30 Creating Custom Unified Audit Policies
Oracle Database provides the flexibility to create and manage custom unified audit policies for your specialized needs.
- About Custom Unified Audit Policies
You can create custom unified audit policies for specialized needs that are typically not met with predefined unified audit policies. - Best Practices for Creating Custom Unified Audit Policies
You can optimize the number of enabled policies as a best practice though you can enable multiple policies at a time in the database. - Syntax for Creating a Custom Unified Audit Policy
To create a custom unified audit policy, you must use theCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement. - Auditing Standard Oracle Database Components
You can create unified audit policies to monitor components such as roles, system privileges, administrative users, and actions performed on objects such as tables. - Unified Auditing with Configurable Conditions
You can use theCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement to create conditions for a unified audit policy. - Auditing for Multitier or Multitenant Configurations
You can create unified audit policies using conditions and application contexts, and in multitier and multitenant environments. - Extending Unified Auditing to Capture Custom Attributes
You can extend the unified audit trail to capture custom attributes by auditing application context values. - Auditing Components of Other Oracle Products and Features
You can create unified audit policies for Oracle products and features such as Oracle Database Vault, Oracle Real Application Security, Oracle Data Pump, and Oracle Machine Learning for SQL events. - Managing Unified Audit Policies
After you create a unified audit policy, you must enable it. You can alter disable, and drop unified audit policies. - Tutorial: Auditing Nondatabase Users
Auditing nondatabase users who are typical application service accounts is crucial. They are identified in the database using theCLIENT_IDENTIFIERattribute. - Unified Audit Policy Data Dictionary Views
You can query data dictionary and dynamic views to find detailed auditing information about custom unified audit policies.
Parent topic: Monitoring Database Activity with Auditing
30.1 About Custom Unified Audit Policies
You can create custom unified audit policies for specialized needs that are typically not met with predefined unified audit policies.
For example, you may have the following audit requirements:
- Audit access to the database from untrusted database connection paths.
- Audit access to specific sensitive database objects.
- Audit use of certain system privileges.
To create the unified audit policy, you use the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement. The AUDIT and NOAUDIT SQL statements enable and disable audit policies respectively. The AUDIT statement also lets you include or exclude specific users for the policy.
You can have more than one custom unified audit policy effective at any given time. An audit policy can contain both system-wide and object-specific audit options. To find system actions to audit, you can query the AUDITABLE_SYSTEM_ACTIONS system table.
Parent topic: Creating Custom Unified Audit Policies
30.2 Best Practices for Creating Custom Unified Audit Policies
You can optimize the number of enabled policies as a best practice though you can enable multiple policies at a time in the database.
This optimization has the following benefits:
-
It reduces the logon overhead that is associated with loading the audit policy's details into the session's UGA memory. If the enabled policy count is less, then less time is spent in loading the policy information.
-
It makes the internal audit check functionality more efficient, which determines whether to generate an audit record for its associated event.
-
If you have configured a unified audit policy for
LOGONstatements, then audit records for both direct logins as well asALTER SESSIONandSET CONTAINERstatements are generated.
The unified audit policy syntax is designed to group multiple audit settings in a single policy. Refer to predefined audit policies of Oracle Database to see how multiple audit settings are grouped within one unified audit policy.
Parent topic: Creating Custom Unified Audit Policies
30.3 Syntax for Creating a Custom Unified Audit Policy
To create a custom unified audit policy, you must use the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement.
When you create a unified audit policy, Oracle Database stores it in a first class object that is owned by the SYS schema, not in the schema of the user who created the policy.
Example 30-1 shows the syntax for the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement.
Example 30-1 Syntax for the CREATE AUDIT POLICY Statement
CREATE AUDIT POLICY policy_name { {privilege_audit_clause [action_audit_clause ] [role_audit_clause ]} | { action_audit_clause [role_audit_clause ] } | { role_audit_clause } } [WHEN audit_condition EVALUATE PER {STATEMENT|SESSION|INSTANCE}] [ONLY TOPLEVEL] [CONTAINER = {CURRENT | ALL}];
In this specification:
-
privilege_audit_clausedescribes privilege-related audit options. The detailed syntax for configuring privilege audit options is as follows:privilege_audit_clause := PRIVILEGES privilege1 [, privilege2]
-
action_audit_clauseandstandard_actionsdescribe object action-related audit options. The syntax is as follows:action_audit_clause := {standard_actions | component_actions} [, component_actions ] standard_actions := ACTIONS action1 [ ON {schema.obj_name | DIRECTORY directory_name | MINING MODEL schema.obj_name } ] [, action2 [ ON {schema.obj_name | DIRECTORY directory_name | MINING MODEL schema.obj_name } ]
-
component_actionsenables you to create an audit policy for Oracle Label Security, Oracle Database Real Application Security, Oracle Database Vault, Oracle Data Pump, or Oracle SQL*Loader. The syntax is:component_actions := ACTIONS COMPONENT=[OLS|XS] action1 [,action2 ] | ACTIONS COMPONENT=DV DV_action ON DV_object_name | ACTIONS COMPONENT=DATAPUMP [ EXPORT | IMPORT | ALL ] | ACTIONS COMPONENT=DIRECT_LOAD [ LOAD | ALL ] | ACTIONS COMPONENT=PROTOCOL [ HTTP | FTP ] | ACTIONS COMPONENT=SQL_FIREWALL [SQL VIOLATION | CONTEXT VIOLATION | ALL]
-
role_audit_clauseenables you to audit roles. The syntax is:role_audit_clause := ROLES role1 [, role2]
-
WHENaudit_conditionEVALUATE PERenables you to specify a function to create a condition for the audit policy and the evaluation frequency. You must include theEVALUATE PERclause with theWHENcondition. The syntax is:WHEN 'audit_condition := function operation value_list' EVALUATE PER {STATEMENT|SESSION|INSTANCE}
ONLY TOPLEVELallows users to audit only the top-level operations that are performed for the actions that were configured as part of this audit policy.-
CONTAINER, allows users to audit only the top-level operations that were performed for the actions that were configured as part of this audit policy.
This syntax is designed to audit any of the components listed in the policy. For example, suppose you create the following policy:
CREATE AUDIT POLICY table_pol PRIVILEGES CREATE ANY TABLE, DROP ANY TABLE ROLES emp_admin, sales_admin;
The audit trail will capture SQL statements that require the CREATE ANY TABLE system privilege or the DROP ANY TABLE system privilege or any system privilege directly granted to the role emp_admin or any system privilege directly granted to the role sales_admin.
After you create the policy, you must enable it by using the AUDIT statement. Optionally, you can apply the policy to one or more users, exclude one or more users from the policy, and designate whether an audit record is written when the audited action succeeds, fails, or both succeeds or fails.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Creating Custom Unified Audit Policies
30.4 Auditing Standard Oracle Database Components
You can create unified audit policies to monitor components such as roles, system privileges, administrative users, and actions performed on objects such as tables.
- Auditing Roles
You can use theCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement to audit database roles. - Auditing System Privileges
You can use theCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement to audit system privileges. - Auditing Administrative Users
You can create unified audit policies to capture the actions of administrative user accounts, such asSYS. - Auditing Object Actions
You can use theCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement to audit object actions. - Auditing the READ ANY TABLE and SELECT ANY TABLE Privileges
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can audit theREAD ANY TABLEandSELECT ANY TABLEprivileges. - Auditing Only Top-Level Statements
You can audit top-level user-initiated SQL or PL/SQL statements to reduce audit volume.
Parent topic: Creating Custom Unified Audit Policies
30.4.1 Auditing Roles
You can use the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement to audit database roles.
- About Role Auditing
Role auditing audits all system privileges that have been assigned directly (or indirectly) to the role if that system privilege is used. This type of auditing does not audit the use of privileges apart from system privileges. - Configuring Role Unified Audit Policies
To create a unified audit policy to capture role use, you must include theROLESclause in theCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement. - Example: Auditing the Predefined Common DBA Role
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can audit roles in both the root and in PDBs.
Parent topic: Auditing Standard Oracle Database Components
30.4.1.1 About Role Auditing
Role auditing audits all system privileges that have been assigned directly (or indirectly) to the role if that system privilege is used. This type of auditing does not audit the use of privileges apart from system privileges.
You can audit any role, including user-defined roles. If you create a common unified audit policy for roles with the ROLES audit option, then you must specify only common roles in the role list. When such a policy is enabled, Oracle Database audits all system privileges that are commonly and directly granted to the common role. The system privileges that are locally granted to the common role will not be audited. To find if a role was commonly granted, query the DBA_ROLES data dictionary view. To find if the privileges granted to the role were commonly granted, query the ROLE_SYS_PRIVS view.
Note:
Role auditing will audit all the system privileges that are assigned directly (or indirectly) to the role if a user uses that system privilege.Related Topics
Parent topic: Auditing Roles
30.4.1.2 Configuring Role Unified Audit Policies
To create a unified audit policy to capture role use, you must include the ROLES clause in the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement.
-
Use the following syntax to create a unified audit policy that audits roles:
CREATE AUDIT POLICY policy_name ROLES role1 [, role2];
For example:
CREATE AUDIT POLICY audit_roles_pol ROLES IMP_FULL_DATABASE, EXP_FULL_DATABASE;
You can build more complex role unified audit policies, such as those that include conditions. Remember that after you create the policy, you must use the AUDIT statement to enable it.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Auditing Roles
30.4.1.3 Example: Auditing the Predefined Common DBA Role
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit roles in both the root and in PDBs.
The following example shows how to audit a predefined common role DBA.
Example 30-2 Auditing the Predefined Common DBA Role
CREATE AUDIT POLICY role_dba_audit_pol
ROLES DBA
CONTAINER = ALL;
AUDIT POLICY role_dba_audit_pol;Parent topic: Auditing Roles
30.4.2 Auditing System Privileges
You can use the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement to audit system privileges.
- About System Privilege Auditing
System privilege auditing audits activities that successfully use a system privilege, such asREADANYTABLE. - System Privileges That Can Be Audited
To find a list of auditable system privileges, you can query theSYSTEM_PRIVILEGE_MAPtable. - System Privileges That Cannot Be Audited
A few system privileges cannot be audited. - Configuring a Unified Audit Policy to Capture System Privilege Use
ThePRIVILEGESclause in theCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement audits system privilege use. - Example: Auditing a User Who Has ANY Privileges
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can audit users forANYprivileges. - Example: Using a Condition to Audit a System Privilege
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can create an audit policy that uses a condition to audit a system privilege. - How System Privilege Unified Audit Policies Appear in the Audit Trail
TheUNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAILdata dictionary view lists system privilege audit events.
Parent topic: Auditing Standard Oracle Database Components
30.4.2.1 About System Privilege Auditing
System privilege auditing audits activities that successfully use a system privilege, such as READ ANY TABLE.
A single unified audit policy can contain both privilege and action audit options. Do not audit the privilege use of administrative users such as SYS. Instead, audit their object actions.
Note:
Use privilege analysis in the Oracle database to find the system privileges which are used and unused..
Parent topic: Auditing System Privileges
30.4.2.2 System Privileges That Can Be Audited
To find a list of auditable system privileges, you can query the SYSTEM_PRIVILEGE_MAP table.
For example:
SELECT NAME FROM SYSTEM_PRIVILEGE_MAP; NAME ------------- ALTER ANY CUBE BUILD PROCESS SELECT ANY CUBE BUILD PROCESS ALTER ANY MEASURE FOLDER ...
Similar to action audit options, privilege auditing audits the use of system privileges that have been granted to database users. If you set similar audit options for both SQL statement and privilege auditing, then only a single audit record is generated. For example, if two policies exist, with one auditing EXECUTE PROCEDURE specifically on the HR.PROC procedure and the second auditing EXECUTE PROCEDURE in general (all procedures), then only one audit record is written.
Privilege auditing does not occur if the action is already permitted by the existing owner and object privileges. Privilege auditing is triggered only if the privileges are insufficient, that is, only if what makes the action possible is a system privilege. For example, suppose that user SCOTT has been granted the SELECT ANY TABLE privilege and SELECT ANY TABLE is being audited. If SCOTT selects his own table (for example, SCOTT.EMP), then the SELECT ANY TABLE privilege is not used. Because SCOTT performed the SELECT statement within his own schema, no audit record is generated. On the other hand, if SCOTT selects from another schema (for example, the HR.EMPLOYEES table), then an audit record is generated. Because SCOTT selected a table outside his own schema, he needed to use the SELECT ANY TABLE privilege.
Parent topic: Auditing System Privileges
30.4.2.3 System Privileges That Cannot Be Audited
A few system privileges cannot be audited.
These privileges are:
-
INHERIT ANY PRIVILEGE -
INHERIT PRIVILEGE -
TRANSLATE ANY SQL -
TRANSLATE SQL
Parent topic: Auditing System Privileges
30.4.2.4 Configuring a Unified Audit Policy to Capture System Privilege Use
The PRIVILEGES clause in the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement audits system privilege use.
-
Use the following syntax to create a unified audit policy that audits privileges:
CREATE AUDIT POLICY policy_name PRIVILEGES privilege1 [, privilege2];
For example:
CREATE AUDIT POLICY my_simple_priv_policy PRIVILEGES SELECT ANY TABLE, CREATE LIBRARY;
You can build more complex privilege unified audit policies, such as those that include conditions. Remember that after you create the policy, you must use the AUDIT statement to enable it.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Auditing System Privileges
30.4.2.5 Example: Auditing a User Who Has ANY Privileges
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit users for ANY privileges.
Example 30-3 shows how to audit several ANY privileges of the user HR_MGR.
Example 30-3 Auditing a User Who Has ANY Privileges
CREATE AUDIT POLICY hr_mgr_audit_pol PRIVILEGES DROP ANY TABLE, DROP ANY CONTEXT, DROP ANY INDEX, DROP ANY LIBRARY; AUDIT POLICY hr_mgr_audit_pol BY HR_MGR;
Parent topic: Auditing System Privileges
30.4.2.6 Example: Using a Condition to Audit a System Privilege
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can create an audit policy that uses a condition to audit a system privilege.
Example 30-4 shows how to use a condition to audit privileges that are used by two operating system users, psmith and jrawlins.
Example 30-4 Using a Condition to Audit a System Privilege
CREATE AUDIT POLICY os_users_priv_pol
PRIVILEGES SELECT ANY TABLE, CREATE LIBRARY
WHEN 'SYS_CONTEXT (''USERENV'', ''OS_USER'') IN (''psmith'', ''jrawlins'')'
EVALUATE PER SESSION;
AUDIT POLICY os_users_priv_pol;Parent topic: Auditing System Privileges
30.4.2.7 How System Privilege Unified Audit Policies Appear in the Audit Trail
The UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view lists system privilege audit events.
The following example shows a list of privileges used by the operating system user psmith.
SELECT SYSTEM_PRIVILEGE_USED FROM UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL WHERE OS_USERNAME = 'PSMITH' AND UNIFIED_AUDIT_POLICIES = 'OS_USERS_PRIV_POL'; SYSTEM_PRIVILEGE_USED ---------------------- SELECT ANY TABLE DROP ANY TABLE
Note:
If you have created an audit policy for the SELECT ANY TABLE system privilege, whether the user has exercised the READ object privilege or the SELECT object privilege will affect the actions that the audit trail captures.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Auditing System Privileges
30.4.3 Auditing Administrative Users
You can create unified audit policies to capture the actions of administrative user accounts, such as SYS.
- Administrative User Accounts That Can Be Audited
Oracle Database provides administrative user accounts that are associated with administrative privileges. - Configuring a Unified Audit Policy to Capture Administrator Activities
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can audit administrative users. - Example: Auditing the SYS User
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can audit theSYSuser.
Parent topic: Auditing Standard Oracle Database Components
30.4.3.1 Administrative User Accounts That Can Be Audited
Oracle Database provides administrative user accounts that are associated with administrative privileges.
Table 30-1 lists default administrative user accounts and the administrative privileges with which they are typically associated.
Table 30-1 Administrative Users and Administrative Privileges
| Administrative User Account | Administrative Privilege |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Footnote 1
PUBLIC refers to the user PUBLIC, which is the effective user when you log in with the SYSOPER administrative privilege. It does not refer to the PUBLIC role.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Auditing Administrative Users
30.4.3.2 Configuring a Unified Audit Policy to Capture Administrator Activities
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit administrative users.
-
To audit administrative users, create a unified audit policy and then apply this policy to the user, the same as you would for non-administrative users. Note that top-level statements by administrative users are mandatorily audited until the database opens.
Parent topic: Auditing Administrative Users
30.4.3.3 Example: Auditing the SYS User
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit the SYS user.
Example 30-5 shows how to audit grants of the DBMS_FGA PL/SQL package by user SYS.
Example 30-5 Auditing the SYS User
CREATE AUDIT POLICY dbms_fga_grants ACTIONS GRANT ON DBMS_FGA; AUDIT POLICY dbms_fga_grants BY SYS;
Parent topic: Auditing Administrative Users
30.4.4 Auditing Object Actions
You can use the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement to audit object actions.
- About Auditing Object Actions
You can audit actions performed on specific objects, such asUPDATEstatements on theHR.EMPLOYEEStable. - Object Actions That Can Be Audited
Auditing object actions can be broad or focused (for example, auditing all user actions or only a select list of user actions). - Guidelines for Column Level Auditing and Virtual Columns
When you create unified audit policies for columns, you should be aware of guidelines for handling virtual columns. - Configuring an Object Action Unified Audit Policy
TheACTIONSclause in theCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement creates a policy that captures object actions. - Example: Auditing Actions on SYS Objects
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can audit actions onSYSobjects. - Example: Auditing Multiple Actions on One Object
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can audit multiple actions on one object. - Example: Auditing GRANT and REVOKE Operations on an Object
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can auditGRANTandREVOKEoperations on objects, such as tables. - Example: Auditing Both Actions and Privileges on an Object
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can audit both actions and privileges on an object, using a single policy. - Example: Auditing an Action on a Table Column
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can audit actions on table or view columns. - Example: Auditing All Actions on a Table
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can audit all actions on a table. - Example: Auditing All Actions in the Database
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can audit all actions in the database. - How Object Action Unified Audit Policies Appear in the Audit Trail
TheUNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAILdata dictionary view lists object action audit events. - Auditing Functions, Procedures, Packages, and Triggers
You can audit functions, procedures, PL/SQL packages, and triggers. - Auditing of Oracle Virtual Private Database Predicates
The unified audit trail automatically captures the predicates that are used in Oracle Virtual Private Database (VPD) policies. - Audit Policies for Oracle Virtual Private Database Policy Functions
Auditing can affect dynamic VPD policies, static VPD policies, and context-sensitive VPD policies. - Unified Auditing with Editioned Objects
An audit policy created to audit an action on an editioned object will be applied to all its editions.
Parent topic: Auditing Standard Oracle Database Components
30.4.4.1 About Auditing Object Actions
You can audit actions performed on specific objects, such as UPDATE statements on the HR.EMPLOYEES table.
The audit can include both DDL and DML statements that were used on the object. A single unified audit policy can contain both privilege and action audit options, as well as audit options set for multiple objects.
For tables that contain sensitive information, Oracle recommends that you include the ACTIONS ALL clause in the unified audit policy so that the audit record will capture indirect SELECT operations.
Parent topic: Auditing Object Actions
30.4.4.2 Object Actions That Can Be Audited
Auditing object actions can be broad or focused (for example, auditing all user actions or only a select list of user actions).
