CREATE SCHEMA
Purpose
Use the CREATE SCHEMA statement to create multiple tables and views and perform multiple grants in your own schema in a single transaction.
To execute a CREATE SCHEMA statement, Oracle Database executes each included statement. If all statements execute successfully, then the database commits the transaction. If any statement results in an error, then the database rolls back all the statements.
Note:
This statement does not actually create a schema. Oracle Database automatically creates a schema when you create a user (see CREATE USER). This statement lets you populate your schema with tables and views and grant privileges on those objects without having to issue multiple SQL statements in multiple transactions.
Prerequisites
The CREATE SCHEMA statement can include CREATE TABLE, CREATE VIEW, and GRANT statements. To issue a CREATE SCHEMA statement, you must have the privileges necessary to issue the included statements.
Syntax
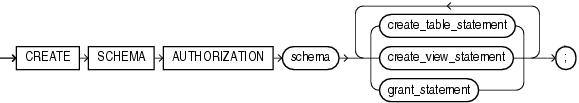
create_schema::=
Semantics
schema
Specify the name of the schema. The schema name must be the same as your Oracle Database username.
Restrictions
While CREATE SCHEMA supports CREATE TABLE , CREATE BLOCKCHAIN TABLE is unsupported.
create_table_statement
Specify a CREATE TABLE statement to be issued as part of this CREATE SCHEMA statement. Do not end this statement with a semicolon (or other terminator character).
See Also:
create_view_statement
Specify a CREATE VIEW statement to be issued as part of this CREATE SCHEMA statement. Do not end this statement with a semicolon (or other terminator character).
See Also:
grant_statement
Specify a GRANT statement to be issued as part of this CREATE SCHEMA statement. Do not end this statement with a semicolon (or other terminator character). You can use this clause to grant object privileges on objects you own to other users. You can also grant system privileges to other users if you were granted those privileges WITH ADMIN OPTION.
See Also:
The CREATE SCHEMA statement supports the syntax of these statements only as defined by standard SQL, rather than the complete syntax supported by Oracle Database.
The order in which you list the CREATE TABLE, CREATE VIEW, and GRANT statements is unimportant. The statements within a CREATE SCHEMA statement can reference existing objects or objects you create in other statements within the same CREATE SCHEMA statement.
Restriction on Granting Privileges to a Schema
The syntax of the parallel_clause is allowed for a CREATE TABLE statement in CREATE SCHEMA, but parallelism is not used when creating the objects.
See Also:
The parallel_clause in the CREATE TABLE documentation
Examples
Creating a Schema: Example
The following statement creates a schema named oe for the sample order entry user oe, creates the table new_product, creates the view new_product_view, and grants the SELECT object privilege on new_product_view to the sample human resources user hr.
CREATE SCHEMA AUTHORIZATION oe
CREATE TABLE new_product
(color VARCHAR2(10) PRIMARY KEY, quantity NUMBER)
CREATE VIEW new_product_view
AS SELECT color, quantity FROM new_product WHERE color = 'RED'
GRANT select ON new_product_view TO hr;