS_SQL.RETURN_RESULT( rc IN OUT INTEGER, to_client IN BOOLEAN DEFAULT TRUE);
Parameters
Table 187-30 RETURN_RESULT Procedure Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Statement cursor or ref cursor |
|
|
Returns (or does not return) the statement result to the client. If not, it is returned to the immediate caller. |
Usage Notes
-
Currently only a SQL query can be returned, and the return of statement results over remote procedure calls is not supported.
-
Once the statement is returned, it is no longer accessible except by the client or the immediate caller to which it is returned.
-
Statement results cannot be returned when the statement being executed by the client or any intermediate recursive statement is a SQL query and an error is raised.
-
A ref cursor being returned can be strongly or weakly-typed.
-
A query being returned can be partially fetched.
-
Because
EXECUTEIMMEDIATEstatement provides no interface to retrieve the statement results returned from its recursive statement, the cursors of the statement results returned to the caller of theEXECUTEIMMEDIATEstatement will be closed when the statement completes. To retrieve the returned statement results from a recursive statement in PL/SQL, useDBMS_SQLto execute the recursive statement.
Examples
CREATE PROCEDURE proc AS rc1 sys_refcursor; rc2 sys_refcursor; BEGIN OPEN rc1 FOR SELECT * FROM t1; DBMS_SQL.RETURN_RESULT(rc1); OPEN rc2 FOR SELECT * FROM t2; DBMS_SQL.RETURN_RESULT(rc2); END; /
187.9.28 TO_CURSOR_NUMBER Function
This function takes an OPENed strongly or weakly-typed ref cursor and transforms it into a DBMS_SQL cursor number.
Syntax
DBMS_SQL.TO_CURSOR_NUMBER( rc IN OUT SYS_REFCURSOR) RETURN INTEGER;
Parameters
Table 187-31 TO_CURSOR_NUMBER Function Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
|
Return Values
Returns a DBMS_SQL manageable cursor number transformed from a REF CURSOR
Usage Notes
-
The
REFCURSORpassed in has to beOPENed, otherwise an error is raised. -
Once the
REFCURSORis transformed into aDBMS_SQLcursor number, theREFCURSORis no longer accessible by any native dynamic SQL operations. -
The
DBMS_SQLcursor that is returned by this subprogram performs in the same way as aDBMS_SQLcursor that has already been executed.
Examples
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE DO_QUERY(sql_stmt VARCHAR2) IS
TYPE CurType IS REF CURSOR;
src_cur CurType;
curid NUMBER;
desctab DBMS_SQL.DESC_TAB;
colcnt NUMBER;
namevar VARCHAR2(50);
numvar NUMBER;
datevar DATE;
empno NUMBER := 100;
BEGIN
-- sql_stmt := 'select ...... from employees where employee_id = :b1';
OPEN src_cur FOR sql_stmt USING empno;
-- Switch from native dynamic SQL to DBMS_SQL
curid := DBMS_SQL.TO_CURSOR_NUMBER (src_cur);
DBMS_SQL.DESCRIBE_COLUMNS(curid, colcnt, desctab);
-- Define columns
FOR i IN 1 .. colcnt LOOP
IF desctab(i).col_type = 2 THEN
DBMS_SQL.DEFINE_COLUMN(curid, i, numvar);
ELSIF desctab(i).col_type = 12 THEN
DBMS_SQL.DEFINE_COLUMN(curid, i, datevar);
.......
ELSE
DBMS_SQL.DEFINE_COLUMN(curid, i, namevar, 25);
END IF;
END LOOP;
-- Fetch Rows
WHILE DBMS_SQL.FETCH_ROWS(curid) > 0 LOOP
FOR i IN 1 .. colcnt LOOP
IF (desctab(i).col_type = 1) THEN
DBMS_SQL.COLUMN_VALUE(curid, i, namevar);
ELSIF (desctab(i).col_type = 2) THEN
DBMS_SQL.COLUMN_VALUE(curid, i, numvar);
ELSIF (desctab(i).col_type = 12) THEN
DBMS_SQL.COLUMN_VALUE(curid, i, datevar);
....
END IF;
END LOOP;
END LOOP;
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(curid);
END;
/ 187.9.29 TO_REFCURSOR Function
This function takes an OPENed, PARSEd, and EXECUTEd cursor and transforms/migrates it into a PL/SQL manageable REF CURSOR (a weakly-typed cursor) that can be consumed by PL/SQL native dynamic SQL switched to use native dynamic SQL.
This subprogram is only used with SELECT cursors.
Syntax
DBMS_SQL.TO_REFCURSOR( cursor_number IN OUT INTEGER) RETURN SYS_REFCURSOR;
Parameters
Table 187-32 TO_REFCURSOR Function Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Cursor number of the cursor to be transformed into |
Return Values
Returns a PL/SQL REF CURSOR transformed from a DBMS_SQL cursor number
Usage Notes
-
The cursor passed in by the
cursor_numberhas to beOPENed,PARSEd, andEXECUTEd; otherwise an error is raised. -
Once the cursor_number is transformed into a
REFCURSOR, thecursor_numberis no longer accessible by anyDBMS_SQLoperations. -
After a cursor_number is transformed into a
REFCURSOR, usingDBMS_SQL.IS_OPENto check to see if thecursor_numberis still open results in an error. -
If the cursor number was last parsed with a valid container parameter, it cannot be converted to a
REF CURSOR.
