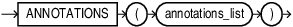annotations_clause
Purpose
Annotations provide a mechanism to store application metadata centrally in the database, so that they can be shared across applications, modules and microservices.
You can add annotations to any supported schema objects that you own at creation time via CREATE statements.
On supported schema objects that you have alter privileges on, you can add and drop annotations via ALTER statements. You do not need to qualify the annotation name with the schema name. Whenever a schema object drops an annotation, or when a schema object is dropped altogether, the usage of the annotation is updated to reflect the drop.
An individual annotation has a name and an optional value. Both the name and the value are freeform text fields. Annotations are additive, meaning that multiple annotations can be specified for the same schema object in a single DDL.
When an annotation name is specified for a schema object for the first time, an annotation is automatically created. Supported schema objects include tables, views, materialized views, and indexes. The annotation is represented as a subordinate element to the database object to which it has been added. Whenever a schema object drops an annotation, or when a schema object is dropped altogether, the usage of the annotation is updated to reflect the drop.
Dictionary views track the list of annotations and their usage across all schema objects. You can query dictionary views USER|ALL|DBA_ANNOTATIONS_USAGE to list the annotations for a schema object.
Prerequisites
You must own the schema object or have ALTER privileges on the schema object in order to specify annotations on the object.
Syntax
annotations_clause::=
annotations_list::=
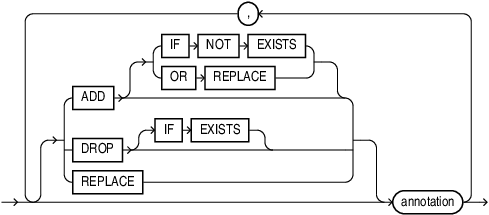
annotation::=
annotation_name::=
annotation_value::=
Semantics
annotations_clause
Specify ADD, DROP, or REPLACE to create, remove, or change annotations respectively.
-
ADDcreatesannotation_name. This is the default when no keyword is specified before annotation. If the object already has an annotation with this name, the statement raises an error.Use
ADD IF NOT EXISTSto allow the statement to complete without error. Ifannotation_nameis already present, it keeps its original value when using theIF NOT EXISTSclause.ADD [IF NOT EXISTS]is the only valid option to use withCREATEstatements. -
DROPremovesannotation_namefrom the object. If the object has no annotation with this name, the statement raises an error. UseDROP IF EXISTSto allow the statement to complete without error. This clause is only valid inALTERstatements. -
REPLACEchangesannotation_valueforannotation_nameto the supplied value. If you omit the value, this removes any existing value forannotation_name. Ifannotation_namedoes not exist the statement will raise an error. This clause is only valid inALTERstatements.
The annotation_name is an identifier that can have up to 1024 characters. If the annotation name is a reserved word it must be provided in double quotes. When a double quoted identifier is used, the identifier can also contain whitespace characters. However, identifiers that contain only whitespace characters are not accepted.
An annotation is either a name-value pair or a name by itself. The name and the optional value are freeform text fields. Value can have a maximum of 4000 characters. An annotation Display_Label, ‘Employee Salary’ has a name and a value, whereas an annotation UI_Hidden has only a name and it does not need a value. UI_Hidden is a standalone annotation used to specify that the column should be hidden.
Examples
Add Annotations to a Table
The following example adds two operations with values Sort and Group, and a standalone Hidden without a value, to table t1:
CREATE TABLE t1 (T NUMBER) ANNOTATIONS(Operations '["Sort", "Group"]', Hidden);
The annotation can be preceded by the keyword ADD which is the default operation if nothing is specified as the following example shows:
CREATE TABLE t1 (T NUMBER) ANNOTATIONS (ADD Hidden);
Alter Annotations at the Table Level
The following example drops all annotations from t1:
ALTER TABLE t1 ANNOTATIONS(DROP Operations, DROP Hidden);
Add Annotations to Table Columns
CREATE TABLE t1 (T NUMBER ANNOTATIONS(Operations 'Sort' , Hidden) );
Add Annotations to Table and Columns
CREATE TABLE employee (
id NUMBER(5)
ANNOTATIONS(Identity, Display 'Employee ID', "Group" 'Emp_Info'),
ename VARCHAR2(50)
ANNOTATIONS(Display 'Employee Name', "Group" 'Emp_Info'),
sal NUMBER
ANNOTATIONS(Display 'Employee Salary', UI_Hidden)
) ANNOTATIONS (Display 'Employee Table');Alter Annotations at the Column Level
ALTER TABLE employee
MODIFY ename ANNOTATIONS (
DROP "Group",
DROP IF EXISTS missing_annotation,
REPLACE Display 'Emp name'
);