Table 30-2 lists the object-level standard database action options. Audit policies for the SELECT SQL statement will capture READ actions as well as SELECT actions.
Table 30-2 Object-Level Standard Database Action Audit Option
| Object | SQL Action That Can Be Audited |
|---|---|
|
Directory |
|
|
Function |
|
|
Java schema objects (source, class, resource) |
|
|
Library |
|
|
Materialized views |
|
|
Mining Model |
|
|
Object type |
|
|
Package |
|
|
Procedure (including triggers) |
|
|
Sequence |
|
|
Table |
|
|
Table or view column |
|
|
View |
|
30.4.4.3 Guidelines for Column Level Auditing and Virtual Columns
When you create unified audit policies for columns, you should be aware of guidelines for handling virtual columns.
-
An audit record is not be generated if an audit policy is defined on a virtual column and the base column is updated, causing an update to the virtual column.
For example, suppose a table has a column
col1and a virtual columnc_vir. Depending on the value ofcol1, a column level audit policy defined onc_virfor action update will not generate an audit record whencol1is updated, causing an update toc_vir. The same behavior is true forINSERToperation. -
If the value of a column is accessed through a virtual column, then an audit record is generated.
For example, suppose a table has a column
col1and a virtual columnc_vir. Depending on the value ofcol1, a column level unified audit policy is defined oncol1. In this case, accessingc_virgenerates a unified audit record.
Parent topic: Auditing Object Actions
30.4.4.4 Configuring an Object Action Unified Audit Policy
The ACTIONS clause in the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement creates a policy that captures object actions.
-
Use the following syntax to create a unified audit policy that audits object actions:
CREATE AUDIT POLICY policy_name ACTIONS action1 [, action2 ON object1] [, action3 ON object2];
For example:
CREATE AUDIT POLICY my_simple_obj_policy ACTIONS SELECT ON OE.ORDERS, UPDATE ON HR.EMPLOYEES;
Note that you can audit multiple actions on multiple objects, as shown in this example.
You can build complex object action unified audit policies, such as those that include conditions. Remember that after you create the policy, you must use the AUDIT statement to enable it.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Auditing Object Actions
30.4.4.5 Example: Auditing Actions on SYS Objects
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit actions on SYS objects.
Example 30-6 shows how to create an audit policy that audits SELECT statements on the SYS.USER$ system table. The audit policy applies to all users, including SYS and SYSTEM.
Example 30-6 Auditing Actions on SYS Objects
CREATE AUDIT POLICY select_user_dictionary_table_pol ACTIONS SELECT ON SYS.USER$; AUDIT POLICY select_user_dictionary_table_pol;
Parent topic: Auditing Object Actions
30.4.4.6 Example: Auditing Multiple Actions on One Object
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit multiple actions on one object.
Example 30-7 shows how to audit multiple SQL statements performed by users jrandolph and phawkins on the app_lib library.
Example 30-7 Auditing Multiple Actions on One Object
CREATE AUDIT POLICY actions_on_hr_emp_pol1 ACTIONS EXECUTE, GRANT ON app_lib; AUDIT POLICY actions_on_hr_emp_pol1 BY jrandolph, phawkins;
Parent topic: Auditing Object Actions
30.4.4.7 Example: Auditing GRANT and REVOKE Operations on an Object
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit GRANT and REVOKE operations on objects, such as tables.
Enabling auditing on GRANT operations on an object automatically enables the audit of REVOKE operations on the object as well.
Example 30-8 Auditing GRANT and REVOKE Operations
CREATE AUDIT POLICY grant_revoke_pol ACTIONS GRANT ON HR.EMPLOYEES; AUDIT POLICY grant_revoke_pol;
The UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL view captures the relevant information for a grant operation as shown in the following query. The grantee name (to whom the privilege is granted) is recorded in the TARGET_USER column.
SELECT DBUSERNAME, OBJECT_PRIVILEGES, ACTION_NAME, OBJECT_SCHEMA, OBJECT_NAME, TARGET_USER
FROM UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL
WHERE ACTION_NAME IN ('GRANT', 'REVOKE');Parent topic: Auditing Object Actions
30.4.4.8 Example: Auditing Both Actions and Privileges on an Object
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit both actions and privileges on an object, using a single policy.
Example 30-9 shows how all EXECUTE and GRANT statements on the app_lib library using the CREATE LIBRARY privilege are audited.
Example 30-9 Auditing Both Actions and Privileges on an Object
CREATE AUDIT POLICY actions_on_hr_emp_pol2 PRIVILEGES CREATE LIBRARY ACTIONS EXECUTE, GRANT ON app_lib; AUDIT POLICY actions_on_hr_emp_pol2 BY jrandolph, phawkins;
You can audit directory objects. For example, suppose you create a directory object that contains a preprocessor program that the ORACLE_LOADER access driver will use. You can audit anyone who runs this program within this directory object.
Parent topic: Auditing Object Actions
30.4.4.9 Example: Auditing an Action on a Table Column
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit actions on table or view columns.
Example 30-10 shows how to create an audit policy that audits SELECT statements on the SALARY column of the HR.EMPLOYEES table.
Example 30-10 Auditing Actions on a Table Column
CREATE AUDIT POLICY emp_hr_emp_sal_access_pol ACTIONS SELECT(SALARY) ON HR.EMPLOYEES; AUDIT POLICY emp_hr_emp_sal_access_pol;
Parent topic: Auditing Object Actions
30.4.4.10 Example: Auditing All Actions on a Table
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit all actions on a table.
You can use the ALL keyword to audit all actions. Oracle recommends
that you audit all actions only on sensitive objects. ALL is useful in that it
captures indirect SELECT operations. Example 30-11 shows how to audit all actions on the HR.EMPLOYEES table by
user pmulligan.
Example 30-11 Auditing All Actions on a Table
CREATE AUDIT POLICY all_actions_on_hr_emp_pol ACTIONS ALL ON HR.EMPLOYEES; AUDIT POLICY all_actions_on_hr_emp_pol BY pmulligan;
Related Topics
Parent topic: Auditing Object Actions
30.4.4.11 Example: Auditing All Actions in the Database
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit all actions in the database.
Ensure that you include the ONLY TOPLEVEL clause to audit only the top-level user initiated actions. Consider adding conditions when you use the ACTIONS ALL clause to further reduce the audit volume.
Note:
UseACTIONS ALL auditing with caution. Do not enable it for users who must perform online transaction processing (OLTP) workloads. This will avoid generating a large number of audit records.
Example 30-12 shows how to audit all actions in the entire database.
Example 30-12 Auditing All Actions in the Database
CREATE AUDIT POLICY all_actions_pol ACTIONS ALL ONLY TOPLEVEL; AUDIT POLICY all_actions_pol;
Related Topics
Parent topic: Auditing Object Actions
30.4.4.12 How Object Action Unified Audit Policies Appear in the Audit Trail
The UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view lists object action audit events.
For example:
SELECT ACTION_NAME, OBJECT_SCHEMA, OBJECT_NAME FROM UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL WHERE DBUSERNAME = 'SYS'; ACTION_NAME OBJECT_SCHEMA OBJECT_NAME ----------- ------------- ------------ SELECT HR EMPLOYEES
Parent topic: Auditing Object Actions
30.4.4.13 Auditing Functions, Procedures, Packages, and Triggers
You can audit functions, procedures, PL/SQL packages, and triggers.
Points to consider:
-
You can individually audit standalone functions, standalone procedures, and PL/SQL packages.
-
If you audit a PL/SQL package, Oracle Database audits all functions and procedures within the package.
-
If you enable auditing for all executions, Oracle Database audits all triggers in the database, as well as all the functions and procedures within PL/SQL packages.
-
You cannot audit individual functions or procedures within a PL/SQL package.
-
When you audit the
EXECUTEoperation on a PL/SQL stored procedure or stored function, the database considers only its ability to find the procedure or function and authorize its execution when determining the success or failure of the operation for the purposes of auditing. Therefore, if you specify theWHENEVER NOT SUCCESSFULclause, then only invalid object errors, non-existent object errors, and authorization failures are audited; errors encountered during the execution of the procedure or function are not audited. If you specify theWHENEVER SUCCESSFULclause, then all executions that are not blocked by invalid object errors, non-existent object errors, or authorization failures are audited, regardless of whether errors are encountered during execution.
Parent topic: Auditing Object Actions
30.4.4.14 Auditing of Oracle Virtual Private Database Predicates
The unified audit trail automatically captures the predicates that are used in Oracle Virtual Private Database (VPD) policies.
You do not need to create a unified audit policy to capture the VPD predicate audit information.
This type of audit enables you to identify the predicate expression that was run as part of a DML operation and thereby help you to identify other actions that may have occurred as part of the DML operation. For example, if a malicious attack on your database is performed using a VPD predicate, then you can track the attack by using the unified audit trail. In addition to predicates from user-created VPD policies, the internal predicates from Oracle Label Security and Oracle Real Application Security policies are captured as well. For example, Oracle Label Security internally creates a VPD policy while applying an OLS policy to a table. Oracle Real Application Security generates a VPD policy while enabling an Oracle RAS policy.
The unified audit trail writes this predicate information to the RLS_INFO column of the UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view. If you have fine-grained audit policies, then the RLS_INFO column of these views captures VPD predicate information as well.
The audit trail can capture the predicates and their corresponding policy names if multiple VPD policies are enforced on the object. The audit trail captures the policy schema and policy name to enable you to differentiate predicates that are generated from different policies. By default, this information is concatenated in the RLS_INFO column, but Oracle Database provides a function in the DBMS_AUDIT_UTIL PL/SQL package that enables you to reformat the results in an easy-to-read format.
The following example shows how you can audit the predicates of a VPD policy:
-
Create the following VPD policy function:
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION auth_orders( schema_var IN VARCHAR2, table_var IN VARCHAR2 ) RETURN VARCHAR2 IS return_val VARCHAR2 (400); BEGIN return_val := 'SALES_REP_ID = 159'; RETURN return_val; END auth_orders; /
-
Create the following VPD policy:
BEGIN DBMS_RLS.ADD_POLICY ( object_schema => 'oe', object_name => 'orders', policy_name => 'orders_policy', function_schema => 'sec_admin', policy_function => 'auth_orders', statement_types => 'select, insert, update, delete' ); END; / -
Create and enable the following the unified audit policy:
CREATE AUDIT POLICY oe_pol ACTIONS SELECT ON OE.ORDERS; AUDIT POLICY oe_pol;
-
Connect as user
OEand query theOE.ORDERStable.CONNECT OE@pdb_name Enter password: password SELECT COUNT(*) FROM ORDERS;
-
Connect as a user who has been granted the
AUDIT_ADMINrole, and then query theUNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAILdata dictionary view.CONNECT sec_admin@pdb_name Enter password: password SELECT RLS_INFO FROM UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL;
Output similar to the following should appear:
((POLICY_TYPE=[3]'VPD'),(POLICY_SCHEMA=[9]'SEC_ADMIN'),(POLICY_NAME=[13]'ORDERS_POLICY'),(PREDICATE=[16]'SALES_REP_ID=159'));
-
To extract these details and add them to their own columns, run the appropriate function from the
DBMS_AUDIT_UTILPL/SQL package.For unified auditing, you must run the
DBMS_AUDIT_UTIL.DECODE_RLS_INFO_ATRAIL_UNIfunction.For example:
SELECT DBUSERNAME, ACTION_NAME, OBJECT_NAME, SQL_TEXT, RLS_PREDICATE, RLS_POLICY_TYPE, RLS_POLICY_OWNER, RLS_POLICY_NAME FROM TABLE (DBMS_AUDIT_UTIL.DECODE_RLS_INFO_ATRAIL_UNI (CURSOR (SELECT * FROM UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL)));
The reformatted audit trail output appears similar to the following:
DBUSERNAME ACTION_NAME OBJECT_NAME SQL_TEXT ---------- ----------- ----------- --------------------------- RLS_PREDICATE RLS_POLICY_TYPE RLS_POLICY_OWNER RLS_POLICY_NAME ------------------ --------------- ---------------- --------------- OE SELECT ORDERS SELECT COUNT(*) FROM ORDERS SALES_REP_ID = 159 VPD SEC_ADMIN ORDERS_POLICY
30.4.4.15 Audit Policies for Oracle Virtual Private Database Policy Functions
Auditing can affect dynamic VPD policies, static VPD policies, and context-sensitive VPD policies.
-
Dynamic policies: Oracle Database evaluates the policy function twice, once during SQL statement parsing and again during execution. As a result, two audit records are generated for each evaluation.
-
Static policies: Oracle Database evaluates the policy function once and then caches it in the SGA. As a result, only one audit record is generated.
-
Context-sensitive policies: Oracle Database executes the policy function once, during statement parsing. As a result, only one audit record is generated.
Parent topic: Auditing Object Actions
30.4.4.16 Unified Auditing with Editioned Objects
An audit policy created to audit an action on an editioned object will be applied to all its editions.
In addition, newly created objects in an edition will inherit unified audit policies from the existing edition.
You can find the editions in which audited objects appear by querying the OBJECT_NAME and OBJ_EDITION_NAME columns in the UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Auditing Object Actions
30.4.5 Auditing the READ ANY TABLE and SELECT ANY TABLE Privileges
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit the READ ANY TABLE and SELECT ANY TABLE privileges.
- About Auditing the READ ANY TABLE and SELECT ANY TABLE Privileges
You can create unified audit policies that capture the use of theREAD ANY TABLEandSELECT ANY TABLEsystem privileges. - Creating a Unified Audit Policy to Capture READ Object Privilege Operations
You can create unified audit policies that captureREADobject privilege operations. - How the Unified Audit Trail Captures READ ANY TABLE and SELECT ANY TABLE
The unified audit trail capturesSELECTbehavior based on whether a user has theREAD ANY TABLEor theSELECT ANY TABLEprivilege.
Parent topic: Auditing Standard Oracle Database Components
30.4.5.1 About Auditing the READ ANY TABLE and SELECT ANY TABLE Privileges
You can create unified audit policies that capture the use of the READ ANY TABLE and SELECT ANY TABLE system privileges.
Based on the action that the user tried to perform and the privilege that was granted to the user, the SYSTEM_PRIVILEGE_USED column of the UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view will record either the READ ANY TABLE system privilege or the SELECT ANY TABLE system privilege. For example, suppose the user has been granted the SELECT ANY TABLE privilege and then performs a query on a table. The audit trail will record that the user used the SELECT ANY TABLE system privilege. If the user was granted READ ANY TABLE and performed the same query, then the READ ANY TABLE privilege is recorded.
30.4.5.2 Creating a Unified Audit Policy to Capture READ Object Privilege Operations
You can create unified audit policies that capture READ object privilege operations.
-
To create a unified audit policy to capture any
READobject operations, create the policy for theSELECTstatement, not for theREADstatement.
For example:
CREATE AUDIT POLICY read_hr_employees ACTIONS SELECT ON HR.EMPLOYEES;
For any SELECT object operations, also create the policy on the SELECT statement, as with other object actions that you can audit.
Related Topics
30.4.5.3 How the Unified Audit Trail Captures READ ANY TABLE and SELECT ANY TABLE
The unified audit trail captures SELECT behavior based on whether a user has the READ ANY TABLE or the SELECT ANY TABLE privilege.
Table 30-3 describes how the unified audit trail captures these actions.
Table 30-3 Auditing Behavior for READ ANY TABLE and SELECT ANY TABLE
| Statement User Issues | Privilege Granted to User | System Privilege Being Audited | Expected UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL Behavior |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
Record inserted into
|
|
|
|
|
No record |
|
|
|
Both |
Record inserted into
|
|
|
|
Neither |
No record |
|
|
|
|
No record |
|
|
|
|
Record inserted into
|
|
|
|
Both |
Record inserted into
|
|
|
|
Neither |
No record |
|
|
Both |
|
No record, because |
|
|
Both |
|
Record inserted into
|
|
|
Both |
Both |
Record inserted into
|
|
|
Both |
Neither |
No record |
|
|
Neither |
|
No record |
|
|
Neither |
|
No record |
|
|
Neither |
Both |
No record |
|
|
Neither |
Neither |
No record |
|
|
|
|
Record inserted into
|
|
|
|
|
No record |
|
|
|
Both |
Record inserted into
|
|
|
|
Neither |
No record |
|
|
|
|
No record |
|
|
|
|
No record |
|
|
|
Both |
No record |
|
|
|
Neither |
No record |
|
|
Both |
|
Record inserted into
|
|
|
Both |
|
No record, because |
|
|
Both |
Both |
Record inserted into
|
|
|
Both |
Neither |
No record |
|
|
Neither |
|
No record |
|
|
Neither |
|
No record |
|
|
Neither |
Both |
No record |
|
|
Neither |
Neither |
No record |
30.4.6 Auditing Only Top-Level Statements
You can audit top-level user-initiated SQL or PL/SQL statements to reduce audit volume.
- About Auditing Only Top-Level SQL Statements
A top-level statement is a statement that is executed directly by a user, not a statement that is run from within a PL/SQL procedure. - Configuring a Unified Audit Policy to Capture Only Top-Level Statements
TheONLY TOPLEVELclause in theCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement enables you to audit only the SQL statements that are directly issued by an end user by honoring the audit configuration in the audit policy. - Example: Auditing Top-Level Statements
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can include or exclude top-level statement audit records in the unified audit trail for any user. - Example: Comparison of Top-Level SQL Statement Audits
You can generate top-level SQL statement audit records from SQL statements that are run directly in SQL or from within a PL/SQL procedure. - How the Unified Audit Trail Captures Top-Level SQL Statements
TheONLY TOPLEVELclause has no impact on the output for an individual unified audit trail record.
Parent topic: Auditing Standard Oracle Database Components
30.4.6.1 About Auditing Only Top-Level SQL Statements
A top-level statement is a statement that is executed directly by a user, not a statement that is run from within a PL/SQL procedure.
Consider auditing top-level statements from all users, including user SYS to reduce the volume of audit. The feature audits all the user-initiated actions and ignores the recursive SQL statements. For example, auditing the DBMS_STATS.GATHER_DATABASE_STATS SQL statement can generate over 200,000 individual audit records and by adding top-level this reduces to a single audit record.
Parent topic: Auditing Only Top-Level Statements
30.4.6.2 Configuring a Unified Audit Policy to Capture Only Top-Level Statements
The ONLY TOPLEVEL clause in the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement enables you to audit only the SQL statements that are directly issued by an end user by honoring the audit configuration in the audit policy.
ONLY TOPLEVEL clause, query the AUDIT_ONLY_TOPLEVEL column of the AUDIT_UNIFIED_POLICIES data dictionary view.
CREATE AUDIT POLICY policy_name all_existing_options ONLY TOPLEVEL;
For example, to limit the audit trail to top-level instances of the SELECT statement on the HR.EMPLOYEES table:
CREATE AUDIT POLICY actions_on_hr_emp_pol ACTIONS SELECT ON HR.EMPLOYEES ONLY TOPLEVEL;
Parent topic: Auditing Only Top-Level Statements
30.4.6.3 Example: Auditing Top-Level Statements
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can include or exclude top-level statement audit records in the unified audit trail for any user.
The following example shows an audit policy that will capture all top level statements executed by user SYS.