Examples
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE DO_QUERY(mgr_id NUMBER) IS
TYPE CurType IS REF CURSOR;
src_cur CurType;
curid NUMBER;
sql_stmt VARCHAR2(200);
ret INTEGER;
empnos DBMS_SQL.Number_Table;
depts DBMS_SQL.Number_Table;
BEGIN
-- DBMS_SQL.OPEN_CURSOR
curid := DBMS_SQL.OPEN_CURSOR;
sql_stmt := 'SELECT EMPLOYEE_ID, DEPARTMENT_ID from employees where MANAGER_ID = :b1';
DBMS_SQL.PARSE(curid, sql_stmt, DBMS_SQL.NATIVE);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE(curid, 'b1', mgr_id);
ret := DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE(curid);
-- Switch from DBMS_SQL to native dynamic SQL
src_cur := DBMS_SQL.TO_REFCURSOR(curid);
-- Fetch with native dynamic SQL
FETCH src_cur BULK COLLECT INTO empnos, depts;
IF empnos.COUNT > 0 THEN
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('EMPNO DEPTNO');
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('----- ------');
-- Loop through the empnos and depts collections
FOR i IN 1 .. empnos.COUNT LOOP
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(empnos(i) || ' ' || depts(i));
END LOOP;
END IF;
-- Close cursor
CLOSE src_cur;
END;
/ 187.9.30 VARIABLE_VALUE Procedures
This procedure returns the value of the named variable for a given cursor. It is used to return the values of bind variables inside PL/SQL blocks or DML statements with returning clause.
Syntax
DBMS_SQL.VARIABLE_VALUE ( c IN INTEGER, name IN VARCHAR2, value OUT NOCOPY <datatype>);
Where <datatype> can be any one of the following types:
ADT (user-defined object types)
BINARY_DOUBLE
BINARY_FLOAT
BFILE
BLOB
BOOLEAN
CLOB CHARACTER SET ANY_CS
DATE
DSINTERVAL_UNCONSTRAINED
JSON
NESTED table
NUMBER
OPAQUE types
REF
TIME_UNCONSTRAINED
TIME_TZ_UNCONSTRAINED
TIMESTAMP_LTZ_UNCONSTRAINED
TIMESTAMP_TZ_UNCONSTRAINED
TIMESTAMP_UNCONSTRAINED
UROWID
VARCHAR2 CHARACTER SET ANY_CS
VARRAY
VECTOR
YMINTERVAL_UNCONSTRAINEDFor variables containing CHAR, RAW, and
ROWID data, you can use the following variations on the syntax:
DBMS_SQL.VARIABLE_VALUE_CHAR ( c IN INTEGER, name IN VARCHAR2, value OUT CHAR CHARACTER SET ANY_CS); DBMS_SQL.VARIABLE_VALUE_RAW ( c IN INTEGER, name IN VARCHAR2, value OUT RAW); DBMS_SQL.VARIABLE_VALUE_ROWID ( c IN INTEGER, name IN VARCHAR2, value OUT ROWID);
The following syntax enables the VARIABLE_VALUE procedure
to accommodate bulk
operations:
DBMS_SQL.VARIABLE_VALUE ( c IN INTEGER, name IN VARCHAR2, value OUT NOCOPY <table_type>);
For bulk operations, <table_type> must be a
supported DBMS_SQL predefined TABLE type.
Pragmas
pragma restrict_references(variable_value,RNDS,WNDS);
Parameters
Table 187-33 VARIABLE_VALUE Procedure Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
ID number of the cursor from which to get the values. |
|
|
Name of the variable for which you are retrieving the value. |
|
|
|
187.9.31 VARIABLE_VALUE_PKG Procedure
This procedure returns the value of the named variable for a given cursor.
It is used to return the values of bind variables of collection or record types inside PL/SQL blocks or DML statements with returning clause for a declared package. The type of the variable must be declared in the package specification. Bulk operations are not supported for these types.
Syntax
DBMS_SQL.VARIABLE_VALUE_PKG ( c IN INTEGER, name IN VARCHAR2, value OUT NOCOPY <table_type>);
Where <datatype> can be any one of the following data types:
-
RECORD
-
VARRAY
-
NESTED TABLE
-
INDEX BY PLS_INTEGER TABLE
-
INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER TABLE
Parameters
Table 187-34 VARIABLE_VALUE_PKG Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
ID number of the cursor from which to get the values. |
|
|
Name of the variable for which you are retrieving the value. |
|
|
|
Example 187-7 Dynamic SQL using DBMS_SQL.VARIABLE_VALUE_PKG to Get the Value of a Bind Variable
The data types are declared in the package specification. The VARIABLE_VALUE_PKG is used to get the value of the bind variable v2 in the cursor SQL statement.
CREATE OR REPLACE PACKAGE ty_pkg AS
TYPE rec IS RECORD
( n1 NUMBER,
n2 NUMBER);
TYPE trect IS TABLE OF NUMBER;
END ty_pkg;
/
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE dyn_sql_nt AS
dummy NUMBER;
cur NUMBER;
v1 ty_pkg.trect;
v2 ty_pkg.trect;
str VARCHAR2(3000);
BEGIN
v1 := ty_pkg.trect(1000);
str := 'declare v1 ty_pkg.trect; begin v1:=:v1; v1(1) := 2000; :v2 := v1; end;' ;
cur := DBMS_SQL.OPEN_CURSOR();
DBMS_SQL.PARSE(cur, str, DBMS_SQL.NATIVE);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE_PKG(cur, ':v1', v1);
DBMS_SQL.BIND_VARIABLE_PKG(cur, ':v2', v2);
dummy := DBMS_SQL.EXECUTE(cur);
DBMS_SQL.VARIABLE_VALUE_PKG(cur, ':v2', v2);
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('n = '
|| V2(1));
DBMS_SQL.CLOSE_CURSOR(cur);
END dyn_sql_nt;
/
EXEC dyn_sql_nt;
n = 2000