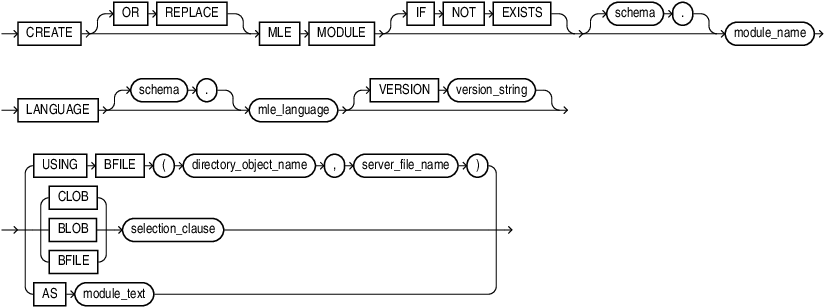
CREATE MLE MODULE
Purpose
Multilingual Engine (MLE) allows developers to write, store, and execute JavaScript code in Oracle Database Release 23 on Linux x86-64 by using MLE Modules to encapsulate JavaScript.
Use CREATE MLE MODULE to create a new MLE module in the database.
See Also:
Semantics
OR REPLACE
Specify OR REPLACE to re-create the module if it already exists. You can use this clause to change the definition of an existing module without dropping, re-creating, and regranting object privileges previously granted on it.
IF NOT EXISTS
Specifying IF NOT EXISTS has the following effects:
-
If the MLE module does not exist, a new MLE module is created at the end of the statement.
-
If the MLE module exists, this is the MLE module you have at the end of the statement. A new one is not created because the older one is detected.
You can have one of OR REPLACE or IF NOT EXISTS in a statement at a time. Using both OR REPLACE with IF NOT EXISTS in the very same statement results in the following error: ORA-11541: REPLACE and IF NOT EXISTS cannot coexist in the same DDL statement.
schema
Use schema to fully qualify the module name. If you do not specify schema, then the current schema is used.
The length of the module name must not exceed 128 bytes. MLE modules use the same namespace as tables and procedures.
LANGUAGE, VERSION
Use LANGUAGE to specify the MLE language of the created module. You must use the value JAVASCRIPT when you create JavaScript modules. An ORA-04101 error is thrown if an unsupported MLE language is used.
The optional VERSION clause specifies a version string for the MLE module. Version strings are purely informational and do not influence any behavior of MLE or the RDBMS. The version string must fit into a VARCHAR2(256).
CLOB, BLOB, BFILE
Use USING to create MLE modules from code contained in CLOBs, BLOBs, or BFILEs.
You can specify the BFILE clause with a subquery or with a directory using directory_object_name and server_file_name to specify the directory and filename of the MLE module you want to use. Note that you must create the directory object before this step using CREATE DIRECTORY .
The CLOB | BLOB | BFILE clause specifies a subquery whose result must be a single row and column of the specified type (CLOB, BLOB, or BFILE) that holds the contents of the MLE module to be deployed. The CLOB option is available only if the MLE module contains textual data. The textual data in MLE modules contained in BLOBs and BFILEs is encoded in UTF-8.
AS
Use AS to specify the contents of the MLE module as a sequence of characters inlined in the DDL statement. As with CLOBs, the AS clause is only available when the source of the MLE module contains textual data. Do not encapsulate the character sequence within quotes. The character sequence is delimited by the end of the DDL statement.