Example 30-13 Example: Auditing Top-Level Statements Run by User SYS
CREATE AUDIT POLICY actions_all_pol ACTIONS ALL ONLY TOPLEVEL; AUDIT POLICY actions_all_pol BY SYS;
Parent topic: Auditing Only Top-Level Statements
30.4.6.4 Example: Comparison of Top-Level SQL Statement Audits
You can generate top-level SQL statement audit records from SQL statements that are run directly in SQL or from within a PL/SQL procedure.
This example shows how generating audit records differs when you access a view outside a PL/SQL procedure as opposed to accessing the view inside the PL/SQL procedure. The output illustrates the difference in volume in audit records that are generated from the two different audit policies.
- Log in to the database instance as user
SYSwith theSYSDBAadministrative privilege.In a multitenant environment, log in to the PDB. To find the available PDBs in a CDB, log in to the CDB root container and then query the
PDB_NAMEcolumn of theDBA_PDBSdata dictionary view. To check the current container, run theshow con_namecommand. - Create the following procedure:
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE proc1 AS cnt number; BEGIN SELECT COUNT(*) INTO CNT FROM SYS.DBA_USERS WHERE USER_ID=9999; END; / - Create the and enable following audit policy to capture top-level actions:
CREATE AUDIT POLICY toplevel_pol ACTIONS ALL ONLY TOPLEVEL; AUDIT POLICY toplevel_pol; - Run the following query to generate an audit record and to access the
SYS.DBA_USERSview outside of theproc1procedure that you just created:SELECT /* TOPLEVEL */ COUNT(*) FROM SYS.DBA_USERS WHERE USER_ID=0000;The output should be as follows:
COUNT(*) ---------- 1 - Run the
proc1procedure that you created earlier, to access theSYS.DBA_USERSview again, but from within a procedure.EXEC proc1; - Query the
UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAILdata dictionary view as follows:SELECT ACTION_NAME, OBJECT_SCHEMA,OBJECT_NAME,STATEMENT_ID,ENTRY_ID, UNIFIED_AUDIT_POLICIES,SQL_TEXT FROM UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL ORDER BY EVENT_TIMESTAMP;Output similar to the following appears:
ACTION_NAME OBJECT_SCHEMA -------------------- ------------------------------ OBJECT_NAME STATEMENT_ID ENTRY_ID ------------------------------ ------------ ---------- UNIFIED_AUDIT_POLICIES ------------------------------ SQL_TEXT ------------------------------------------------------------ LOGON 1 1 TOPLEVEL_POL COMMIT 3 2 TOPLEVEL_POL COMMIT 4 3 TOPLEVEL_POL SELECT SYS USER$ 5 4 TOPLEVEL_POL select /* toplevel */ count(*) from sys.dba_users where user _id=0000 SELECT SYS RESOURCE_GROUP_MAPPING$ 5 5 TOPLEVEL_POL select /* toplevel */ count(*) from sys.dba_users where user _id=0000 SELECT SYS TS$ 5 6 TOPLEVEL_POL select /* toplevel */ count(*) from sys.dba_users where user _id=0000 SELECT SYS TS$ 5 7 TOPLEVEL_POL select /* toplevel */ count(*) from sys.dba_users where user _id=0000 SELECT SYS TS$ 5 8 TOPLEVEL_POL select /* toplevel */ count(*) from sys.dba_users where user _id=0000 SELECT SYS PROFNAME$ 5 9 TOPLEVEL_POL select /* toplevel */ count(*) from sys.dba_users where user _id=0000 SELECT SYS USER_ASTATUS_MAP 5 10 TOPLEVEL_POL select /* toplevel */ count(*) from sys.dba_users where user _id=0000 SELECT SYS PROFILE$ 5 11 TOPLEVEL_POL select /* toplevel */ count(*) from sys.dba_users where user _id=0000 SELECT SYS PROFILE$ 5 12 TOPLEVEL_POL select /* toplevel */ count(*) from sys.dba_users where user _id=0000 SELECT SYS DBA_USERS 5 13 TOPLEVEL_POL select /* toplevel */ count(*) from sys.dba_users where user _id=0000 EXECUTE SYS PROC1 7 14 TOPLEVEL_POL BEGIN proc1; END; 14 rows selected. - Disable and then drop the
toplevel_polaudit policy.NOAUDIT POLICY toplevel_pol; DROP AUDIT POLICY toplevel_pol; - Create and enable a new audit policy to capture all actions.
CREATE AUDIT POLICY recursive_pol ACTIONS ALL; AUDIT POLICY recursive_pol; - Clean up the audit trail.
DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.CLEAN_AUDIT_TRAIL(DBMS_AUDIT_MGMT.AUDIT_TRAIL_UNIFIED,FALSE); - Run the following query to generate an audit record and to access the
SYS.DBA_USERSview outside of theproc1procedure:SELECT /* TOPLEVEL */ COUNT(*) FROM SYS.DBA_USERS WHERE USER_ID=0000;The output should be as follows:
COUNT(*) ---------- 1 - Run the
proc1procedure to access theSYS.DBA_USERSagain, but from within theproc1procedure.EXEC proc1; - Query the
UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAILdata dictionary view as follows:SELECT ACTION_NAME, OBJECT_SCHEMA,OBJECT_NAME,STATEMENT_ID,ENTRY_ID, UNIFIED_AUDIT_POLICIES,SQL_TEXT FROM UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL ORDER BY EVENT_TIMESTAMP;Output similar to the following should appear:
ACTION_NAME OBJECT_SCHEMA -------------------- ------------------------------ OBJECT_NAME UNIFIED_AUDIT_POLICIES STATEMENT_ID ------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------ ENTRY_ID SQL_TEXT ---------- ------------------------------------------------------------ LOGON RECURSIVE_POL 1 1 ALTER SESSION RECURSIVE_POL 1 2 ALTER SESSION SET TIME_ZONE='-07:00' COMMIT RECURSIVE_POL 3 3 COMMIT RECURSIVE_POL 4 4 SELECT SYS USER$ RECURSIVE_POL 5 5 select /* toplevel */ count(*) from sys.dba_users where user _id=0000 SELECT SYS RESOURCE_GROUP_MAPPING$ RECURSIVE_POL 5 6 select /* toplevel */ count(*) from sys.dba_users where user _id=0000 SELECT SYS TS$ RECURSIVE_POL 5 7 select /* toplevel */ count(*) from sys.dba_users where user _id=0000 SELECT SYS TS$ RECURSIVE_POL 5 8 select /* toplevel */ count(*) from sys.dba_users where user _id=0000 SELECT SYS TS$ RECURSIVE_POL 5 9 select /* toplevel */ count(*) from sys.dba_users where user _id=0000 SELECT SYS PROFNAME$ RECURSIVE_POL 5 10 select /* toplevel */ count(*) from sys.dba_users where user _id=0000 SELECT SYS USER_ASTATUS_MAP RECURSIVE_POL 5 11 select /* toplevel */ count(*) from sys.dba_users where user _id=0000 SELECT SYS PROFILE$ RECURSIVE_POL 5 12 select /* toplevel */ count(*) from sys.dba_users where user _id=0000 SELECT SYS PROFILE$ RECURSIVE_POL 5 13 select /* toplevel */ count(*) from sys.dba_users where user _id=0000 SELECT SYS DBA_USERS RECURSIVE_POL 5 14 select /* toplevel */ count(*) from sys.dba_users where user _id=0000 SELECT SYS USER$ RECURSIVE_POL 7 15 SELECT COUNT(*) FROM SYS.DBA_USERS WHERE USER_ID=9999 SELECT SYS RESOURCE_GROUP_MAPPING$ RECURSIVE_POL 7 16 SELECT COUNT(*) FROM SYS.DBA_USERS WHERE USER_ID=9999 SELECT SYS TS$ RECURSIVE_POL 7 17 SELECT COUNT(*) FROM SYS.DBA_USERS WHERE USER_ID=9999 SELECT SYS TS$ RECURSIVE_POL 7 18 SELECT COUNT(*) FROM SYS.DBA_USERS WHERE USER_ID=9999 SELECT SYS TS$ RECURSIVE_POL 7 19 SELECT COUNT(*) FROM SYS.DBA_USERS WHERE USER_ID=9999 SELECT SYS PROFNAME$ RECURSIVE_POL 7 20 SELECT COUNT(*) FROM SYS.DBA_USERS WHERE USER_ID=9999 SELECT SYS USER_ASTATUS_MAP RECURSIVE_POL 7 21 SELECT COUNT(*) FROM SYS.DBA_USERS WHERE USER_ID=9999 SELECT SYS PROFILE$ RECURSIVE_POL 7 22 SELECT COUNT(*) FROM SYS.DBA_USERS WHERE USER_ID=9999 SELECT SYS PROFILE$ RECURSIVE_POL 7 23 SELECT COUNT(*) FROM SYS.DBA_USERS WHERE USER_ID=9999 SELECT SYS DBA_USERS RECURSIVE_POL 7 24 SELECT COUNT(*) FROM SYS.DBA_USERS WHERE USER_ID=9999 EXECUTE SYS PROC1 RECURSIVE_POL 7 25 BEGIN proc1; END; 25 rows selected.The output in this query generates 25 records, as opposed to the 14 that were generated earlier.
- Disable and remove the
recursive_polpolicy.NOAUDIT POLICY recursive_pol; DROP AUDIT POLICY recursive_pol;
Parent topic: Auditing Only Top-Level Statements
30.4.6.5 How the Unified Audit Trail Captures Top-Level SQL Statements
The ONLY TOPLEVEL clause has no impact on the output for an individual unified audit trail record.
The only effect that ONLY TOPLEVEL has on a policy is to limit the number of records generated for the given unified audit policy.
Parent topic: Auditing Only Top-Level Statements
30.5 Unified Auditing with Configurable Conditions
You can use the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement to create conditions for a unified audit policy.
- About Conditions in Unified Audit Policies
You can use conditions in unified audit policies to create focused and selective audit policies. - Configuring a Unified Audit Policy with a Condition
TheWHENclause in theCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement defines the condition in the audit policy. - Example: Auditing Access to SQL*Plus
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can audit access to SQL*Plus. - Example: Auditing Actions Not in Specific Hosts
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can audit actions that are not in specific hosts. - Example: Auditing Both a System-Wide and a Schema-Specific Action
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can audit both system-wide and schema-specific actions. - Example: Auditing a Condition Per Statement Occurrence
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can audit conditions. - Example: Unified Audit Session ID of a Current Administrative User Session
TheSYS_CONTEXTfunction can be used to find session IDs. - Example: Unified Audit Session ID of a Current Non-Administrative User Session
TheSYS_CONTEXTfunction can find the session ID of a current non-administrative user session. - How Audit Records from Conditions Appear in the Audit Trail
The audit record conditions from a unified audit policy do not appear in the audit trail.
Parent topic: Creating Custom Unified Audit Policies
30.5.1 About Conditions in Unified Audit Policies
You can use conditions in unified audit policies to create focused and selective audit policies.
You can use the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement to create conditions for a unified audit policy. For example, you can create policy that audits only when access is from a specific host or IP address. If the audit condition is satisfied, then only then the audit record is generated for the event. As part of the condition definition, you must specify whether the audited condition is evaluated per statement occurrence, session, or database instance.
Note:
Audit conditions can use attributes from the USERENV namespace, or from named application contexts (both secure and insecure).
Parent topic: Unified Auditing with Configurable Conditions
30.5.2 Configuring a Unified Audit Policy with a Condition
The WHEN clause in the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement defines the condition in the audit policy.
-
Use the following syntax to create a unified audit policy that uses a condition:
CREATE AUDIT POLICY policy_name action_privilege_role_audit_option [WHEN function_operation_value_list_1 [[AND | OR] function_operation_value_list_n] EVALUATE PER STATEMENT | SESSION | INSTANCE];
In this specification:
-
action_privilege_role_audit_optionrefers to audit options for system actions, object actions, privileges, and roles. -
WHENdefines the condition. It has the following components:-
functionuses the following types of functions:Numeric functions, such as
BITAND,CEIL,FLOOR, andLNPOWERCharacter functions that return character values, such as
CONCAT,LOWER, andUPPERCharacter functions that return numeric values, such as
LENGTHorINSTREnvironment and identifier functions, such as
SYS_CONTEXTandUID. ForSYS_CONTEXT, in most cases, you may want to use theUSERENVnamespace. -
operationcan be any the following operators:AND,OR,IN,NOT IN,=,<,>,<> -
value_listrefers to the condition for which you are testing.
You can include additional conditions for each
function_operation_value_listset, separated byANDorOR.When you write the
WHENclause, follow these guidelines:-
Enclose the entire
function operation valuesetting in single quotation marks. Within the clause, enclose each quoted component within two pairs of single quotation marks. Do not use double quotation marks. -
Do not exceed 4000 bytes for the
WHENcondition.
-
-
EVALUATE PERrefers to the following options:-
STATEMENTevaluates the condition for each relevant auditable statement that occurs. -
SESSIONevaluates the condition only once during the session, and then caches and re-uses the result during the remainder of the session. Oracle Database evaluates the condition the first time the policy is used, and then stores the result in UGA memory afterward. -
INSTANCEevaluates the condition only once during the database instance lifetime. After Oracle Database evaluates the condition, it caches and re-uses the result for the remainder of the instance lifetime. As with theSESSIONevaluation, the evaluation takes place the first time it is needed, and then the results are stored in UGA memory afterward.
-
For example:
CREATE AUDIT POLICY oe_orders_pol
ACTIONS UPDATE ON OE.ORDERS
WHEN 'SYS_CONTEXT(''USERENV'', ''IDENTIFICATION_TYPE'') = ''EXTERNAL'''
EVALUATE PER STATEMENT;
Remember that after you create the policy, you must use the AUDIT statement to enable it.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Unified Auditing with Configurable Conditions
30.5.3 Example: Auditing Access to SQL*Plus
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit access to SQL*Plus.
Example 30-14 shows how to audit access to the database with SQL*Plus by users who have been directly granted the roles emp_admin and sales_admin.
Example 30-14 Auditing Access to SQL*Plus
CREATE AUDIT POLICY logon_pol
ACTIONS LOGON
WHEN 'INSTR(UPPER(SYS_CONTEXT(''USERENV'', ''CLIENT_PROGRAM_NAME'')), ''SQLPLUS'') > 0'
EVALUATE PER SESSION;
AUDIT POLICY logon_pol BY USERS WITH GRANTED ROLES emp_admin, sales_admin;Parent topic: Unified Auditing with Configurable Conditions
30.5.4 Example: Auditing Actions Not in Specific Hosts
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit actions that are not in specific hosts.
Example 30-15 shows how to audit two actions (UPDATE and DELETE statements) on the OE.ORDERS table, but excludes the host names sales_24 and sales_12 from the audit. It performs the audit on a per session basis and writes audit records for failed attempts only.
Example 30-15 Auditing Actions Not in Specific Hosts
CREATE AUDIT POLICY oe_table_audit1
ACTIONS UPDATE ON OE.ORDERS, DELETE ON OE.ORDERS
WHEN 'SYS_CONTEXT (''USERENV'', ''HOST'') NOT IN (''sales_24'',''sales_12'')'
EVALUATE PER SESSION;
AUDIT POLICY oe_table_audit1 WHENEVER NOT SUCCESSFUL;Parent topic: Unified Auditing with Configurable Conditions
30.5.5 Example: Auditing Both a System-Wide and a Schema-Specific Action
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit both system-wide and schema-specific actions.
Example 30-16 shows a variation of Example 30-15 in which the UPDATE statement is audited system wide. The DELETE statement audit is still specific to the OE.ORDERS table.
Example 30-16 Auditing Both a System-Wide and a Schema-Specific Action
CREATE AUDIT POLICY oe_table_audit2
ACTIONS UPDATE, DELETE ON OE.ORDERS
WHEN 'SYS_CONTEXT (''USERENV'', ''HOST'') NOT IN (''sales_24'',''sales_12'')'
EVALUATE PER SESSION;
AUDIT POLICY oe_table_audit2;Parent topic: Unified Auditing with Configurable Conditions
30.5.6 Example: Auditing a Condition Per Statement Occurrence
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit conditions.
Example 30-17 shows how to audit a condition based on each occurrence of the DELETE statement on the OE.ORDERS table and exclude user jmartin from the audit.
Example 30-17 Auditing a Condition Per Statement Occurrence
CREATE AUDIT POLICY sales_clerk_pol
ACTIONS DELETE ON OE.ORDERS
WHEN 'SYS_CONTEXT(''USERENV'', ''CLIENT_IDENTIFIER'') = ''sales_clerk'''
EVALUATE PER STATEMENT;
AUDIT POLICY sales_clerk_pol EXCEPT jmartin;Parent topic: Unified Auditing with Configurable Conditions
30.5.7 Example: Unified Audit Session ID of a Current Administrative User Session
The SYS_CONTEXT function can be used to find session IDs.
Example 30-18 shows how to find the unified audit session ID of current user session for an administrative user.
Example 30-18 Unified Audit Session ID of a Current Administrative User Session
CONNECT SYS AS SYSDBA
Enter password: password
SELECT SYS_CONTEXT('USERENV', 'UNIFIED_AUDIT_SESSIONID') FROM DUAL;
Output similar to the following appears:
SYS_CONTEXT('USERENV','UNIFIED_AUDIT_SESSIONID')
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2318470183Note that in mixed mode auditing, the UNIFIED_AUDIT_SESSIONID value in the USERENV namespace is different from the value that is recorded by the SESSIONID parameter. Hence, if you are using mixed mode auditing and want to find the correct audit session ID, you should use the USERENV UNIFIED_AUDIT_SESSIONID parameter, not the SESSIONID parameter. In pure unified auditing, the SESSIONID and UNIFIED_AUDIT_SESSIONID values are the same.
Parent topic: Unified Auditing with Configurable Conditions
30.5.8 Example: Unified Audit Session ID of a Current Non-Administrative User Session
The SYS_CONTEXT function can find the session ID of a current non-administrative user session.
Example 30-19 shows how to find the unified audit session ID of a current user session for a non-administrative user.
Example 30-19 Unified Audit Session ID of a Current Non-Administrative User Session
CONNECT mblake@pdb_name
Enter password: password
SELECT SYS_CONTEXT('USERENV', 'UNIFIED_AUDIT_SESSIONID') FROM DUAL;
Output similar to the following appears:
SYS_CONTEXT('USERENV','UNIFIED_AUDIT_SESSIONID')
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2776921346Parent topic: Unified Auditing with Configurable Conditions
30.5.9 How Audit Records from Conditions Appear in the Audit Trail
The audit record conditions from a unified audit policy do not appear in the audit trail.
If the condition evaluates to true and the record is written, then the record appears in the audit trail. You can check the audit trail by querying the UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Unified Auditing with Configurable Conditions
30.6 Auditing for Multitier or Multitenant Configurations
You can create unified audit policies using conditions and application contexts, and in multitier and multitenant environments.
- Auditing in a Multitier Deployment
You can create a unified audit policy to audit the activities of a client in a multitier environment. - Auditing in a Multitenant Deployment
You can create unified audit policies for individual PDBs and in the root.
Parent topic: Creating Custom Unified Audit Policies
30.6.1 Auditing in a Multitier Deployment
You can create a unified audit policy to audit the activities of a client in a multitier environment.
In a multitier environment, Oracle Database preserves the identity of a client through all tiers. Thus, you can audit actions taken on behalf of the client by a middle-tier application, by using the BY user clause in the AUDIT statement for your policy. The audit applies to all user sessions, including proxy sessions.
The middle tier can also set the user client identity in a database session, enabling the auditing of end-user actions through the middle-tier application. The end-user client identity then shows up in the audit trail.
