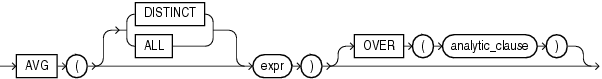AVG
Syntax
See Also:
Analytic Functions for information on syntax, semantics, and restrictions
Purpose
AVG returns average value of expr.
It takes as an argument any numeric data type or any nonnumeric data type that can be implicitly converted to a numeric data type or an interval data type.
The function returns the same data type as the numeric data type of the argument. If the input is an interval, this returns an interval with the same units as the input.
See Also:
Table 2-9 for more information on implicit conversion
If you specify DISTINCT, then you can specify only the query_partition_clause of the analytic_clause. The order_by_clause and windowing_clause are not allowed.
See Also:
About SQL Expressions for information on valid forms of expr and Aggregate Functions
Vector Aggregate Operations
You can use AVG on vectors to return the average on non-null inputs.
expr must evaluate to VECTOR and must not be BINARY vectors. The returned vector has the same number of dimensions as the input, and the format is always FLOAT64. For flexible number of dimensions, all inputs must have the same number of dimensions within each aggregation group.
NULL vectors are ignored. They are not counted when calculating the average vector. If all inputs within an aggregation group are NULL, the result is NULL for that group. If a certain dimension overflows when applying arithmetic operations, an error is raised.
Rules
-
DISTINCTsyntax is not allowed. -
Only
GROUP BYandGROUP BY ROLLUPare supported. -
Analytic functions are not supported for input arguments of type
VECTOR.
See Arithmetic Operatorsof the AI Vector Search User's Guide for examples.
Aggregate Example
The following example calculates the average salary of all employees in the hr.employees table:
SELECT AVG(salary) "Average"
FROM employees;
Average
--------------
6461.83178Analytic Example
The following example calculates, for each employee in the employees table, the average salary of the employees reporting to the same manager who were hired in the range just before through just after the employee:
SELECT manager_id, last_name, hire_date, salary,
AVG(salary) OVER (PARTITION BY manager_id ORDER BY hire_date
ROWS BETWEEN 1 PRECEDING AND 1 FOLLOWING) AS c_mavg
FROM employees
ORDER BY manager_id, hire_date, salary;
MANAGER_ID LAST_NAME HIRE_DATE SALARY C_MAVG
---------- ------------------------- --------- ---------- ----------
100 De Haan 13-JAN-01 17000 14000
100 Raphaely 07-DEC-02 11000 11966.6667
100 Kaufling 01-MAY-03 7900 10633.3333
100 Hartstein 17-FEB-04 13000 9633.33333
100 Weiss 18-JUL-04 8000 11666.6667
100 Russell 01-OCT-04 14000 11833.3333
100 Partners 05-JAN-05 13500 13166.6667
100 Errazuriz 10-MAR-05 12000 11233.3333
. . .