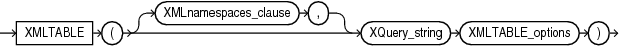XMLTABLE
Syntax
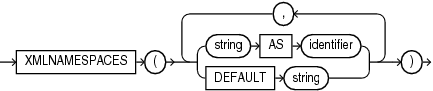
XMLnamespaces_clause::=
Note:
You can specify at most one DEFAULT string clause.
XMLTABLE_options::=
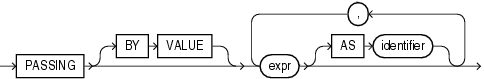
XML_passing_clause::=
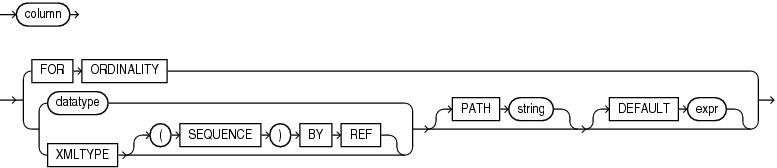
XML_table_column::=
Purpose
XMLTable maps the result of an XQuery evaluation into relational rows and columns. You can query the result returned by the function as a virtual relational table using SQL.
-
The
XMLNAMESPACESclause contains a set of XML namespace declarations. These declarations are referenced by the XQuery expression (the evaluatedXQuery_string), which computes the row, and by the XPath expression in thePATHclause ofXML_table_column, which computes the columns for the entireXMLTablefunction. If you want to use qualified names in thePATHexpressions of theCOLUMNSclause, then you need to specify theXMLNAMESPACESclause. -
XQuery_stringis a literal string. It is a complete XQuery expression and can include prolog declarations. The value of XQuery_string serves as input to the XMLTable function; it is this XQuery result that is decomposed and stored as relational data. -
The
exprin theXML_passing_clauseis an expression returning anXMLTypeor an instance of a SQL scalar data type that is used as the context for evaluating the XQuery expression. You can specify only oneexprin thePASSINGclause without an identifier. The result of evaluating eachexpris bound to the corresponding identifier in theXQuery_string. If anyexprthat is not followed by anASclause, then the result of evaluating that expression is used as the context item for evaluating theXQuery_string. This clause supports only passing by value, not passing by reference. Therefore, theBYVALUEkeywords are optional and are provided for semantic clarity. -
The optional
RETURNINGSEQUENCEBYREFclause causes the result of the XQuery evaluation to be returned by reference. This allows you to refer to any part of the source data in theXML_table_columnclause.If you omit this clause, then the result of the XQuery evaluation is returned by value. That is, a copy of the targeted nodes is returned instead of a reference to the actual nodes. In this case, you cannot refer to any data that is not in the returned copy in the
XML_table_columnclause. In particular, you cannot refer to data that precedes the targeted nodes in the source data. -
The optional
COLUMNSclause defines the columns of the virtual table to be created byXMLTable.-
If you omit the
COLUMNSclause, thenXMLTablereturns a row with a singleXMLTypepseudocolumn namedCOLUMN_VALUE. -
FORORDINALITYspecifies thatcolumnis to be a column of generated row numbers. There must be at most oneFORORDINALITYclause. It is created as aNUMBERcolumn. -
For each resulting column except the
FORORDINALITYcolumn, you must specify the column data type, which can beXMLTypeor any other data type.If the column data type is
XMLType, then specify theXMLTYPEclause. If you specify the optional(SEQUENCE)BYREFclause, then a reference to the source data targeted by thePATHexpression is returned as the column content. Otherwise,columncontains a copy of that targeted data.Returning the
XMLTypedata by reference lets you specify other columns whose paths target nodes in the source data that are outside those targeted by thePATHexpression for column.If the column data type is any other data type, then specify
datatype_clause.datatype
The
datatypespecified can be:-
BLOB, orCLOBwith optionsreferenceorvalue. The default isreference. -
Any other data type.
-
-
The optional
PATHclause specifies that the portion of the XQuery result that is addressed by XQuery expression string is to be used as the column content.If you omit
PATH, then the XQuery expressioncolumnis assumed. For example:XMLTable(... COLUMNS xyz)
is equivalent to
XMLTable(... COLUMNS xyz PATH 'XYZ')
You can use different
PATHclauses to split the XQuery result into different virtual-table columns. -
The optional
DEFAULTclause specifies the value to use when thePATHexpression results in an empty sequence. Itsexpris an XQuery expression that is evaluated to produce the default value.
-
See Also:
-
Oracle XML DB Developer's Guide for more information on the
XMLTablefunction, including additional examples, and on XQuery in general -
Appendix C in Oracle Database Globalization Support Guide for the collation derivation rules, which define the collation assigned to each character data type column in the table generated by
XMLTABLE
Examples
The following example converts the result of applying the XQuery '/Warehouse' to each value in the warehouse_spec column of the warehouses table into a virtual relational table with columns Water and Rail:
SELECT warehouse_name warehouse,
warehouse2."Water", warehouse2."Rail"
FROM warehouses,
XMLTABLE('/Warehouse'
PASSING warehouses.warehouse_spec
COLUMNS
"Water" varchar2(6) PATH 'WaterAccess',
"Rail" varchar2(6) PATH 'RailAccess')
warehouse2;
WAREHOUSE Water Rail
----------------------------------- ------ ------
Southlake, Texas Y N
San Francisco Y N
New Jersey N N
Seattle, Washington N Y