For example, suppose the proxy user apphr can connect as user jackson. The policy and enablement can be as follows:
CREATE AUDIT POLICY prox_pol ACTIONS LOGON;
AUDIT POLICY prox_pol BY jackson;You can audit user activity in a multitier environment. Once audited, you can verify these activities by querying the UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view. For example:
SELECT DBUSERNAME, DB_PROXY_USERNAME, PROXY_SESSIONID, ACTION_NAME
FROM UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL
WHERE DBPROXY_USERNAME IS NOT NULL;Output similar to the following appears:
DBUSERNAME DBPROXY_USERNAME PROXY_SESSIONID ACTION_NAME
---------- ---------------- --------------- -----------
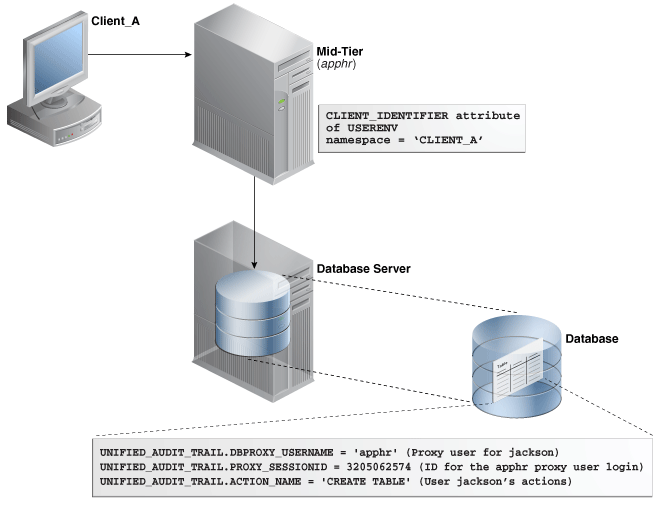
JACKSON APPHR 1214623540 LOGON Figure 30-1 illustrates how you can audit proxy users by querying the PROXY_SESSIONID, ACTION_NAME, and SESSION_ID columns of the UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL view. In this scenario, both the database user and proxy user accounts are known to the database. Session pooling can be used.
Figure 30-2 illustrates how you can audit client identifier information across multiple database sessions by querying the CLIENT_ID column of the DBA_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view. In this scenario, the client identifier has been set to CLIENT_A. As with the proxy user-database user scenario described in Figure 30-1, session pooling can be used.
Figure 30-2 Auditing Client Identifier Information Across Sessions
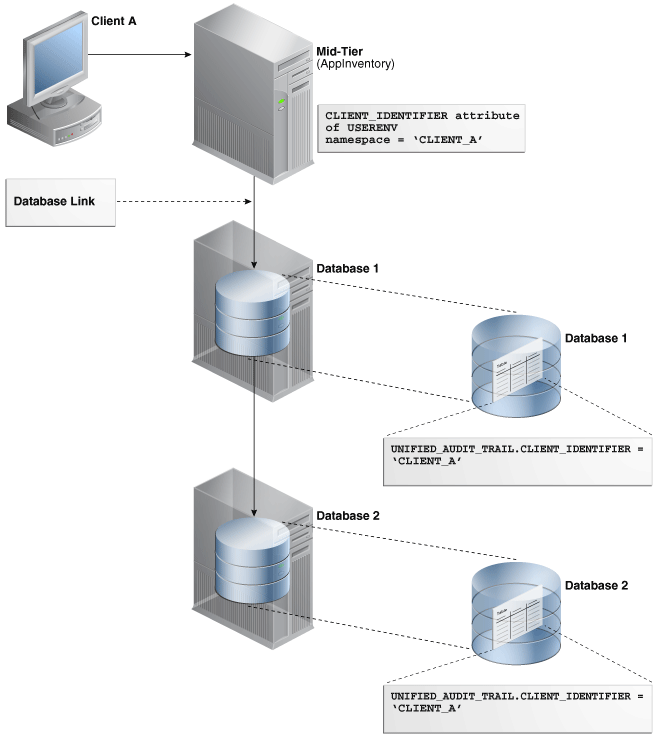
Description of "Figure 30-2 Auditing Client Identifier Information Across Sessions"
Related Topics
Parent topic: Auditing for Multitier or Multitenant Configurations
30.6.2 Auditing in a Multitenant Deployment
You can create unified audit policies for individual PDBs and in the root.
- About Local, CDB Common, and Application Common Audit Policies
An audit policy can be either a local audit policy, a CDB common audit policy, or an application common audit policy. - Common Audit Configurations Across All PDBs
A common audit configuration is visible and enforced across all PDBs. - Unified Audit Policies in an Application Root
When you create an application root from a regular PDB, any local unified audit policies in this PDB are added to this application root. - Configuring a Local Unified Audit Policy or Common Unified Audit Policy
TheCONTAINERclause is specific to multitenant environment use for theCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement. - Example: Local Unified Audit Policy
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can create a local unified audit policy in either the root or a PDB. - Example: CDB Common Unified Audit Policy
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can create a CDB common unified audit policy. - Example: Application Common Unified Audit Policy
For application container common unified audit policies, you can audit action options and system privilege options, and refer to common objects and roles. - How Local or Common Audit Policies or Settings Appear in the Audit Trail
You can query unified audit policy views from either the root or the PDB in which the action occurred.
Parent topic: Auditing for Multitier or Multitenant Configurations
30.6.2.1 About Local, CDB Common, and Application Common Audit Policies
An audit policy can be either a local audit policy, a CDB common audit policy, or an application common audit policy.
This applies to both unified audit policies and policies that are created using the AUDIT SQL statement.
-
Local audit policy. This type of policy can exist in either the root (CDB or application) or the PDB (CDB or application). A local audit policy that exists in the root can contain object audit options for both local and common objects. Both local and common users who have been granted the
AUDIT_ADMINrole can enable local policies: local users from their PDBs and common users from the root or the PDB to which they have privileges. You can enable a local audit policy for both local and common users and roles.You can create local audit policies for application local objects and application local roles, as well as system action options and system privilege options. You cannot enforce a local audit policy for a common user across all containers, nor can you enforce a common audit policy for a local user.
-
CDB common audit policy. This type of policy is available to all PDBs in the multitenant environment. Only common users who have been granted the
AUDIT_ADMINrole can create and maintain common audit policies. You can enable common audit policies only for common users. You must create common audit policies only in the root. This type of policy can contain object audit options of only common objects, and be enabled only for common users. You can enable a common audit policy for common users and roles only.The name of a CDB common audit policy must begin with the value of the
COMMON_USER_PREFIXinitialization parameter. The default value of theCOMMON_USER_PREFIXparameter isc##. For example,c##hr_adminis a valid common audit policy name. The length of the audit policy name cannot exceed 128 bytes and must contain ASCII characters only.You cannot enforce a common audit policy for a local user across all containers.
-
Application common audit policy. Similar to CDB common audit policies, this type of policy is available to all PDBs in the multitenant environment. You can create common audit policies for application common objects and application common roles, as well as system action options and system privilege options. You can only create this type of policy in the application root container, but you can enable it on both application common users and CDB common users. If you want to audit objects, then ensure that these objects are application common objects. You can determine whether an object is an application common object by querying the
SHARINGcolumn of theDBA_OBJECTSdata dictionary view.The naming conventions for application common audit policies follow the same rules as those for CDB common audit policies, except that the value of the
COMMON_USER_PREFIXis fetched from the application root. The default value in application root is an empty string. For example,hr_adminis a valid application common audit policy name.
By default, audit policies are local to the current PDB, for both CDB and application scenarios.
The following table explains how audit policies apply in different multitenant environments.
Table 30-4 How Audit Policies Apply to the CDB Root, Application Root, and Individual PDBs
| Audit Option Type | CDB Root | Application Root | Individual PDB |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Common audit statement or audit policy |
Applies to CDB common users |
Applies to CDB common users |
Applies to CDB common users |
|
Application container common audit statement or audit policy |
Not applicable |
|
|
|
Local audit statement or audit policy |
Local configurations not allowed |
Local configurations not allowed |
|
Parent topic: Auditing in a Multitenant Deployment
30.6.2.2 Common Audit Configurations Across All PDBs
A common audit configuration is visible and enforced across all PDBs.
Audit configurations are either local or common. The scoping rules that apply to other local or common phenomena, such as users and roles, all apply to audit configurations.
Note:
Audit initialization parameters exist at the CDB level and not in each PDB.
PDBs support the following auditing options:
-
Object auditing
Object auditing refers to audit configurations for specific objects. Only common objects can be part of the common audit configuration. A local audit configuration cannot contain common objects.
-
Audit policies
Audit policies can be local or common:
-
Local audit policies
A local audit policy applies to a single PDB. You can enforce local audit policies for local and common users in this PDB only. Attempts to enforce local audit policies across all containers result in an error.
In all cases, enforcing of a local audit policy is part of the local auditing framework.
-
Common audit policies
A common audit policy applies to all containers. When you create a common audit policy, prefix the name with
C##orc##(for example,c##all_select_pol). This policy can only contain actions, system privileges, common roles, and common objects. You can apply a common audit policy only to common users. Attempts to enforce a common audit policy for a local user across all containers result in an error.
-
A common audit configuration is stored in the SYS schema of the root. A local audit configuration is stored in the SYS schema of the PDB to which it applies.
Audit trails are stored in the SYS or AUDSYS schemas of the relevant CDB or PDB container. Operating system and XML audit trails for PDBs are stored in subdirectories of the directory specified by the AUDIT_FILE_DEST (deprecated) initialization parameter.
Parent topic: Auditing in a Multitenant Deployment
30.6.2.3 Unified Audit Policies in an Application Root
When you create an application root from a regular PDB, any local unified audit policies in this PDB are added to this application root.
This applies to both unified audit policies and policies that are created using the AUDIT SQL statement.
In this situation, you will need to convert the local unified audit policies to common unified audit policies. To do so, drop each existing local unified audit policy from the application root and then use the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement to recreate it as an application common audit policy.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Auditing in a Multitenant Deployment
30.6.2.4 Configuring a Local Unified Audit Policy or Common Unified Audit Policy
The CONTAINER clause is specific to multitenant environment use for the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement.
CONTAINER clause in the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement.
-
Use the following syntax to create a local or common unified audit policy:
CREATE AUDIT POLICY policy_name action1 [,action2 ] [CONTAINER = {CURRENT | ALL}];
In this specification:
-
CURRENTsets the audit policy to be local to the current PDB. -
ALLmakes the audit policy a common audit policy, that is, available to the entire multitenant environment.
For example, for a common unified audit policy:
CREATE AUDIT POLICY dict_updates
ACTIONS UPDATE ON SYS.USER$,
DELETE ON SYS.USER$,
UPDATE ON SYS.LINK$,
DELETE ON SYS.LINK$
CONTAINER = ALL;
Note the following:
-
You can set the
CONTAINERclause for theCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement but not forALTER AUDIT POLICYorDROP AUDIT POLICY. If you want to change the scope of an existing unified audit policy to use this setting, then you must drop and re-create the policy. -
For
AUDITstatements, you can set theCONTAINERclause for audit settings only if you have an Oracle database that has not been migrated to the Release 12.x and later audit features. You cannot use theCONTAINERclause in anAUDITstatement that is used to enable a unified audit policy. -
If you are in a PDB, then you can only set the
CONTAINERclause toCURRENT, notALL. If you omit the setting while in the PDB, then the default isCONTAINER = CURRENT. -
If you are in the root, then you can set the
CONTAINERclause to eitherCURRENTif you want the policy to apply to the root only, or toALLif you want the policy to apply to the entire CDB. If you omit theCONTAINERclause, then default isCONTAINER = CURRENT. -
For objects:
-
Common audit policies can have common objects only and local audit policies can have both local objects and common objects.
-
You cannot set
CONTAINERtoALLif the objects involved are local. They must be common objects.
-
-
For privileges:
-
You can set the
CONTAINERtoCURRENT(or omit theCONTAINERclause) if the user accounts involved are a mixture of local and common accounts. This creates a local audit configuration that applies only to the current PDB. -
You cannot set
CONTAINERtoALLif the users involved are local users. They must be common users. -
If you set
CONTAINERtoALLand do not specify a user list (using theBYclause in theAUDITstatement), then the configuration applies to all common users in each PDB.
-
-
For application containers, you can run a common unified audit policy from the application container script that is used for application install, upgrade, patch, and uninstall operations. To do so:
-
Create a common unified audit policy in the application container root, and set this policy to
CONTAINER = ALL. Alternatively, you can include this policy in the script that is described in this next step. -
Create a custom version of the script you normally would use to install, upgrade, patch, or uninstall Oracle Database.
-
Within this script, include the SQL statements that you want to audit within the following lines:
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION BEGIN INSTALL List SQL statements here. Separate each statement with a semi-colon. ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION END INSTALLIf you include the unified audit policy in the script, then ensure that you include both the
CREATE AUDIT POLICYandAUDIT POLICYstatements.
After the audit policy is created and enabled, all user access to the application common objects is audited irrespective of whether the audit policy is defined in the database or from the script.
-
-
To audit application install, upgrade, patch, and uninstall operations locally in an application root or an application PDB, follow a procedure similar to the preceding procedure for common unified audit policies, but synchronize the application PDB afterward. For example:
ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE APPLICATION application_name SYNC;
Related Topics
Parent topic: Auditing in a Multitenant Deployment
30.6.2.5 Example: Local Unified Audit Policy
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can create a local unified audit policy in either the root or a PDB.
When you create a local unified audit policy in the root, it only applies to the root and not across the multitenant environment.
The following example shows a local unified audit policy that has been created by the common user c##sec_admin from a PDB and applied to common user c##hr_admin.
Example 30-20 Local Unified Audit Policy
CONNECT c##sec_admin@pdb_name
Enter password: password
Connected.
CREATE AUDIT POLICY table_privs
PRIVILEGES CREATE ANY TABLE, DROP ANY TABLE
CONTAINER = CURRENT;
AUDIT POLICY table_privs BY c##hr_admin;Parent topic: Auditing in a Multitenant Deployment
30.6.2.6 Example: CDB Common Unified Audit Policy
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can create a CDB common unified audit policy.
Example 30-21 shows a common unified audit policy that has been created by the common user c##sec_admin from the root and applied to common user c##hr_admin.
Example 30-21 Common Unified Audit Policy
CONNECT c##sec_admin
Enter password: password
Connected.
CREATE AUDIT POLICY admin_pol
ACTIONS CREATE TABLE, ALTER TABLE, DROP TABLE
ROLES c##hr_mgr, c##hr_sup
CONTAINER = ALL;
AUDIT POLICY admin_pol BY c##hr_admin;Parent topic: Auditing in a Multitenant Deployment
30.6.2.7 Example: Application Common Unified Audit Policy
For application container common unified audit policies, you can audit action options and system privilege options, and refer to common objects and roles.
You can create the application common audit policy only from the application root, and enable the policy for both application common users and CDB common users.
The following example shows how to create a policy that audits the application common user SYSTEM for the application container app_pdb. The audit policy audits SELECT actions on the SYSTEM.utils_tab table and on DROP TABLE actions on any of the PDBs in the container database, including the CDB root. The policy also audits the use of the SELECT ANY TABLE system privilege across all containers.
Example 30-22 Application Common Unified Audit Policy
CONNECT c##sec_admin@app_pdb
Enter password: password
Connected.
CREATE AUDIT POLICY app_pdb_admin_pol
ACTIONS SELECT ON hr_app_cdb.utils_tab, DROP TABLE
PRIVILEGES SELECT ANY TABLE
CONTAINER = ALL;
AUDIT POLICY app_pdb_admin_pol by SYSTEM, c##hr_admin;In the preceding example, setting CONTAINER to ALL applies the policy only to all the relevant object accesses in the application root and on all the application PDBs that belong to the application root. It does not apply the policy outside this scope.
Parent topic: Auditing in a Multitenant Deployment
30.6.2.8 How Local or Common Audit Policies or Settings Appear in the Audit Trail
You can query unified audit policy views from either the root or the PDB in which the action occurred.
You can perform the following types of queries:
-
Audit records from all PDBs. The audit trail reflects audited actions that have been performed in the PDBs. For example, if user
lbrowninPDB1performs an action that has been audited by either a common or a local audit policy, then the audit trail will capture this action. TheDBIDcolumn in theUNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAILdata dictionary view indicates the PDB in which the audited action takes place and to which the policy applies. If you want to see audit records from all PDBs, you should query theCDB_UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAILdata dictionary view from the root. -
Audit records from common audit policies. This location is where the common audit policy results in an audit record. The audit record can be generated anywhere in the multitenant environment—the root or the PDBs, depending on where the action really occurred. For example, the common audit policy
fga_polaudits theEXECUTEprivilege on theDBMS_FGAPL/SQL package, and if this action occurs inPDB1, then the audit record is generated inPDB1and not in the root. Hence, the audit record can be seen in PDB1.You can query the
UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAILdata dictionary view for the policy from either the root or a PDB if you include aWHEREclause for the policy name (for example,WHERE UNIFIED_AUDIT_POLICIES = 'FGA_POL').
The following example shows how to find the results of a common unified audit policy:
CONNECT c##sec_admin
Enter password: password
Connected.
SELECT DBID, ACTION_NAME, OBJECT_SCHEMA, OBJECT_NAME FROM CDB_UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL WHERE DBUSERNAME = 'c##hr_admin';
46892-1
DBID ACTION_NAME OBJECT_SCHEMA OBJECT_NAME
----------- ----------- ------------- -----------
653916017 UPDATE HR EMPLOYEES
653916018 UPDATE HR JOB_HISTORY
653916017 UPDATE HR JOBS Parent topic: Auditing in a Multitenant Deployment
30.7 Extending Unified Auditing to Capture Custom Attributes
You can extend the unified audit trail to capture custom attributes by auditing application context values.
- About Auditing Application Context Values
In many cases, you may want to bring your custom attributes into the unified audit trail while auditing (for example, application attributes from the application session). - Configuring Application Context Audit Settings
TheAUDITstatement with theCONTEXTkeyword configures auditing for application context values. - Disabling Application Context Audit Settings
TheNOAUDITstatement disables application context audit settings. - Example: Auditing Application Context Values in a Default Database
TheAUDIT CONTEXT NAMESPACEstatement can audit application context values. - Example: Auditing Application Context Values from Oracle Label Security
TheAUDIT CONTEXT NAMESPACEstatement can audit application context values from Oracle Label Security. - How Audited Application Contexts Appear in the Audit Trail
TheUNIFIED_AUDIT_POLICIESdata dictionary view lists application context audit events.
Parent topic: Creating Custom Unified Audit Policies
30.7.1 About Auditing Application Context Values
In many cases, you may want to bring your custom attributes into the unified audit trail while auditing (for example, application attributes from the application session).
You can extend the unified audit trail to capture such custom attributes by auditing application context values. This feature enables you to capture any application context values set by the database applications, while executing the audited statement.
This feature enables you to capture any application context values set by the database applications, while executing the audited statement.
If you plan to audit Oracle Label Security, then this feature captures session label activity for the database audit trail. The audit trail records all the values retrieved for the specified context-attribute value pairs.
The application context audit setting or the audit policy have session static semantics. In other words, if a new policy is enabled for a user, then the subsequent user sessions will see an effect of this command. After the session is established, then the policies and contexts settings are loaded and the subsequent AUDIT statements have no effect on that session.
Note that the application context audit policy applies only to the current PDB.
