ALTER SEQUENCE
Purpose
Use the ALTER SEQUENCE statement to change the increment, minimum and maximum values, cached numbers, and behavior of an existing sequence. This statement affects only future sequence numbers.
See Also:
CREATE SEQUENCE for additional information on sequences
Prerequisites
The sequence must be in your own schema, or you must have the ALTER object privilege on the sequence, or you must have the ALTER ANY SEQUENCE system privilege.
Syntax
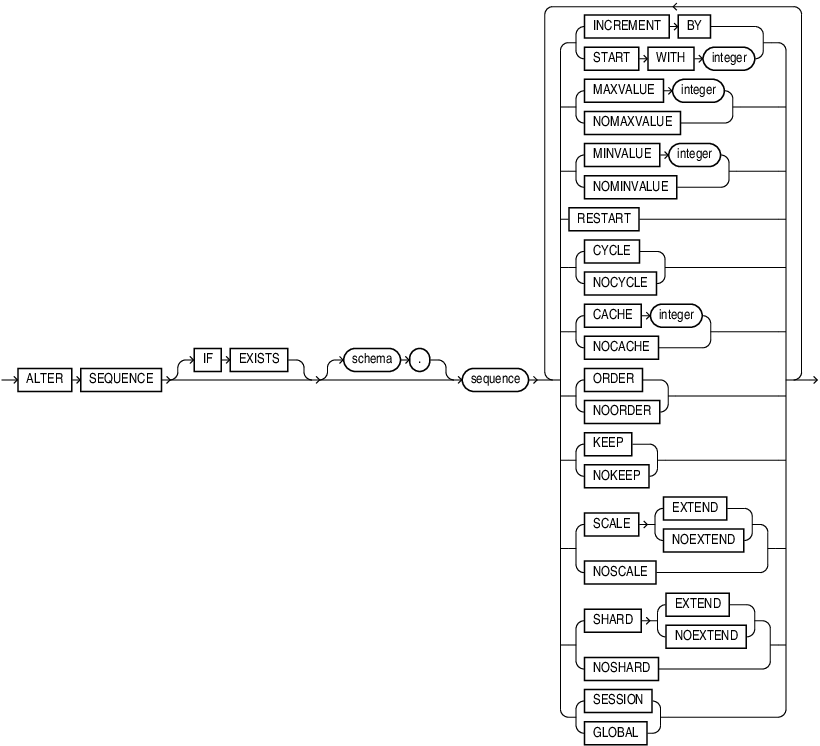
alter_sequence::=
Semantics
The keywords and parameters in this statement serve the same purposes they serve when you create a sequence.
-
If you change the
INCREMENTBYvalue before the first invocation ofNEXTVAL, then some sequence numbers will be skipped. Therefore, if you want to retain the originalSTARTWITHvalue, you must drop the sequence and re-create it with the originalSTARTWITHvalue and the newINCREMENTBYvalue. -
Specify
RESTARTto resetNEXTVALtoMINVALUEfor an ascending sequence. For a descending sequenceRESTARTresetsNEXTVALtoMAXVALUE. -
To restart the sequence at a different number, specify
RESTARTwith theSTARTWITHclause to set the value at which the sequence restarts. -
If you alter the sequence by specifying the
KEEPorNOKEEPclause between runtime and failover of a request, then the original value ofNEXTVALis not retained during replay for Application Continuity for that request. -
Oracle Database performs some validations. For example, a new
MAXVALUEcannot be imposed that is less than the current sequence number.See Also:
CREATE SEQUENCE for information on creating a sequence and DROP SEQUENCE for information on dropping and re-creating a sequence
IF EXISTS
Specify IF EXISTS to alter an existing table.
Specifying IF NOT EXISTS with ALTER VIEW results in ORA-11544: Incorrect IF EXISTS clause for ALTER/DROP statement.
SCALE
Use SCALE to enable sequence scalability. When SCALE is specified, a numeric offset is affixed to the beginning of the sequence which removes all duplicates in generated values.
EXTEND
If you specify EXTEND with SCALE the generated sequence values are all of length (x+y), where x is the length of the scalable offset (default value is 6), and y is the maximum number of digits in the sequence (maxvalue/minvalue).
When you use SCALE it is highly recommended that you not use ORDER simultaneously on the sequence.
NOEXTEND
NOEXTEND is the default setting for the SCALE clause. With the NOEXTEND setting, the generated sequence values are at most as wide as the maximum number of digits in the sequence (maxvalue/minvalue). This setting is useful for integration with existing applications where sequences are used to populate fixed width columns.
SHARD
Use this clause to generate unique sequence numbers across shards.
The sequence object is created as a global, all-shards sharded object that returns unique sequence values across all shards. The sequence object is also created at the catalog database that returns unique sequence values relative to the shard databases.
The EXTEND and NOEXTEND keywords define the behavior of a sharded sequence.
EXTEND
When you specify EXTEND with the SHARD clause, the generated sequence values are all of length (x + y), where x is the length of an(a) SHARD offset of size 3. The size 3 corresponds to the width of the maximum number of shards i.e. 1000 affixed at the beginning of the sequence values. y is the maximum number of digits in the sequence maxvalue/minvalue.
NOEXTEND
The default setting for the SHARD clause is NOEXTEND.
When you specify NOEXTEND, the generated sequence values are at most as wide as the maximum number of digits in the sequence maxvalue/minvalue. This setting is useful for integration with existing applications where sequences are used to populate fixed width columns.
If you call NEXTVAL on a sequence with SHARD NOEXTEND specified, a user error is thrown, if the generated value requires more digits of representation than the maxvalue/minvalue of the sequence.
Sequence with SHARD and SCALE
If you specify the SCALE and the SHARD clauses together, the sequence generates scalable, globally unique values within a shard database for multiple instances and sessions.
If you specify EXTEND with the SCALE and SHARD clauses, the generated sequence values are all of length (x+y+z), where x is the length of a SHARD offset with a default value of size 4, y is the length of the scalable offset with a default value of 6(5), and z is the maximum number of digits in the sequence maxvalue/minvalue .
If you specify EXTEND or NOEXTEND with the SHARD and SCALE clauses, it applies to both SHARD and SCALE. You do not need to specify EXTEND or NOEXTEND separately. If you specify the EXTEND or NOEXTEND option separately for both the SHARD and SCALE clauses, with the same or different value, a parsing error results, with a message of a duplicate or conflicting EXTEND clause.
When you use SHARD it is highly recommended that you not use ORDER simultaneously on the sequence.
You can use SHARD with CACHE and NOCACHE modes of operation.
Note:
-
Starting with Oracle Database Release 23 a sharded sequence without scale will have the leading "1" of the offset removed.
-
Starting with Oracle Database Release 23 a sharded sequence with scale will have the leading "1" of the offset removed.
Prior to Release 23, a a sharded sequence with scale had one leading "1" for the combined offset. This leading "1" is removed from Release 23 onwards.
Examples
Modifying a Sequence: Examples
This statement sets a new maximum value for the customers_seq sequence, which was created in "Creating a Sequence: Example":
ALTER SEQUENCE customers_seq MAXVALUE 1500;
This statement turns on CYCLE and CACHE for the customers_seq sequence:
ALTER SEQUENCE customers_seq CYCLE CACHE 5;