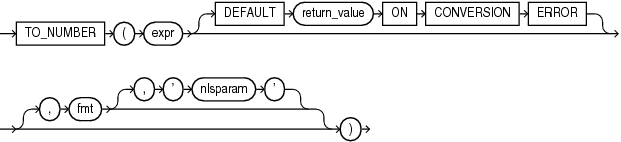
TO_NUMBER
Syntax
Purpose
TO_NUMBER converts expr to a value of NUMBER data type.
expr can be any expression that evaluates to a character string of type CHAR, VARCHAR2, NCHAR, or NVARCHAR2, a numeric value of type NUMBER, BINARY_FLOAT, or BINARY_DOUBLE, BOOLEAN, or null. If expr is NUMBER, then the function returns expr. If expr evaluates to null, then the function returns null. Otherwise, the function converts expr to a NUMBER value.
-
If you specify an
exprofCHAR,VARCHAR2,NCHAR, orNVARCHAR2data type, then you can optionally specify the format modelfmt. -
If you specify an
exprofBINARY_FLOATorBINARY_DOUBLEdata type, then you cannot specify a format model because a float can be interpreted only by its internal representation. -
If you specify an
exprof typeBOOLEAN, thenTRUEwill be converted to 1 andFALSEwill be converted to 0. You cannot specify a format model with inputs of typeBOOLEAN.
Refer to "Format Models" for information on number formats.
The 'nlsparam' argument in this function has the same purpose as it does in the TO_CHAR function for number conversions. Refer to TO_CHAR (number) for more information.
This function does not support CLOB data directly. However, CLOBs can be passed in as arguments through implicit data conversion.
See Also:
"Data Type Comparison Rules" for more information.
Examples
The following examples convert character string data into a number:
UPDATE employees SET salary = salary +
TO_NUMBER('100.00', '9G999D99')
WHERE last_name = 'Perkins';
SELECT TO_NUMBER('-AusDollars100','L9G999D99',
' NLS_NUMERIC_CHARACTERS = '',.''
NLS_CURRENCY = ''AusDollars''
') "Amount"
FROM DUAL;
Amount
----------
-100The following example returns the default value of 0 because the specified expression cannot be converted to a NUMBER value:
SELECT TO_NUMBER('2,00' DEFAULT 0 ON CONVERSION ERROR) "Value"
FROM DUAL;
Value
--------
0