30.7.2 Configuring Application Context Audit Settings
The AUDIT statement with the CONTEXT keyword configures auditing for application context values.
You do not create an unified audit policy for this type of auditing.
-
Use the following syntax to configure auditing for application context values:
AUDIT CONTEXT NAMESPACE context_name1 ATTRIBUTES attribute1 [, attribute2] [, CONTEXT NAMESPACE context_name2 ATTRIBUTES attribute1 [, attribute2]] [BY user_list];
In this specification:
-
context_name1: Optionally, you can include one additionalCONTEXTname-attribute value pair. -
user_listis an optional list of database user accounts. Separate multiple names with a comma. If you omit this setting, then Oracle Database configures the application context policy for all users. When each user logs in, a list of all pertinent application contexts and their attributes is cached for the user session.
For example:
AUDIT CONTEXT NAMESPACE clientcontext3 ATTRIBUTES module, action, CONTEXT NAMESPACE ols_session_labels ATTRIBUTES ols_pol1, ols_pol3 BY appuser1, appuser2;
To find a list of currently configured application context audit settings, query the AUDIT_UNIFIED_CONTEXTS data dictionary view.
Parent topic: Extending Unified Auditing to Capture Custom Attributes
30.7.3 Disabling Application Context Audit Settings
The NOAUDIT statement disables application context audit settings.
-
To disable an application context audit setting, specify the namespace and attribute settings in the
NOAUDITstatement. You can enter the attributes in any order (that is, they do not need to match the order used in the correspondingAUDIT CONTEXTstatement.)
For example:
NOAUDIT CONTEXT NAMESPACE client_context ATTRIBUTES module, CONTEXT NAMESPACE ols_session_labels ATTRIBUTES ols_pol1, ols_pol3 BY USERS WITH GRANTED ROLES emp_admin;
To find the currently audited application contexts, query the AUDIT_UNIFIED_CONTEXTS data dictionary view.
Parent topic: Extending Unified Auditing to Capture Custom Attributes
30.7.4 Example: Auditing Application Context Values in a Default Database
The AUDIT CONTEXT NAMESPACE statement can audit application context values.
Example 30-23 shows how to audit the clientcontext application values for the module and action attributes, by the user appuser1.
Example 30-23 Auditing Application Context Values in a Default Database
AUDIT CONTEXT NAMESPACE clientcontext ATTRIBUTES module, action BY appuser1;
Parent topic: Extending Unified Auditing to Capture Custom Attributes
30.7.5 Example: Auditing Application Context Values from Oracle Label Security
The AUDIT CONTEXT NAMESPACE statement can audit application context values from Oracle Label Security.
Example 30-24 shows how to audit an application context for Oracle Label Security called ORA_OLS_SESSION_LABELS, for the attributes ols_pol1 and ols_pol2.
Example 30-24 Auditing Application Context Values from Oracle Label Security
AUDIT CONTEXT NAMESPACE ORA_OLS_SESSION_LABELS ATTRIBUTES ols_pol1, ols_pol2;
Parent topic: Extending Unified Auditing to Capture Custom Attributes
30.7.6 How Audited Application Contexts Appear in the Audit Trail
The UNIFIED_AUDIT_POLICIES data dictionary view lists application context audit events.
The APPLICATION_CONTEXTS column of the UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view shows application context audit data. The application contexts appear as a list of semi-colon separated values.
For example:
SELECT APPLICATION_CONTEXTS FROM UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL WHERE UNIFIED_AUDIT_POLICIES = 'app_audit_pol'; APPLICATION_CONTEXTS ---------------------------------------------------------- CLIENT_CONTEXT.APPROLE=MANAGER;E2E_CONTEXT.USERNAME=PSMITH
Parent topic: Extending Unified Auditing to Capture Custom Attributes
30.8 Auditing Components of Other Oracle Products and Features
You can create unified audit policies for Oracle products and features such as Oracle Database Vault, Oracle Real Application Security, Oracle Data Pump, and Oracle Machine Learning for SQL events.
- Auditing Oracle SQL Firewall
You can audit Oracle SQL Firewall violations with a unified audit policy. - Auditing Oracle Database Vault Events
In an Oracle Database Vault environment, theCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can audit Database Vault activities. - Auditing Oracle Database Real Application Security Events
You can useCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement to audit Oracle Database Real Application Security events. - Auditing Oracle Recovery Manager Events
You can use theCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement to audit Oracle Recovery Manager events. - Auditing Oracle Label Security Events
In an Oracle Label Security environment, theCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can audit Oracle Label Security activities. - Auditing Oracle Data Pump Events
You can use theCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement to audit Oracle Data Pump. - Auditing Oracle SQL*Loader Direct Load Path Events
You can use theCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement to audit Oracle SQL*Loader direct load path events. - Auditing Oracle XML DB HTTP and FTP Protocols
You can use theCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement to audit Oracle XML DB HTTP and FTP protocol messages. - Auditing Oracle Machine Learning for SQL Events
You can use theCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement to audit Oracle Machine Learning for SQL events.
Parent topic: Creating Custom Unified Audit Policies
30.8.1 Auditing Oracle SQL Firewall
You can audit Oracle SQL Firewall violations with a unified audit policy.
- About Auditing Oracle SQL Firewall
The occurrence of Oracle SQL Firewall violations potentially indicates abnormal database access attempts, including SQL injection and credential theft or abuse. - Example: Auditing Oracle SQL Firewall Violations
You can use theCOMPONENTclause to set the unified audit policy to track all Oracle SQL Firewall violations. - How Oracle SQL Firewall Events Appear in the Audit Trail
TheUNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAILdata dictionary view lists Oracle SQL Firewall audit events.
30.8.1.1 About Auditing Oracle SQL Firewall
The occurrence of Oracle SQL Firewall violations potentially indicates abnormal database access attempts, including SQL injection and credential theft or abuse.
Auditing violations record the violation in the database audit trail, which can be protected from tampering. As an administrator with AUDIT_ADMIN role, you can create unified audit policy with the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement and with the COMPONENT clause set to SQL Firewall.
The data dictionary views for SQL Firewall begin with the name DBA_SQL_FIREWALL_. The columns FW_ACTION_NAME and FW_RETURN_CODE in the UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view stores the relevant information on Oracle SQL Firewall violations.
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle SQL Firewall
30.8.1.2 Example: Auditing Oracle SQL Firewall Violations
You can use the COMPONENT clause to set the unified audit policy to track all Oracle SQL Firewall violations.
Example 30-25 shows how to create and enable this type of a unified audit policy. You can consider setting the SQL_FIREWALL component to SQL VIOLATION or CONTEXT VIOLATION to be more specific.
Example 30-25 Auditing SQL Firewall Violations
CREATE AUDIT POLICY sql_firewall_pol
ACTIONS COMPONENT = SQL_FIREWALL ALL
ON pfitch;
AUDIT POLICY sql_firewall_pol;Parent topic: Auditing Oracle SQL Firewall
30.8.1.3 How Oracle SQL Firewall Events Appear in the Audit Trail
The UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view lists Oracle SQL Firewall audit events.
The FW_ACTION_NAME and FW_RETURN_CODE columns of the UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view track SQL Firewall violations. To retrieve all the audited Oracle SQL Firewall violations, consider filtering the AUDIT_TYPE component to include the Oracle SQL Firewall component from V$UNIFIED_AUDIT_RECORD_FORMAT. For example:
SELECT DBUSERNAME, ACTION_NAME, CURRENT_USER, SQL_TEXT, UNIFIED_AUDIT_POLICIES, FW_ACTION_NAME, FW_RETURN_CODE
FROM UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL
WHERE AUDIT_TYPE
IN (SELECT UNIQUE COMPONENT FROM V$UNIFIED_AUDIT_RECORD_FORMAT WHERE COMPONENT = 'SQL Firewall')
AND ACTION_NAME <> 'FW ADMIN ACTION';Output similar to the following appears:
DBUSERNAME ACTION_NAME CURRENT_USER SQL_TEXT UNIFIED_AUDIT_POLICIES FW_ACTION_NAME FW_RETURN_CODE
---------- ------------- ------------ –------------------------------ –--------------------- –------------- –------------
PFITCH SQL VIOLATION PFITCH SELECT SALARY FROM HS.EMPLOYEES HR_FW_POL SQL Violation 0Parent topic: Auditing Oracle SQL Firewall
30.8.2 Auditing Oracle Database Vault Events
In an Oracle Database Vault environment, the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit Database Vault activities.
- About Auditing Oracle Database Vault Events
As an administrator with theAUDIT_ADMINrole, you can create unified audit policies with theCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement and with theCOMPONENTclause set toDV. - Who Is Audited in Oracle Database Vault?
Audited Oracle Database Vault users include administrators and users whose activities affect Database Vault enforcement policies. - About Oracle Database Vault Unified Audit Trail Events
The audit trail in an Oracle Database Vault environment captures all configuration changes or attempts at changes to Database Vault policies. - Oracle Database Vault Realm Audit Events
The unified audit trail captures Oracle Database Vault realm events. - Oracle Database Vault Rule Set and Rule Audit Events
The unified audit trail can capture Oracle Database Vault rule set and rule audit events. - Oracle Database Vault Command Rule Audit Events
The unified audit trail can capture Oracle Database Vault command rule audit events. - Oracle Database Vault Factor Audit Events
The unified audit trail can capture Oracle Database Vault factor events. - Oracle Database Vault Secure Application Role Audit Events
The unified audit trail can capture Oracle Database Vault secure application role audit events. - Oracle Database Vault Oracle Label Security Audit Events
The unified audit trail can capture Oracle Database Vault Oracle Label Security audit events. - Oracle Database Vault Oracle Data Pump Audit Events
The unified audit trail can capture Oracle Database Vault Oracle Data Pump audit events. - Oracle Database Vault Enable and Disable Audit Events
The unified audit trail can capture Oracle Database Vault enable and disable audit events. - Configuring a Unified Audit Policy for Oracle Database Vault
TheACTIONSandACTIONS COMPONENTclauses in theCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can create unified audit policies for Oracle Database Vault events. - Example: Auditing an Oracle Database Vault Realm
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can audit Oracle Database Vault realms. - Example: Auditing an Oracle Database Vault Rule Set
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can audit Oracle Database Vault rule sets. - Example: Auditing Two Oracle Database Vault Events
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can audit multiple Oracle Database Vault events. - Example: Auditing Oracle Database Vault Factors
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can audit Oracle Database Vault factors. - How Oracle Database Vault Audited Events Appear in the Audit Trail
TheUNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAILdata dictionary view lists Oracle Database Vault audited events.
30.8.2.1 About Auditing Oracle Database Vault Events
As an administrator with the AUDIT_ADMIN role, you can create unified audit policies with the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement and with the COMPONENT clause set to DV.
To do so, you must specify an action, such as Rule Set Failure, and an object, such as the name of a rule set.
To create Oracle Database Vault unified audit policies, you must set the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement's COMPONENT clause to DV, and then specify an action, such as Rule Set Failure, and an object, such as the name of a rule set.
To access the audit trail, you can query the following views:
-
UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL -
AUDSYS.DV$CONFIGURATION_AUDIT -
AUDSYS.DV$ENFORCEMENT_AUDIT
In the UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL view, the Oracle Database Vault-specific columns begin with DV_. You must have the AUDIT_VIEWER role before you can query the UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL view.
In addition to these views, the Database Vault reports capture the results of Database Vault-specific unified audit policies.
30.8.2.2 Who Is Audited in Oracle Database Vault?
Audited Oracle Database Vault users include administrators and users whose activities affect Database Vault enforcement policies.
These users are as follows:
-
Database Vault administrators. All configuration changes that are made to Oracle Database Vault are mandatorily audited. The auditing captures activities such as creating, modifying, or deleting realms, factors, command rules, rule sets, rules, and so on. The
AUDSYS.DV$CONFIGURATION_AUDITdata dictionary view captures configuration changes made by Database Vault administrators. -
Users whose activities affect Oracle Database Vault enforcement policies. The
AUDSYS.DV$ENFORCEMENT_AUDITdata dictionary view captures enforcement-related audits
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Database Vault Events
30.8.2.3 About Oracle Database Vault Unified Audit Trail Events
The audit trail in an Oracle Database Vault environment captures all configuration changes or attempts at changes to Database Vault policies.
It also captures violations by users to existing Database Vault policies.
You can audit the following kinds of Oracle Database Vault events:
-
All configuration changes or attempts at changes to Oracle Database Vault policies. It captures both Database Vault administrator changes and attempts made by unauthorized users.
-
Violations by users to existing Database Vault policies. For example, if you create a policy to prevent users from accessing a specific schema table during non-work hours, the audit trail will capture this activity.
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Database Vault Events
30.8.2.4 Oracle Database Vault Realm Audit Events
The unified audit trail captures Oracle Database Vault realm events.
Table 30-5 describes these events.
Table 30-5 Oracle Database Vault Realm Audit Events
| Audit Event | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Creates a realm through the |
|
|
Updates a realm through the |
|
|
Renames a realm through the |
|
|
Deletes a realm through the |
|
|
Deletes a realm and its related Database Vault configuration information through the |
|
|
Adds an authorization to the realm through the |
|
|
Removes an authorization from the realm through the |
|
|
Updates a realm authorization through the |
|
|
Adds an object to a realm authorization through the |
|
|
Removes an object from a realm authorization through the |
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Database Vault Events
30.8.2.5 Oracle Database Vault Rule Set and Rule Audit Events
The unified audit trail can capture Oracle Database Vault rule set and rule audit events.
Table 30-6 describes these events.
Table 30-6 Oracle Database Vault Rule Set and Rule Audit Events
| Audit Event | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Creates a rule set through the |
|
|
Updates a rule set through the |
|
|
Renames a rule set through the |
|
|
Deletes a rule set through the |
|
|
Adds a rule to an existing rule set through the |
|
|
Removes a rule from an existing rule set through the |
|
|
Creates a rule through the |
|
|
Updates a rule through the |
|
|
Renames a rule through the |
|
|
Deletes a rule through the |
|
|
Synchronizes the rules in Oracle Database Vault and Advanced Queuing Rules engine through the |
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Database Vault Events
30.8.2.6 Oracle Database Vault Command Rule Audit Events
The unified audit trail can capture Oracle Database Vault command rule audit events.
Table 30-7 describes these events.
Table 30-7 Oracle Database Vault Command Rule Audit Events
| Audit Event | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Creates a command rule through the |
|
|
Deletes a command rule through the |
|
|
Updates a command rule through the |
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Database Vault Events
30.8.2.7 Oracle Database Vault Factor Audit Events
The unified audit trail can capture Oracle Database Vault factor events.
Table 30-8 describes these events.
Table 30-8 Oracle Database Vault Factor Audit Events
| Audit Event | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Creates a factor type through the |
|
|
Deletes a factor type through the |
|
|
Updates a factor type through the |
|
|
Renames a factor type through the |
|
|
Creates a factor through the |
|
|
Updates a factor through the |
|
|
Deletes a factor through the |
|
|
Renames a factor through the |
|
|
Specifies a parent-child relationship between two factors through the |
|
|
Removes the parent-child relationship between two factors through the |
|
|
Specifies that the label for a factor contributes to the Oracle Label Security label for a policy, through the |
|
|
Removes factor label from being associated with an Oracle Label Security label for a policy, through the |
|
|
Creates a factor identity through the |
|
|
Updates a factor identity through the |
|
|
Associates an identity with a different factor through the |
|
|
Updates the value of an identity through the |
|
|
Deletes an existing factor identity through the |
|
|
Creates a factor identity map through the |
|
|
Deletes a factor identity map through the |
|
|
Adds an Oracle Database Real Application Clusters database node to the domain factor identities and labels it according to the Oracle Label Security policy, through the |
|
|
Drops an Oracle RAC node from the domain factor identities through the |
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Database Vault Events
30.8.2.8 Oracle Database Vault Secure Application Role Audit Events
The unified audit trail can capture Oracle Database Vault secure application role audit events.
Table 30-9 describes these events.
Table 30-9 Oracle Database Vault Secure Application Role Audit Events
| Audit Event | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Creates an Oracle Database Vault secure application role through the |
|
|
Deletes an Oracle Database Vault secure application role through the |
|
|
Updates an Oracle Database Vault secure application role through the |
|
|
Renames an Oracle Database Vault secure application role through the |
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Database Vault Events
30.8.2.9 Oracle Database Vault Oracle Label Security Audit Events
The unified audit trail can capture Oracle Database Vault Oracle Label Security audit events.
Table 30-10 describes these events.
Table 30-10 Oracle Database Vault Oracle Label Security Audit Events
| Audit Event | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Creates an Oracle Label Security policy label through the |
|
|
Deletes an Oracle Label Security policy label through the |
|
|
Specifies the algorithm that is used to merge labels when computing the label for a factor, or the Oracle Label Security Session label, through the |
|
|
Changes the Oracle Label Security merge label algorithm through the |
|
|
Deletes all Oracle Database Vault objects related to an Oracle Label Security policy, through the |
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Database Vault Events
30.8.2.10 Oracle Database Vault Oracle Data Pump Audit Events
The unified audit trail can capture Oracle Database Vault Oracle Data Pump audit events.
Table 30-11 describes these events.
Table 30-11 Oracle Database Vault Oracle Data Pump Audit Events
| Audit Event | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Authorizes an Oracle Data Pump user through the |
|
|
Removes from authorization an Oracle Data Pump user through the |
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Database Vault Events
30.8.2.11 Oracle Database Vault Enable and Disable Audit Events
The unified audit trail can capture Oracle Database Vault enable and disable audit events.
Table 30-12 describes these events.
Table 30-12 Oracle Database Vault Enable and Disable Audit Events
| Event | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Database Vault Events
30.8.2.12 Configuring a Unified Audit Policy for Oracle Database Vault
The ACTIONS and ACTIONS COMPONENT clauses in the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can create unified audit policies for Oracle Database Vault events.
-
Use the following syntax to create an Oracle Database Vault unified audit policy:
CREATE AUDIT POLICY policy_name ACTIONS COMPONENT= DV DV_action ON DV_object [,DV_action2 ON DV_object2]
In this specification:
-
DV_actionis one of the following:-
Realm-related actions:
Realm Violationaudits realm violations (for example, when an unauthorized user attempts to access a realm-protected object).Realm Successaudits when a realm-protected object is successfully accessed by an authorized user.Realm Accessaudits both realm violation and realm success cases, that is, audits whenever the realm access attempt has been made, whether the access succeeded or failed. -
Rule set-related actions:
Rule Set Failure,Rule Set Success,Rule Set Eval -
Factor-related actions:
Factor Error,Factor Null,Factor Validate Error,Factor Validate False,Factor Trust Level Null,Factor Trust Level Neg,Factor All
-
-
DV_objectsis one of the following:-
Realm_Name -
Rule_Set_Name -
Factor_Name
-
If the object was created in lower or mixed case, then you must enclose DV_objects in double quotation marks. If you had created the object in all capital letters, then you can omit the quotation marks.
For example, to audit realm violations on the Database Vault Account Management realm:
CREATE AUDIT POLICY audit_dv ACTIONS COMPONENT=DV Realm Violation ON "Database Vault Account Management";
Remember that after you create the policy, you must use the AUDIT statement to enable it.
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Database Vault Events
30.8.2.13 Example: Auditing an Oracle Database Vault Realm
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit Oracle Database Vault realms.
Example 30-26 shows how to audit a realm violation on the HR schema.
Example 30-26 Auditing a Realm Violation
CREATE AUDIT POLICY dv_realm_hr ACTIONS COMPONENT=DV Realm Violation ON "HR Schema Realm"; AUDIT POLICY dv_realm_hr;
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Database Vault Events
30.8.2.14 Example: Auditing an Oracle Database Vault Rule Set
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit Oracle Database Vault rule sets.
Example: Auditing an Oracle Database Vault Rule Set shows how to audit the Can Maintain Accounts/Profile rule set.
Example 30-27 Auditing a Rule Set
CREATE AUDIT POLICY dv_rule_set_accts ACTIONS COMPONENT=DV RULE SET FAILURE ON "Can Maintain Accounts/Profile"; AUDIT POLICY dv_rule_set_accts;
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Database Vault Events
30.8.2.15 Example: Auditing Two Oracle Database Vault Events
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit multiple Oracle Database Vault events.
Example 30-28 shows how to audit a realm violation and a rule set failure.
Example 30-28 Auditing Two Oracle Database Vault Events
CREATE AUDIT POLICY audit_dv ACTIONS COMPONENT=DV REALM VIOLATION ON "Oracle Enterprise Manager", Rule Set Failure ON "Allow Sessions"; AUDIT POLICY audit_dv;
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Database Vault Events
30.8.2.16 Example: Auditing Oracle Database Vault Factors
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit Oracle Database Vault factors.
Example 30-29 shows how to audit two types of errors for one factor.
Example 30-29 Auditing Oracle Database Vault Factor Settings
CREATE AUDIT POLICY audit_dv_factor ACTIONS COMPONENT=DV FACTOR ERROR ON "Database_Domain", Factor Validate Error ON "Client_IP"; AUDIT POLICY audit_dv_factor;
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Database Vault Events
30.8.2.17 How Oracle Database Vault Audited Events Appear in the Audit Trail
The UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view lists Oracle Database Vault audited events.
The DV_* columns of the UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL view show Oracle Database Vault-specific audit data.
For example:
SELECT DBUSERNAME, SQL_TEXT, UNIFIED_AUDIT_POLICIES, DV_ACTION_NAME, DV_ACTION_OBJECT_NAME, DV_RULE_SET_NAME FROM UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL WHERE AUDIT_TYPE = 'DATABASE VAULT' ORDER BY EVENT_TIMESTAMP; DBUSERNAME SQL_TEXT UNIFIED_AUDIT_POLICIES DV_ACTION_NAME DV_ACTION_OBJECT_NAME DV_RULE_SET_NAME ---------- –------------------------- –---------------------- –-------------------- –-------------------- –----------------- PFITCH SELECT * FROM HR.EMPLOYEES DV_AUDIT_POLICY Command Failure Audit SELECT HR_data_protection
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Database Vault Events
30.8.3 Auditing Oracle Database Real Application Security Events
You can use CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement to audit Oracle Database Real Application Security events.
- About Auditing Oracle Database Real Application Security Events
You must have theAUDIT_ADMINrole to audit Oracle Database Real Application Security events. - Oracle Database Real Application Security Auditable Events
Oracle Database provides Real Application Security events that you can audit, suchCREATE USER,UPDATE USER. - Oracle Database Real Application Security User, Privilege, and Role Audit Events
The unified audit trail can capture Oracle Database Real Application Security events for users, privileges, and roles. - Oracle Database Real Application Security Security Class and ACL Audit Events
The unified audit trail can capture Oracle Database Real Application Security security class and ACL audit events. - Oracle Database Real Application Security Session Audit Events
The unified audit trail can capture Oracle Database Real Application Security session audit events. - Oracle Database Real Application Security ALL Events
The unified audit trail can capture Oracle Database Real Application SecurityALLevents. - Configuring a Unified Audit Policy for Oracle Database Real Application Security
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can create a unified audit policy for Oracle Real Application Security. - Example: Auditing Real Application Security User Account Modifications
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can audit Real Application Security user account modifications. - Example: Using a Condition in a Real Application Security Unified Audit Policy
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can set a condition for a Real Application Security unified audit policy. - How Oracle Database Real Application Security Events Appear in the Audit Trail
TheDBA_XS_AUDIT_TRAILdata dictionary view lists Oracle Real Application Security audit events.
30.8.3.1 About Auditing Oracle Database Real Application Security Events
You must have the AUDIT_ADMIN role to audit Oracle Database Real Application Security events.
To access the audit trail, you can query the UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view, whose Real Application Security-specific columns begin with XS_. If you want to find audit information about the internally generated VPD predicate that is created while an Oracle Real Application Security policy is being enabled, then you can query the RLS_INFO column.
Real Application Security-specific views are as follows:
-
DBA_XS_AUDIT_TRAILprovides detailed information about Real Application Security events that were audited. -
DBA_XS_AUDIT_POLICY_OPTIONSdescribes the auditing options that were defined for Real Application Security unified audit policies. -
DBA_XS_ENB_AUDIT_POLICIESlists users for whom Real Application Security unified audit polices are enabled.
Related Topics
30.8.3.2 Oracle Database Real Application Security Auditable Events
Oracle Database provides Real Application Security events that you can audit, such CREATE USER, UPDATE USER.
To find a list of auditable Real Application Security events that you can audit, you can query the COMPONENT and NAME columns of the AUDITABLE_SYSTEM_ACTIONS data dictionary view, as follows:
SELECT NAME FROM AUDITABLE_SYSTEM_ACTIONS WHERE COMPONENT = 'XS'; NAME ------------- CREATE USER UPDATE USER DELETE USER ...
Related Topics
30.8.3.3 Oracle Database Real Application Security User, Privilege, and Role Audit Events
The unified audit trail can capture Oracle Database Real Application Security events for users, privileges, and roles.
Table 30-13 describes these events.
Table 30-13 Oracle Database Real Application Security User, Privilege, and Role Audit Events
| Audit Event | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Creates an Oracle Database Real Application Security user account through the |
|
|
Updates an Oracle Database Real Application Security user account through the following procedures:
|
|
|
Deletes an Oracle Database Real Application Security user account through the through the |
|
|
Audits the |
|
|
Audits the |
|
|
Creates an Oracle Database Real Application Security role through the |
|
|
Updates an Oracle Database Real Application Security role through the following procedures:
|
|
|
Deletes an Oracle Database Real Application Security role through the |
|
|
Grants Oracle Database Real Application Security roles through the |
|
|
Revokes Oracle Database Real Application Security roles through the |
|
|
Adds Oracle Database Real Application Security proxy user account through the |
|
|
Removes an Oracle Database Real Application Security proxy user account through the |
|
|
Sets the Oracle Database Real Application Security user account password through the |
|
|
Sets the Oracle Database Real Application Security proxy user account verifier through the |
30.8.3.4 Oracle Database Real Application Security Security Class and ACL Audit Events
The unified audit trail can capture Oracle Database Real Application Security security class and ACL audit events.
Table 30-14 describes these events.
Table 30-14 Oracle Database Real Application Security Security Class and ACL Audit Events
| Audit Event | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Creates a security class through the |
|
|
Creates a security class through the following procedures:
|
|
|
Deletes a security class through the |
|
|
Creates an Access Control List (ACL) through the |
|
|
Updates an ACL through the following procedures:
|
|
|
Deletes an ACL through the |
|
|
Creates a data security policy through the |
|
|
Updates a data security policy through the following procedures:
|
|
|
Deletes a data security policy through the |
|
|
Enables extensible data security for a database table or view through the |
|
|
Disables extensible data security for a database table or view through the |
30.8.3.5 Oracle Database Real Application Security Session Audit Events
The unified audit trail can capture Oracle Database Real Application Security session audit events.
Table 30-13 describes these events.
Table 30-15 Oracle Database Real Application Security Session Audit Events
| Audit Event | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Creates a session through the |
|
|
Destroys a session through the |
|
|
Creates a namespace through the |
|
|
Deletes a namespace through the |
|
|
Creates a namespace attribute through the |
|
|
Sets a namespace attribute through the |
|
|
Gets a namespace attribute through the |
|
|
Deletes a namespace attribute through the |
|
|
Creates a namespace attribute through the |
|
|
Updates a namespace attribute through the following procedures:
|
|
|
Deletes a namespace through the |
|
|
Adds a global callback through the |
|
|
Deletes a global callback through the |
|
|
Enables a global callback through the |
|
|
Sets a session cookie through the |
|
|
Sets the time-out time for inactive sessions through the |
|
|
Sets the security context of the current lightweight user session to a newly initialized security context for a specified user through the |
|
|
Assigns or removes one or more dynamic roles for the specified user through the |
|
|
Enable a role for a lightweight user session through the |
|
|
Disables a role for a lightweight user session through the |
30.8.3.6 Oracle Database Real Application Security ALL Events
The unified audit trail can capture Oracle Database Real Application Security ALL events.
Table 30-16 describes these events.
Table 30-16 Oracle Database Real Application Security ALL Events
| Audit Event | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Captures all Real Application Security actions |
30.8.3.7 Configuring a Unified Audit Policy for Oracle Database Real Application Security
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can create a unified audit policy for Oracle Real Application Security.
-
Use the following syntax to create a unified audit policy for Oracle Database Real Application Security:
CREATE AUDIT POLICY policy_name ACTIONS COMPONENT=XS component_action1 [, action2];
For example:
CREATE AUDIT POLICY audit_ras_pol ACTIONS COMPONENT=XS SWITCH USER, DISABLE ROLE;
You can build more complex policies, such as those that include conditions. Remember that after you create the policy, you must use the AUDIT statement to enable it.
Related Topics
30.8.3.8 Example: Auditing Real Application Security User Account Modifications
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit Real Application Security user account modifications.
Example 30-30 shows how to audit user bhurst's attempts to switch users and disable roles.
Example 30-30 Auditing Real Application Security User Account Modifications
CREATE AUDIT POLICY ras_users_pol ACTIONS COMPONENT=XS SWITCH USER, DISABLE ROLE; AUDIT POLICY ras_users_pol BY bhurst;
30.8.3.9 Example: Using a Condition in a Real Application Security Unified Audit Policy
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can set a condition for a Real Application Security unified audit policy.
Example 30-31 shows how to create Real Application Security unified audit policy that applies the audit only to actions from the nemosity computer host.
Example 30-31 Using a Condition in a Real Application Security Unified Audit Policy
CREATE AUDIT POLICY ras_acl_pol
ACTIONS DELETE ON OE.CUSTOMERS
ACTIONS COMPONENT=XS CREATE ACL, UPDATE ACL, DELETE ACL
WHEN 'SYS_CONTEXT(''USERENV'', ''HOST'') = ''nemosity'''
EVALUATE PER INSTANCE;
AUDIT POLICY ras_acl_pol BY pfitch;30.8.3.10 How Oracle Database Real Application Security Events Appear in the Audit Trail
The DBA_XS_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view lists Oracle Real Application Security audit events.
The following example queries the Real Application Security-specific view, DBA_XS_AUDIT_TRAIL:
SELECT XS_USER_NAME FROM DBA_XS_AUDIT_TRAIL WHERE XS_ENABLED_ROLE = 'CLERK'; XS_USER_NAME ------------- USER2
30.8.4 Auditing Oracle Recovery Manager Events
You can use the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement to audit Oracle Recovery Manager events.
- About Auditing Oracle Recovery Manager Events
TheUNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAILdata dictionary view automatically stores Oracle Recovery Manager audit events in theRMAN_column. - Oracle Recovery Manager Unified Audit Trail Events
The unified audit trail can capture Oracle Recovery Manager events. - How Oracle Recovery Manager Audited Events Appear in the Audit Trail
The UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view lists Oracle Recovery Manager audit events.
30.8.4.1 About Auditing Oracle Recovery Manager Events
The UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view automatically stores Oracle Recovery Manager audit events in the RMAN_column.
Unlike other Oracle Database components, you do not create a unified audit policy for Oracle Recovery Manager events.
However, you must have the AUDIT_ADMIN or AUDIT_VIEWER role in order to query the UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL view to see these events. If you have the SYSBACKUP or the SYSDBA administrative privilege, then you can find additional information about Recovery Manager jobs by querying views such as V$RMAN_STATUS or V$RMAN_BACKUP_JOB_DETAILS.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Recovery Manager Events
30.8.4.2 Oracle Recovery Manager Unified Audit Trail Events
The unified audit trail can capture Oracle Recovery Manager events.
Table 30-17 describes these events.
Table 30-17 Oracle Recovery Manager Columns in UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL View
| Recovery Manager Column | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Recovery Manager session identifier. Together with the |
|
|
Timestamp for the session. Together with the |
|
|
The Recovery Manager operation executed by the job. One row is added for each distinct operation within a Recovery Manager session. For example, a backup job contains |
|
|
Type of objects involved in a Recovery Manager session. It contains one of the following values. If the Recovery Manager session does not satisfy more than one of them, then preference is given in the following order, from top to bottom of the list.
|
|
|
Device associated with a Recovery Manager session. This column can be |
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Recovery Manager Events
30.8.4.3 How Oracle Recovery Manager Audited Events Appear in the Audit Trail
The UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view lists Oracle Recovery Manager audit events.
Table 30-17 lists the columns in the UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view that you can query to find Oracle Recovery Manager-specific audit data.
For example:
SELECT RMAN_OPERATION FROM UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL WHERE RMAN_OBJECT_TYPE = 'DB FULL'; RMAN_OPERATION --------------- BACKUP
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Recovery Manager Events
30.8.5 Auditing Oracle Label Security Events
In an Oracle Label Security environment, the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit Oracle Label Security activities.
- About Auditing Oracle Label Security Events
As with all unified auditing, you must have theAUDIT_ADMINrole before you can audit Oracle Label Security (OLS) events. - Oracle Label Security Unified Audit Trail Events
The unified audit trail can capture Oracle Label Security audit events. - Oracle Label Security Auditable User Session Labels
TheORA_OLS_SESSION_LABELSapplication context can capture user session label usage for each Oracle Database event. - Configuring a Unified Audit Policy for Oracle Label Security
TheACTIONSandACTIONS COMPONENTclauses in theCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can be used to create Oracle Label Security event audit policies. - Example: Auditing Oracle Label Security Session Label Attributes
TheAUDIT CONTEXT NAMESPACEstatement can audit Oracle Label Security session label attributes. - Example: Excluding a User from an Oracle Label Security Policy
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can exclude users from policies. - Example: Auditing Oracle Label Security Policy Actions
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can audit Oracle Label Security policy actions. - Example: Querying for Audited OLS Session Labels
TheLBACSYS.ORA_GET_AUDITED_LABELfunction can be used in a UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL query to find audited Oracle Label Security session labels. - How Oracle Label Security Audit Events Appear in the Audit Trail
TheUNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAILdata dictionary view lists Oracle Label Security audit events.
30.8.5.1 About Auditing Oracle Label Security Events
As with all unified auditing, you must have the AUDIT_ADMIN role before you can audit Oracle Label Security (OLS) events.
To create Oracle Label Security unified audit policies, you must set the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement COMPONENT clause to OLS.
To audit user session label information, you use the AUDIT statement to audit application context values.
To access the audit trail, you can query the UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view. This view contains Oracle Label Security-specific columns whose names begin with OLS_. If you want to find audit information about the internally generated VPD predicate that is created when you apply an Oracle Label Security policy to a table, then you can query the RLS_INFO column.
30.8.5.2 Oracle Label Security Unified Audit Trail Events
The unified audit trail can capture Oracle Label Security audit events.
To find a list of auditable Oracle Label Security events that you can audit, you can query the COMPONENT and NAME columns of the AUDITABLE_SYSTEM_ACTIONS data dictionary view.
For example:
SELECT NAME FROM AUDITABLE_SYSTEM_ACTIONS WHERE COMPONENT = 'Label Security'; NAME ------------- CREATE POLICY ALTER POLICY DROP POLICY ...
Table 30-18 describes the Oracle Label Security audit events.
Table 30-18 Oracle Label Security Audit Events
| Audit Event | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Creates an Oracle Label Security policy through the |
|
|
Alters an Oracle Label Security policy through the |
|
|
Drops an Oracle Label Security policy through the |
|
|
Applies a table policy through the |
|
|
Removes a table policy through the |
|
|
Covers all Oracle Label Security authorizations, including Oracle Label Security privileges and user labels to either users or trusted stored procedures. The PL/SQL procedures that correspond to the |
|
|
Covers any action that requires the user of an Oracle Label Security privilege. These actions are logons, |
|
|
Enables an Oracle Label Security policy through the following procedures:
|
|
|
Disables an Oracle Label Security policy through the following procedures:
|
|
|
Creates an Oracle Label Security data label through the |
|
|
Alters an Oracle Label Security data label through the |
|
|
Drops an Oracle Label Security data label through the |
|
|
Creates an Oracle Label Security component through the following procedures:
|
|
|
Alters an Oracle Label Security component through the following procedures:
|
|
|
Drops an Oracle Label Security component through the following procedures:
|
|
|
Enables auditing of all Oracle Label Security actions |
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Label Security Events
30.8.5.3 Oracle Label Security Auditable User Session Labels
The ORA_OLS_SESSION_LABELS application context can capture user session label usage for each Oracle Database event.
The attributes used by this application context refer to Oracle Label Security policies. .
The syntax is the same as the syntax used for application context auditing. For example:
AUDIT CONTEXT NAMESPACE ORA_SESSION_LABELS ATTRIBUTES policy1, policy2;
Because the recording of session labels is not user-session specific, the BY user_list clause is not required for auditing Oracle Label Security application contexts.
To disable the auditing of user session label information, you use the NOAUDIT statement. For example, to stop auditing for policies policy1 and policy2, enter the following statement:
NOAUDIT CONTEXT NAMESPACE ORA_SESSION_LABELS ATTRIBUTES policy1, policy2;
Related Topics
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Label Security Events
30.8.5.4 Configuring a Unified Audit Policy for Oracle Label Security
The ACTIONS and ACTIONS COMPONENT clauses in the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can be used to create Oracle Label Security event audit policies.
-
Use the following syntax to create an Oracle Label Security unified audit policy:
CREATE AUDIT POLICY policy_name ACTIONS action1 [,action2 ] ACTIONS COMPONENT=OLS component_action1 [, action2];
For example:
CREATE AUDIT POLICY audit_ols ACTIONS SELECT ON OE.ORDERS ACTIONS COMPONENT=OLS ALL;
You can build more complex policies, such as those that include conditions. Remember that after you create the policy, you must use the AUDIT statement to enable it.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Label Security Events
30.8.5.5 Example: Auditing Oracle Label Security Session Label Attributes
The AUDIT CONTEXT NAMESPACE statement can audit Oracle Label Security session label attributes.
Example 30-32 shows how to audit ORA_OLS_SESSION_LABELS application context attributes for the Oracle Label Security policies usr_pol1 and usr_pol2.
Example 30-32 Auditing Oracle Label Security Session Label Attributes
AUDIT CONTEXT NAMESPACE ORA_SESSION_LABELS ATTRIBUTES usr_pol1, usr_pol2;
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Label Security Events
30.8.5.6 Example: Excluding a User from an Oracle Label Security Policy
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can exclude users from policies.
Example 30-33 shows how to create a unified audit policy that excludes actions from user ols_mgr.
Example 30-33 Excluding a User from an Oracle Label Security Policy
CREATE AUDIT POLICY auth_ols_audit_pol ACTIONS SELECT ON HR.EMPLOYEES ACTIONS COMPONENT=OLS DROP POLICY, DISABLE POLICY; AUDIT POLICY auth_ols_audit_pol EXCEPT ols_mgr;
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Label Security Events
30.8.5.7 Example: Auditing Oracle Label Security Policy Actions
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit Oracle Label Security policy actions.
Example 30-34 shows how to audit the DROP POLICY and DISABLE POLICY events, and UPDATE and DELETE statements on the HR.EMPLOYEES table. Then this policy is applied to the HR and LBACSYS users, and audit records are written to the unified audit trail only when the audited actions are successful.
Example 30-34 Auditing Oracle Label Security Policy Actions
CREATE AUDIT POLICY generic_audit_pol ACTIONS UPDATE ON HR.EMPLOYEES, DELETE ON HR.EMPLOYEES ACTIONS COMPONENT=OLS DROP POLICY, DISABLE POLICY; AUDIT POLICY generic_audit_pol BY HR, LBACSYS WHENEVER SUCCESSFUL;
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Label Security Events
30.8.5.8 Example: Querying for Audited OLS Session Labels
The LBACSYS.ORA_GET_AUDITED_LABEL function can be used in a UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL query to find audited Oracle Label Security session labels.
Example 30-35 shows how to use the LBACSYS.ORA_GET_AUDITED_LABEL function in a UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view query.
Example 30-35 Querying for Audited Oracle Label Security Session Labels
SELECT ENTRY_ID, SESSIONID,
LBACSYS.ORA_GET_AUDITED_LABEL( APPLICATION_CONTEXTS,'GENERIC_AUDIT_POL1') AS SESSION_LABEL1,
LBACSYS.ORA_GET_AUDITED_LABEL( APPLICATION_CONTEXTS,'GENERIC_AUDIT_POL2') AS SESSION_LABEL2
FROM UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL;
/
ENTRY_ID SESSIONID SESSION_LABEL1 SESSION_LABEL2
-------- --------- -------------- --------------
1 1023 SECRET LEVEL_ALPHA
2 1024 TOP_SECRET LEVEL_BETAParent topic: Auditing Oracle Label Security Events
30.8.5.9 How Oracle Label Security Audit Events Appear in the Audit Trail
The UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view lists Oracle Label Security audit events.
The OLS_* columns of the UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL view show Oracle Label Security-specific audit data. For example:
SELECT OLS_PRIVILEGES_USED FROM UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL WHERE DBUSERNAME = 'psmith'; OLS_PRIVILEGES_USED ------------------- READ WRITEUP WRITEACROSS
The session labels that the audit trail captures are stored in the APPLICATION_CONTEXTS column of the UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL view. You can use the LBACSYS.ORA_GET_AUDITED_LABEL function to retrieve session labels that are stored in the APPLICATION_CONTEXTS column. This function accepts the UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL.APPLICATION_CONTEXTS column value, and the Oracle Label Security policy name as arguments, and then returns the session label that is stored in the column for the specified policy.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Label Security Events
30.8.6 Auditing Oracle Data Pump Events
You can use the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement to audit Oracle Data Pump.
- About Auditing Oracle Data Pump Events
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatementCOMPONENTclause must be set toDATAPUMPto create Oracle Data Pump unified audit policies. - Oracle Data Pump Unified Audit Trail Events
The unified audit trail can capture Oracle Data Pump events. - Configuring a Unified Audit Policy for Oracle Data Pump
TheACTIONS COMPONENTclause in theCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can be used to create an Oracle Data Pump event unified audit policy. - Example: Auditing Oracle Data Pump Import Operations
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can audit Oracle Data Pump import operations. - Example: Auditing All Oracle Data Pump Operations
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can audit all Oracle Data Pump operations. - How Oracle Data Pump Audit Events Appear in the Audit Trail
TheUNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAILdata dictionary view lists Oracle Data Pump audited events.
30.8.6.1 About Auditing Oracle Data Pump Events
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement COMPONENT clause must be set to DATAPUMP to create Oracle Data Pump unified audit policies.
You can audit Data Pump export (expdp) and import (impdp) operations.
As with all unified auditing, you must have the AUDIT_ADMIN role before you can audit Oracle Data Pump events.
To access the audit trail, query the UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view. The Data Pump-specific columns in this view begin with DP_.
Oracle Database records the Oracle Data Pump record before the worker process has determined or dispatched the actual workload. Therefore, there is no success or failure code that is captured in the audit record. A return code of 0 is expected behavior irrespective of the success or failure of the Data Pump job. Additionally, because Data Pump is restartable, reports on the success and failure status of the export or import operations might not be feasible to obtain.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Data Pump Events
30.8.6.2 Oracle Data Pump Unified Audit Trail Events
The unified audit trail can capture Oracle Data Pump events.
The unified audit trail captures information about both export (expdp) and import (impdp) operations.
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Data Pump Events
30.8.6.3 Configuring a Unified Audit Policy for Oracle Data Pump
The ACTIONS COMPONENT clause in the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can be used to create an Oracle Data Pump event unified audit policy.
-
Use the following syntax to create a unified audit policy for Oracle Data Pump:
CREATE AUDIT POLICY policy_name ACTIONS COMPONENT=DATAPUMP { EXPORT | IMPORT | ALL };
For example:
CREATE AUDIT POLICY audit_dp_export_pol ACTIONS COMPONENT=DATAPUMP EXPORT;
You can build more complex policies, such as those that include conditions. Remember that after you create the policy, you must use the AUDIT statement to enable it.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Data Pump Events
30.8.6.4 Example: Auditing Oracle Data Pump Import Operations
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit Oracle Data Pump import operations.
Example 30-36 shows how to audit all Oracle Data Pump import operations.
Example 30-36 Auditing Oracle Data Pump Import Operations
CREATE AUDIT POLICY audit_dp_import_pol ACTIONS COMPONENT=DATAPUMP IMPORT; AUDIT POLICY audit_dp_import_pol;
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Data Pump Events
30.8.6.5 Example: Auditing All Oracle Data Pump Operations
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit all Oracle Data Pump operations.
Example 30-37 shows how to audit both Oracle Database Pump export and import operations.
Example 30-37 Auditing All Oracle Data Pump Operations
CREATE AUDIT POLICY audit_dp_all_pol ACTIONS COMPONENT=DATAPUMP ALL; AUDIT POLICY audit_dp_all_pol BY SYSTEM;
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Data Pump Events
30.8.6.6 How Oracle Data Pump Audit Events Appear in the Audit Trail
The UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view lists Oracle Data Pump audited events.
The DP_* columns of the UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL view show Oracle Data Pump-specific audit data. For example:
SELECT DP_TEXT_PARAMETERS1, DP_BOOLEAN_PARAMETERS1, DP_WARNINGS1 FROM UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL WHERE AUDIT_TYPE = 'DATAPUMP'; DP_TEXT_PARAMETERS1 DP_BOOLEAN_PARAMETERS1 DP_WARNINGS1 ---------------------------------------------- ----------------------- –-------------------------------------------------------------------------- MASTER TABLE: "SCOTT"."SYS_EXPORT_TABLE_01", MASTER_ONLY: FALSE, No warnings issued JOB_TYPE: EXPORT, DATA_ONLY: FALSE, METADATA_JOB_MODE: TABLE_EXPORT, METADATA_ONLY: FALSE, JOB VERSION: 23.1.0.0, DUMPFILE_PRESENT: TRUE, ACCESS METHOD: DIRECT_PATH, JOB_RESTARTED: FALSE DATA OPTIONS: 0, ENCRYPTED: TRUE DUMPER DIRECTORY: NULL REMOTE LINK: NULL, TABLE EXISTS: NULL, PARTITION OPTIONS: NONE SCHEMA: SCOTT
(This output was reformatted for easier readability.)
Oracle Database records the Oracle Data Pump record before the worker process has determined or dispatched the actual workload. Therefore, there is no success or failure code that is captured in the audit record. A return code of 0 is expected behavior irrespective of the success or failure of the Data Pump job. Additionally, because Data Pump is restartable reports on the success and failure status of the export or import operations might not be feasible to obtain.
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Data Pump Events
30.8.7 Auditing Oracle SQL*Loader Direct Load Path Events
You can use the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement to audit Oracle SQL*Loader direct load path events.
- About Auditing in Oracle SQL*Loader Direct Path Load Events
You must have theAUDIT_ADMINrole to audit Oracle SQL*Loader direct path events. - Oracle SQL*Loader Direct Load Path Unified Audit Trail Events
The unified audit trail can capture SQL*Loader Direct Load Path events. - Configuring a Unified Audit Trail Policy for Oracle SQL*Loader Direct Path Events
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatementACTIONS COMPONENTclause can create unified audit policies for Oracle SQL*Loader direct path events. - Example: Auditing Oracle SQL*Loader Direct Path Load Operations
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can audit Oracle SQL*Loader direct path load operations. - How SQL*Loader Direct Path Load Audited Events Appear in the Audit Trail
TheUNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAILdata dictionary view lists SQL*Loader direct path load audited events.
30.8.7.1 About Auditing in Oracle SQL*Loader Direct Path Load Events
You must have the AUDIT_ADMIN role to audit Oracle SQL*Loader direct path events.
To create SQL*Loader unified audit policies, you must set the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement's COMPONENT clause to DIRECT_LOAD. You can audit direct path load operations only, not other SQL*Loader loads, such as conventional path loads.
To access the audit trail, you can query the DIRECT_PATH_NUM_COLUMNS_LOADED column in the UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle SQL*Loader Direct Load Path Events
30.8.7.2 Oracle SQL*Loader Direct Load Path Unified Audit Trail Events
The unified audit trail can capture SQL*Loader Direct Load Path events.
The unified audit trail captures information about direct path loads that SQL*Loader performs (that is, when you set direct=true on the SQL*Loader command line or in the SQL*Loader control file).
It also audits Oracle Call Interface (OCI) programs that use the direct path API.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle SQL*Loader Direct Load Path Events
30.8.7.3 Configuring a Unified Audit Trail Policy for Oracle SQL*Loader Direct Path Events
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement ACTIONS COMPONENT clause can create unified audit policies for Oracle SQL*Loader direct path events.
-
Use the following syntax to create an Oracle SQL*Loader unified audit policy:
CREATE AUDIT POLICY policy_name ACTIONS COMPONENT=DIRECT_LOAD { LOAD };
For example:
CREATE AUDIT POLICY audit_sqlldr_pol ACTIONS COMPONENT=DIRECT_LOAD LOAD;
You can build more complex policies, such as those that include conditions. Remember that after you create the policy, you must use the AUDIT statement to enable it.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle SQL*Loader Direct Load Path Events
30.8.7.4 Example: Auditing Oracle SQL*Loader Direct Path Load Operations
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit Oracle SQL*Loader direct path load operations.
Example 30-36 shows how to audit SQL*Loader direct path load operations.
Example 30-38 Auditing Oracle SQL*Loader Direct Path Load Operations
CREATE AUDIT POLICY audit_sqlldr_load_pol ACTIONS COMPONENT=DIRECT_LOAD LOAD; AUDIT POLICY audit_sqlldr_load_pol;
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle SQL*Loader Direct Load Path Events
30.8.7.5 How SQL*Loader Direct Path Load Audited Events Appear in the Audit Trail
The UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view lists SQL*Loader direct path load audited events.
The DIRECT_PATH_NUM_COLUMNS_LOADED column of the UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL view shows the number of columns that were loaded using the SQL*Loader direct path load method. For example:
SELECT DBUSERNAME, ACTION_NAME, OBJECT_SCHEMA, OBJECT_NAME, DIRECT_PATH_NUM_COLUMNS_LOADED FROM UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL WHERE AUDIT_TYPE = 'DIRECT PATH API'; DBUSERNAME ACTION_NAME OBJECT_SCHEMA OBJECT_NAME DIRECT_PATH_NUM_COLUMNS_LOADED ----------- ----------- ------------- ------------ ------------------------------ RLAYTON INSERT HR EMPLOYEES 4
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle SQL*Loader Direct Load Path Events
30.8.8 Auditing Oracle XML DB HTTP and FTP Protocols
You can use the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement to audit Oracle XML DB HTTP and FTP protocol messages.
- About Auditing Oracle XML DB HTTP and FTP Protocols
You must have theAUDIT_ADMINrole to audit Oracle XDB HTTP and FTP protocol messages. - Configuring a Unified Audit Policy to Capture Oracle XML DB HTTP and FTP Protocols
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can create a unified audit policy for Oracle XML DB HTTP and FTP protocols. - Example: Auditing Failed Oracle XML DB HTTP Messages
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can audit failed Oracle XML DB HTTP messages. - Example: Auditing All Oracle XML DB FTP Messages
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can audit all Oracle XML DB FTP messages. - Example: Auditing Oracle XML DB HTTP Messages That Have 401 AUTH Errors
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can audit HTTP messages that have401 AUTHerrors. - How the Unified Audit Trail Captures Oracle XML DB HTTP and FTP Protocol Messages
TheUNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAILdata dictionary view lists Oracle XML DB HTTP and FTP protocol messages.
30.8.8.1 About Auditing Oracle XML DB HTTP and FTP Protocols
You must have the AUDIT_ADMIN role to audit Oracle XDB HTTP and FTP protocol messages.
Oracle Database can audit all or failed HTTP messages, 401 AUTH HTTP return code messages, and all or failed FTP messages. The UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view captures the result of the audit in the PROTOCOL_* columns.
Be aware that a unified audit policy for HTTP and FTP protocols can affect performance.
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle XML DB HTTP and FTP Protocols
30.8.8.2 Configuring a Unified Audit Policy to Capture Oracle XML DB HTTP and FTP Protocols
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can create a unified audit policy for Oracle XML DB HTTP and FTP protocols.
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle XML DB HTTP and FTP Protocols
30.8.8.3 Example: Auditing Failed Oracle XML DB HTTP Messages
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit failed Oracle XML DB HTTP messages.
Example 30-39 shows an example of creating and enabling a unified audit policy that tracks failed HTTP messages.
Example 30-39 Auditing Failed Oracle XML DB HTTP Messages
CREATE AUDIT POLICY failed_http_pol ACTIONS COMPONENT=PROTOCOL HTTP; AUDIT POLICY failed_http_pol WHENEVER NOT SUCCESSFUL;
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle XML DB HTTP and FTP Protocols
30.8.8.4 Example: Auditing All Oracle XML DB FTP Messages
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit all Oracle XML DB FTP messages.
Example 30-40 shows an example of creating and enabling a unified audit policy that tracks all FTP messages.
Example 30-40 Auditing All Oracle XML DB FTP Messages
CREATE AUDIT POLICY all_ftp_pol ACTIONS COMPONENT=PROTOCOL FTP; AUDIT POLICY all_ftp_pol;
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle XML DB HTTP and FTP Protocols
30.8.8.5 Example: Auditing Oracle XML DB HTTP Messages That Have 401 AUTH Errors
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit HTTP messages that have 401 AUTH errors.
Example 30-41 shows an example of creating and enabling a unified audit policy that tracks 401 AUTH messages. When you enable this type of policy, you can set it without using the WHENEVER clause or set it using the WHENEVER SUCCESSFUL clause. Using a WHENEVER NOT SUCCESSFUL will not audit 401 AUTH errors.
Example 30-41 Auditing Oracle XML DB HTTP Messages with 401 AUTH Errors
CREATE AUDIT POLICY 401_error_pol ACTIONS COMPONENT=PROTOCOL AUTHENTICATION; AUDIT POLICY 401_error_pol;
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle XML DB HTTP and FTP Protocols
30.8.8.6 How the Unified Audit Trail Captures Oracle XML DB HTTP and FTP Protocol Messages
The UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view lists Oracle XML DB HTTP and FTP protocol messages.
The PROTOCOL_* columns capture HTTP- and FTP-specific information such as the session ID, the return code, the type of request, and the text of the request or reply.
For example, the following query shows that the HTTP-GET request/reply had a return code of 207, which means the reply may have multiple components with separate return codes:
SELECT PROTOCOL_RETURN_CODE, PROTOCOL_ACTION_NAME FROM UNIFIED_AUDIT_POLICY WHERE USERHOST = "HR_SRV"; PROTOCOL_RETURN_CODE PROTOCOL_ACTION_NAME –------------------- –------------------- 207 HTTP-GET-CMD 207 HTTP-GET
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle XML DB HTTP and FTP Protocols
30.8.9 Auditing Oracle Machine Learning for SQL Events
You can use the CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement to audit Oracle Machine Learning for SQL events.
- About Auditing Oracle Machine Learning for SQL Events
You must have theAUDIT_ADMINrole to audit Oracle Machine Learning for SQL events. - Oracle Machine Learning for SQL Unified Audit Trail Events
The unified audit trail can capture Oracle Machine Learning for SQL audit events.. - Configuring a Unified Audit Policy for Oracle Machine Learning for SQL
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatementACTIONSandON MINING MODELclauses can be used to create Oracle Machine Learning for SQL event unified audit policies. - Example: Auditing Multiple Oracle Machine Learning for SQL Operations by a User
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can audit multiple Oracle Machine Learning for SQL operations. - Example: Auditing All Failed Oracle Machine Learning for SQL Operations by a User
TheCREATE AUDIT POLICYstatement can audit failed Oracle Machine Learning for SQL operations by a user. - How Oracle Machine Learning for SQL Events Appear in the Audit Trail
TheUNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAILdata dictionary view lists Oracle Machine Learning for SQL audit events.
30.8.9.1 About Auditing Oracle Machine Learning for SQL Events
You must have the AUDIT_ADMIN role to audit Oracle Machine Learning for SQL events.
To access the audit trail, you can query the UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Machine Learning for SQL Events
30.8.9.2 Oracle Machine Learning for SQL Unified Audit Trail Events
The unified audit trail can capture Oracle Machine Learning for SQL audit events..
Table 30-19 describes these events.
Table 30-19 Oracle Machine Learning for SQL Audit Events
| Audit Event | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Generates an audit record for a Oracle Machine Learning for SQL model |
|
|
Adds a comment to a Oracle Machine Learning for SQL model |
|
|
Gives permission to a user to access the Oracle Machine Learning for SQL model |
|
|
Changes the name of the Oracle Machine Learning for SQL model |
|
|
Applies the Oracle Machine Learning for SQL model or view its signature |
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Machine Learning for SQL Events
30.8.9.3 Configuring a Unified Audit Policy for Oracle Machine Learning for SQL
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement ACTIONS and ON MINING MODEL clauses can be used to create Oracle Machine Learning for SQL event unified audit policies.
-
Use the following syntax to create a unified audit policy for Oracle Machine Learning for SQL:
CREATE AUDIT POLICY policy_name ACTIONS {operation | ALL} ON MINING MODEL schema_name.model_name;
For example:
CREATE AUDIT POLICY dm_ops ACTIONS RENAME ON MINING MODEL hr.dm_emp;
You can build more complex policies, such as those that include conditions. Remember that after you create the policy, you must use the AUDIT statement to enable it.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Machine Learning for SQL Events
30.8.9.4 Example: Auditing Multiple Oracle Machine Learning for SQL Operations by a User
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit multiple Oracle Machine Learning for SQL operations.
Example 30-42 shows how to audit multiple Oracle Machine Learning for SQL operations by user psmith. Include the ON MINING MODEL schema_name.model_name clause for each event, and separate each with a comma. This example specifies the same schema_name.model name for both actions, but the syntax enables you to specify different schema_name.model_name settings for different schemas and data models.
Example 30-42 Auditing Multiple Oracle Machine Learning for SQL Operations by a User
CREATE AUDIT POLICY dm_ops_pol ACTIONS SELECT ON MINING MODEL dmuser1.nb_model, ALTER ON MINING MODEL dmuser1.nb_model; AUDIT POLICY dm_ops_pol BY psmith;
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Machine Learning for SQL Events
30.8.9.5 Example: Auditing All Failed Oracle Machine Learning for SQL Operations by a User
The CREATE AUDIT POLICY statement can audit failed Oracle Machine Learning for SQL operations by a user.
Example 30-43 shows how to audit all failed Oracle Machine Learning for SQL operations by user psmith.
Example 30-43 Auditing All Failed Oracle Machine Learning for SQL Operations by a User
CREATE AUDIT POLICY dm_all_ops_pol ACTIONS ALL ON MINING MODEL dmuser1.nb_model; AUDIT POLICY dm_all_ops_pol BY psmith WHENEVER NOT SUCCESSFUL;
Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Machine Learning for SQL Events
30.8.9.6 How Oracle Machine Learning for SQL Events Appear in the Audit Trail
The UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view lists Oracle Machine Learning for SQL audit events.
The following example shows how to query the UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view for Machine Learning for SQL audit events.
SELECT DBUSERNAME, ACTION_NAME, SYSTEM_PRIVILEGE_USED, RETURN_CODE,
OBJECT_SCHEMA, OBJECT_NAME, SQL_TEXT
FROM UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL;
DBUSERNAME ACTION_NAME SYSTEM_PRIVILEGE_USED RETURN_CODE
---------- -------------------- ------------------------- -----------
OBJECT_SCHEMA OBJECT_NAME
-------------------- --------------------
SQL_TEXT
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
DMUSER1 CREATE MINING MODEL CREATE MINING MODEL 0
DMUSER1
BEGIN
dbms_data_mining.create_model(model_name => 'nb_model',
mining_function => dbms_data_mining.classification,
data_table_name => 'dm_data',
case_id_column_name => 'case_id',
target_column_name => 'target');
END;
DMUSER1 SELECT MINING MODEL 0
DMUSER1 NB_MODEL
select prediction(nb_model using *) from dual
DMUSER2 SELECT MINING MODEL 40284
DMUSER1 NB_MODEL
select prediction(dmuser1.nb_model using *) from dual
DMUSER1 ALTER MINING MODEL 0
DMUSER1 NB_MODEL
BEGIN dbms_data_mining.rename_model('nb_model', 'nb_model1'); END;
DMUSER2 ALTER MINING MODEL 40284
DMUSER1 NB_MODEL
BEGIN dbms_data_mining.rename_model('dmuser1.nb_model1', 'nb_model'); END;
DMUSER2 ALTER MINING MODEL 40284
DMUSER1 NB_MODEL
BEGIN dbms_data_mining.rename_model('dmuser1.nb_model1', 'nb_model'); END;Parent topic: Auditing Oracle Machine Learning for SQL Events
30.9 Managing Unified Audit Policies
After you create a unified audit policy, you must enable it. You can alter disable, and drop unified audit policies.
- Altering Unified Audit Policies
You can use theALTER AUDIT POLICYstatement to modify a unified audit policy. - Enabling and Applying Unified Audit Policies to Users and Roles
You can use theAUDIT POLICYstatement to enable and apply unified audit policies to users and roles. - Disabling Unified Audit Policies
You can use theNOAUDIT POLICYstatement to disable a unified audit policy. - Dropping Unified Audit Policies
You can use theDROP AUDIT POLICYstatement to drop a unified audit policy.
Parent topic: Creating Custom Unified Audit Policies
30.9.1 Altering Unified Audit Policies
You can use the ALTER AUDIT POLICY statement to modify a unified audit policy.
- About Altering Unified Audit Policies
You can change most properties in a unified audit policy, except for itsCONTAINERsetting. - Altering a Unified Audit Policy
TheALTER AUDIT POLICYstatement can modify a unified audit policy. - Example: Altering a Condition in a Unified Audit Policy
The ALTER AUDIT POLICY statement can alter conditions in unified audit policies. - Example: Altering an Oracle Label Security Component in a Unified Audit Policy
TheALTER AUDIT POLICYstatement can alter Oracle Label Security components in an audit policy. - Example: Altering Roles in a Unified Audit Policy
TheALTER AUDIT POLICYstatement can alter roles in a unified audit policy. - Example: Dropping a Condition from a Unified Audit Policy
TheALTER AUDIT POLICYstatement can drop a condition from a unified audit policy. - Example: Altering an Existing Unified Audit Policy Top-Level Statement Audits
TheALTER AUDIT POLICYstatement can modify an existing unified audit policy so that the unified audit trail captures top-level SQL statements only.
Parent topic: Managing Unified Audit Policies
30.9.1.1 About Altering Unified Audit Policies
You can change most properties in a unified audit policy, except for its CONTAINER setting.
You cannot alter unified audit policies in a multitenant environment. For example, you cannot turn a common unified audit policy into a local unified audit policy.
To find existing unified audit policies, query the AUDIT_UNIFIED_POLICIES data dictionary view. If you want to find only the enabled unified audit policies, then query the AUDIT_UNIFIED_ENABLED_POLICIES view. You can alter both enabled and disabled audit policies. If you alter an enabled audit policy, it remains enabled after you alter it.
After you alter an object unified audit policy, the new audit settings take place immediately, for both the active and subsequent user sessions. If you alter system audit options, or audit conditions of the policy, then they are activated for new user sessions, but not the current user session.
Parent topic: Altering Unified Audit Policies
30.9.1.2 Altering a Unified Audit Policy
The ALTER AUDIT POLICY statement can modify a unified audit policy.
30.9.1.3 Example: Altering a Condition in a Unified Audit Policy
The ALTER AUDIT POLICY statement can alter conditions in unified audit policies.
Example 30-44 shows how to change a condition in an existing unified audit policy.
Example 30-44 Altering a Condition in a Unified Audit Policy
ALTER AUDIT POLICY orders_unified_audpol
ADD ACTIONS INSERT ON SCOTT.EMP
CONDITION 'SYS_CONTEXT(''ENTERPRISE'', ''GROUP'') = ''ACCESS_MANAGER'''
EVALUATE PER SESSION;Parent topic: Altering Unified Audit Policies
30.9.1.4 Example: Altering an Oracle Label Security Component in a Unified Audit Policy
The ALTER AUDIT POLICY statement can alter Oracle Label Security components in an audit policy.
Example 30-45 shows how to alter an Oracle Label Security component in an audit policy.
Example 30-45 Altering an Oracle Label Security Component in a Unified Audit Policy
ALTER AUDIT POLICY audit_ols ADD ACTIONS SELECT ON HR.EMPLOYEES ACTIONS COMPONENT=OLS DROP POLICY, DISABLE POLICY, REMOVE POLICY;
Parent topic: Altering Unified Audit Policies
30.9.1.5 Example: Altering Roles in a Unified Audit Policy
The ALTER AUDIT POLICY statement can alter roles in a unified audit policy.
Example 30-46 shows how to add roles to a common unified audit policy.
Example 30-46 Altering Roles in a Unified Audit Policy
CONNECT c##sec_admin
Enter password: password
Connected.
ALTER AUDIT POLICY RoleConnectAudit
ADD ROLES c##role1, c##role2;Parent topic: Altering Unified Audit Policies
30.9.1.6 Example: Dropping a Condition from a Unified Audit Policy
The ALTER AUDIT POLICY statement can drop a condition from a unified audit policy.
Example 30-47 shows how to drop a condition from an existing unified audit policy.
Example 30-47 Dropping a Condition from a Unified Audit Policy
ALTER AUDIT POLICY orders_unified_audpol CONDITION DROP;
Parent topic: Altering Unified Audit Policies
30.9.1.7 Example: Altering an Existing Unified Audit Policy Top-Level Statement Audits
The ALTER AUDIT POLICY statement can modify an existing
unified audit policy so that the unified audit trail captures top-level SQL statements only.
The following example shows how to modify the
orders_unified_audpol policy to capture only top-level SQL
statements.
Example 30-48 Altering an Existing Unified Audit Policy to Audit for Top-Level Statements
ALTER AUDIT POLICY orders_unified_audpol ADD ONLY TOPLEVEL;Similarly, to remove the top-level SQL statement audit, use the
DROP clause:
ALTER AUDIT POLICY orders_unified_audpol DROP ONLY TOPLEVEL;
Parent topic: Altering Unified Audit Policies
30.9.2 Enabling and Applying Unified Audit Policies to Users and Roles
You can use the AUDIT POLICY statement to enable and apply unified audit policies to users and roles.
- About Enabling Unified Audit Policies
TheAUDITstatement with thePOLICYclause enables a unified audit policy, applying for all types of audit options, including object-level options. - Enabling a Unified Audit Policy
TheAUDIT POLICYstatement can enable a unified audit policy. - Example: Enabling a Unified Audit Policy
TheAUDIT POLICYstatement can enable a unified audit policy using conditions, such asWHENEVER NOT SUCCESSFUL.
Parent topic: Managing Unified Audit Policies
30.9.2.1 About Enabling Unified Audit Policies
The AUDIT statement with the POLICY clause enables a unified audit policy, applying for all types of audit options, including object-level options.
The policy is enabled immediately in the current session and in any ongoing active sessions, including sessions for other users who are logged in.
You can enable the audit policy for individual users or for roles. Enabling the audit policy for roles allows you to enable the policy for a group of users who have been directly granted the role. When the role has been directly granted to a new user, then the policy automatically applies to the user. When the role is revoked from a user, then the policy no longer applies to the user.
You can check the results of the audit by querying the UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view. To find a list of existing unified audit policies, query the AUDIT_UNIFIED_POLICIES data dictionary view.
The AUDIT statement lets you specify the following optional additional settings:
-
Whether to apply the unified audit policy to one or more users or roles.To apply the policy to one or more users or roles, including administrative users who log in with the
SYSDBAadministrative privilege (such asSYS), use theBYclause. For example, to apply the policy to usersSYSandSYSTEM:For example, to apply the policy to two users:
AUDIT POLICY role_connect_audit_pol BY SYS, SYSTEM;
To apply a policy to users who have been directly granted the
DBAandCDB_DBAroles:AUDIT POLICY admin_audit_pol BY USERS WITH GRANTED ROLES DBA, CDB_DBA;
-
Whether to exclude users from the unified audit policy. To exclude users from the audit policy, include the
EXCEPTclause.For example:
AUDIT POLICY role_connect_audit_pol EXCEPT rlee, jrandolph;
-
Whether to create an audit record if the activity succeeds or fails. Auditing the successes and failures of actions helps to narrow down the events that matter the most. Enter one of the following clauses:
-
WHENEVER SUCCESSFULaudits only successful executions of the user’s activity. -
WHENEVER NOT SUCCESSFULaudits only failed executions of the user’s activity. Monitoring unsuccessful SQL statement can expose users who are snooping or acting maliciously, though most unsuccessful SQL statements are neither.
For example:
AUDIT POLICY role_connect_audit_pol WHENEVER NOT SUCCESSFUL;
If you omit this clause, then both failed and successful user activities are written to the audit trail.
-
Note the following:
-
The unified audit policy only can have either the
BY,BY USERS WITH GRANTED ROLES, or theEXCEPTclause, but not more than one of these clauses for the same policy. -
If you run multiple
AUDITstatements on the same unified audit policy but specify different BY users or differentBY USERS WITH GRANTED ROLESroles, then Oracle Database audits all of these users or roles. -
If you run multiple
AUDITstatements on the same unified audit policy but specify differentEXCEPTusers, then Oracle Database uses the last exception user list, not any of the users from the preceding lists. This means the effect of the earlierAUDIT POLICY ... EXCEPTstatements are overridden by the latestAUDIT POLICY ... EXCEPTstatement. -
You cannot use the
EXCEPTclause for roles. It applies to users only. -
You can only enable common unified audit policies for common users or roles.
-
You can enable a common audit policy only from the root and a local audit policy only from the PDB to which it applies.
30.9.2.2 Enabling a Unified Audit Policy
The AUDIT POLICY statement can enable a unified audit policy.
UNIFIED_AUDIT_TRAIL data dictionary view.
Related Topics
30.9.2.3 Example: Enabling a Unified Audit Policy
The AUDIT POLICY statement can enable a unified audit policy using conditions, such as WHENEVER NOT SUCCESSFUL.
Example 30-49 shows how to enable a unified audit policy to record only failed actions by the user dv_admin.
Example 30-49 Enabling a Unified Audit Policy
AUDIT POLICY dv_admin_pol BY tjones WHENEVER NOT SUCCESSFUL;
30.9.3 Disabling Unified Audit Policies
You can use the NOAUDIT POLICY statement to disable a unified audit policy.
- About Disabling Unified Audit Policies
TheNOAUDITstatement with thePOLICYclause can disable a unified audit policy. - Disabling a Unified Audit Policy
TheNOAUDITstatement can disable a unified audit policy using supported audit options. - Example: Disabling a Unified Audit Policy
TheNOAUDIT POLICYstatement disable a unified audit policy using filtering, such as by user name.
Parent topic: Managing Unified Audit Policies
30.9.3.1 About Disabling Unified Audit Policies
The NOAUDIT statement with the POLICY clause can disable a unified audit policy.
In the NOAUDIT statement, you can specify a BY user or BY USERS WITH GRANTED ROLES role list, but not an EXCEPT user list. The disablement of a unified audit policy takes effect on subsequent user sessions.
You can find a list of existing unified audit policies by querying the AUDIT_UNIFIED_POLICIES data dictionary view.
You can disable a common audit policy only from the root and a local audit policy only from the PDB to which it applies.
Parent topic: Disabling Unified Audit Policies
30.9.3.2 Disabling a Unified Audit Policy
The NOAUDIT statement can disable a unified audit policy using supported audit options.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Disabling Unified Audit Policies
30.9.3.3 Example: Disabling a Unified Audit Policy
The NOAUDIT POLICY statement disable a unified audit policy using filtering, such as by user name.
Example 30-50 shows examples of how to disable a unified audit policy for a user and for a role.
Example 30-50 Disabling a Unified Audit Policy
NOAUDIT POLICY dv_admin_pol BY tjones; NOAUDIT POLICY dv_admin_pol BY USERS WITH GRANTED ROLES emp_admin;
Parent topic: Disabling Unified Audit Policies
30.9.4 Dropping Unified Audit Policies
You can use the DROP AUDIT POLICY statement to drop a unified audit policy.
- About Dropping Unified Audit Policies
TheDROP AUDIT POLICYstatement can be used to unified audit policies. - Dropping a Unified Audit Policy
To drop a unified audit policy, you must first disable it, and then run theDROP AUDIT POLICYstatement to remove it. - Example: Disabling and Dropping a Unified Audit Policy
TheNOAUDIT POLICYandDROP AUDIT POLICYstatements can disable and drop a unified audit policy.
Parent topic: Managing Unified Audit Policies
30.9.4.1 About Dropping Unified Audit Policies
The DROP AUDIT POLICY statement can be used to unified audit policies.
If a unified audit policy is already enabled for a session, the effect of dropping the policy is not seen by this existing session. Until that time, the unified audit policy's settings remain in effect. For object-related unified audit policies, however, the effect is immediate.
You can find a list of existing unified audit policies by querying the AUDIT_UNIFIED_POLICIES data dictionary view.
When you disable an audit policy before dropping it, ensure that you disable it using the same settings that you used to enable it. For example, suppose you enabled the logon_pol policy as follows:
AUDIT POLICY logon_pol BY HR, OE;
Before you can drop it, your NOAUDIT statement must include the HR and OE users as follows:
NOAUDIT POLICY logon_pol BY HR, OE;
You can drop a common audit policy only from the root and a local audit policy only from the PDB to which it applies.
Parent topic: Dropping Unified Audit Policies
30.9.4.2 Dropping a Unified Audit Policy
To drop a unified audit policy, you must first disable it, and then run the DROP AUDIT POLICY statement to remove it.
-
Use the following the following syntax to drop a unified audit policy:
DROP AUDIT POLICY policy_name;
The unified audit policy drop applies to the current PDB. If the unified audit policy was created as a common unified audit policy, then you cannot drop it from the local PDB.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Dropping Unified Audit Policies
30.9.4.3 Example: Disabling and Dropping a Unified Audit Policy
The NOAUDIT POLICY and DROP AUDIT POLICY statements can disable and drop a unified audit policy.
Example 30-51 shows how to disable and drop a common unified audit policy.
Example 30-51 Disabling and Dropping a Unified Audit Policy
CONNECT c##sec_admin
Enter password: password
Connected.
NOAUDIT POLICY dv_admin_pol;
DROP AUDIT POLICY dv_admin_pol
Parent topic: Dropping Unified Audit Policies
30.10 Tutorial: Auditing Nondatabase Users
Auditing nondatabase users who are typical application service accounts is crucial. They are identified in the database using the CLIENT_IDENTIFIER attribute.
- Step 1: Create the User Accounts and Ensure the User OE Is Active
You must first create users and ensure that the userOEis active. - Step 2: Create the Unified Audit Policy
Next, you are ready to create the unified audit policy. - Step 3: Test the Policy
To test the policy, useOEmust try to select from theOE.ORDERStable. - Step 4: Remove the Components of This Tutorial
If you no longer need the components of this tutorial, then you can remove them.
Parent topic: Creating Custom Unified Audit Policies
30.10.1 Step 1: Create the User Accounts and Ensure the User OE Is Active
You must first create users and ensure that the user OE is active.
Related Topics
Parent topic: Tutorial: Auditing Nondatabase Users
30.10.2 Step 2: Create the Unified Audit Policy
Next, you are ready to create the unified audit policy.
Parent topic: Tutorial: Auditing Nondatabase Users
30.10.3 Step 3: Test the Policy
To test the policy, use OE must try to select from the OE.ORDERS table.
Parent topic: Tutorial: Auditing Nondatabase Users
30.10.4 Step 4: Remove the Components of This Tutorial
If you no longer need the components of this tutorial, then you can remove them.
Parent topic: Tutorial: Auditing Nondatabase Users
30.11 Unified Audit Policy Data Dictionary Views
You can query data dictionary and dynamic views to find detailed auditing information about custom unified audit policies.
Table 30-20 lists these views.
Tip:
To find error information about audit policies, check the trace files. The USER_DUMP_DEST initialization parameter sets the location of the trace files.
Table 30-20 Views for Use with Custom Unified Audit Policies
| View | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Displays information about all fine-grained audit policies |
|
|
Lists default object-auditing options that are to be applied when objects are created |
|
|
Describes application context values that have been configured to be captured in the audit trail |
|
|
Describes all unified audit policies that are enabled in the database |
|
|
Describes all unified audit policies created in the database |
|
|
Shows the description of each unified audit policy, if a description was entered for the unified audit policy using the |
|
|
Maps the auditable system action numbers to the action names |
|
|
Similar to the |
|
|
Describes audited Oracle Label Security events performed by users, and indicates if the user's action failed or succeeded |
|
|
Displays audit trail information related to Oracle Database Real Application Security |
|
|
Displays configuration changes made by Oracle Database Vault administrators |
|
|
Displays user activities that are affected by Oracle Database Vault policies |
|
|
Describes privilege (auditing option) type codes. This table can be used to map privilege (auditing option) type numbers to type names. |
|
|
Displays all audit records |
Related Topics
Parent topic: Creating Custom Unified Audit Policies